1-s2-0-s1674987118300446-gr61
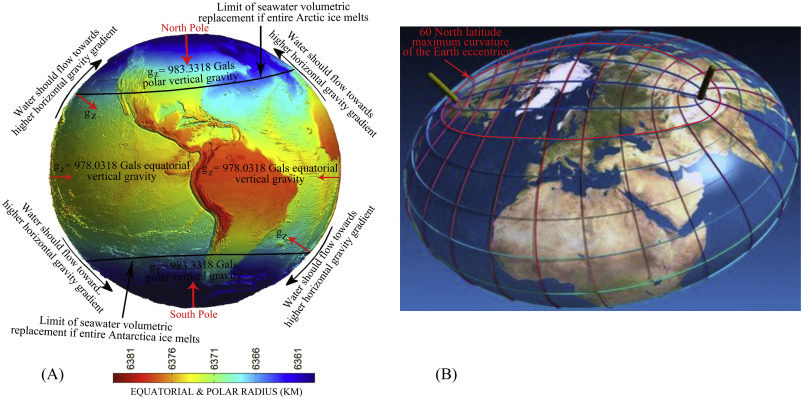
Figure 6. (A) Surface of the earth is defined in terms of gravity values at all surface points known as the reference spheroid. It is related to the mean sea-level (MSL) surface with excess land masses removed and ocean deeps filled. Thus it is an equipotential surface, that is, the force of gravity (gz) (red arrows) is everywhere normal to this surface, or the plumb line is vertical at all points directed to the center of the earth having maximum at the poles and minimum at the equator. Two components work against sea level rise i.e., greater gravity attraction of the polar region and the equatorial bulge (B) Maximum curvature of the spheroidal surface of the Earth coincides with 60oN latitude. Floating ice from Antarctica surrounded by open ocean can freely move to the north likely to be limited maximum upto 60oS latitude where spheroidal surface has the maximum curvature.