Matthew Lau reviews Thomas Sowell’s latest book Social Justice Fallacies in a Financial Post article: No sacred cows in Thomas Sowell’s takedown of social justice fallacies. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
In his latest book, renowned economist and author demolishes
the myths that underpin the social justice movement.
Thomas Sowell, age 93, famed economist and author of more than 40 books, last month published his latest: Social Justice Fallacies. In it he asserts plain facts such as that life is unfair and central planners are fallible, realities too often ignored or downplayed by those looking to impose top-down visions of “social justice.”

Among his targets are:
- price controls,
- minimum wage laws,
- the myth that American Black poverty is due to systemic racism,
- high marginal tax rates,
- teachers unions’ monopoly on schooling,
- exaggerations of income inequality by people who ignore income mobility,
- affirmative action,
- “sex education” in public schools (Sowell uses the scare quotes repeatedly)
To each of these and many other things, Sowell brings facts, examples, and statistics.
On the notion that the United States is a systemically racist or white supremacist society, Sowell notes that the median incomes of Americans of Chinese, Japanese, Indian and Korean ancestry are higher than those of white Americans. Citing a 2019 U.S. Census Bureau survey, he points out that “among full-time, year-round male workers, Asian Indian males earned over $39,000 a year more than white male full-time, year-round workers” — an unlikely outcome if white supremacy were pervasive.
Black family poverty has long been higher than white family poverty but, as Sowell explains, the poverty rate of Black married-couple families is consistently below the national poverty rate. “If black family poverty is caused by ‘systemic racism,’” he asks, “do racists make an exception for blacks who are married?”
Another case-closing rhetorical question from Sowell: “Are Asians ‘kept out’ of professional basketball or Californians ‘kept out’ of the National Hockey League?” In American sports, he notes, “Blacks are very over-represented in professional basketball, whites in professional tennis, and Hispanics in Major League Baseball.” There are more NHL players from Sweden than California even though Sweden is on another continent and has about one-quarter California’s population. But these facts do not mean professional sports leagues all engage in racism or other bigotry.
No affirmative action or other initiative is needed to
“correct” these unequal outcomes between groups.
If Sowell’s arguments about government economic control, race, economic disparities and other questions sound familiar, it is because he has written on these issues for decades. The same fallacies he and others have repeatedly debunked keep reappearing and need to be whacked down again and again — which Sowell continues to do.

In Social Justice Fallacies, Sowell again attacks racial preferences in university admissions, arguing that admitting minority students into university programs for which they are not academically qualified does them no favours. Black students at the 80th percentile are very good students but putting them into elite programs where their classmates are in the 99th percentile sets them up for failure. Under affirmative action, Sowell writes, most Black students admitted to the University of California (Berkeley) during the 1980s failed to graduate.
Another policy that activists promote in the name of social justice, but that hurts Blacks: minimum wage laws, which the data show significantly increase Black teenage unemployment by pricing many of them out of jobs.

There are no sacred cows in Social Justice Fallacies. Sowell argues that “surrogates who introduced ‘sex education’ into public schools in the 1960s” were pre-empting parents’ decisions about when and how to teach their children about sex. He points to data showing that before such education was introduced venereal diseases and teenage pregnancies had been declining for years, but after its introduction teenage pregnancies rapidly rose and the incidence of venereal diseases either rose or declined less rapidly than before. These facts alone do not prove causation between public school “sex education” and venereal diseases and teenage pregnancies, but they are not encouraging, either.
Explaining facts and demolishing fallacies, as Sowell does, is important. When activists distort reality by fashioning narratives to justify their top-down initiatives, they often cause more harm than the original injustices (whether real or perceived) they say they want to correct.
Citing Barack Obama’s memoir, Dreams from My Father, Sowell gives the example of a young Black man who wanted to become a pilot but decided not to pursue it because he thought the Air Force would never let a Black man fly. Sowell points out this was decades after a whole squadron of Black American fighter pilots flew in World War II.
“Whoever indoctrinated this young man,” Sowell concluded,
“did him more harm than a racist could have,
by keeping him from even trying to become a pilot.”
In Addition, Thomas Sowell’s Wisdom and Scholarship on Affirmative Action
Excerpts on Affirmative Action from The Thomas Sowell Reader

Assumptions Behind Affirmative Action
With affirmative action suddenly coming under political attack from many directions, and with even liberals backing away from it, we need to question not only its underlying assumptions but also what some of the alternatives are.
At the heart of the affirmative action approach is the notion that statistical disparities
show discrimination. No dogma has taken a deeper hold with less evidence
—or in the face of more massive evidence to the contrary.
A recent story in the Wall Street Journal revealed that more than four-fifths of all the doughnut shops in California are owned by Cambodians. That is about the same proportion as blacks among basketball stars. Clearly, neither of these disparities is due to discrimination against whites.
Nor are such disparities new or peculiar to the United States. In medieval Europe, most of the inhabitants of the towns in Poland and Hungary were neither Poles nor Hungarians. In nineteenth-century Bombay, most of the shipbuilders were Parsees, a minority in Bombay and less than one percent of the population of India.
In twentieth-century Australia most of the fishermen in the port of Freemantle came from two villages in Italy. In southern Brazil, whole industries were owned by people of German ancestry and such crops as tomatoes and tea have been grown predominantly by people of Japanese ancestry.
Page after page—if not book after book—could be filled with similar statistical disparities from around the world and down through history. Such disparities have been the rule, not the exception.
Yet our courts have turned reality upside down and treated what happens
all over this planet as an anomaly and what is seldom found
anywhere—proportional representation—as a norm.
Why are such disparities so common? Because all kinds of work require particular skills, particular experience, particular locations and particular orientations. And none of these things is randomly distributed.
Local demagogues who thunder against the fact that Koreans run so many stores in black ghettoes merely betray their ignorance when they act as if this were something strange or unusual. For most of the merchants in an area to be of a different race or ethnicity from their customers has been common for centuries in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, West Africa, the Caribbean, Fiji, the Ottoman Empire and numerous other places.
When German and Jewish merchants moved into Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages, they brought with them much more experience in that occupation than that possessed by local Eastern European merchants, who were often wiped out by the new competition. Even when the competition takes place between people who are racially and ethnically identical, all kinds of historical, geographical and other circumstances can make one set of these people far more effective in some activities than the others.
Mountain people have often lagged behind those on the plains below, whether highland Scots versus lowland Scots or the Sinhalese in the highlands of Sri Lanka versus the Sinhalese on the plains. The Slavs living along the Adriatic coast in ports like Dubrovnik were for centuries far more advanced than Slavs living in the interior, just as coastal peoples have tended to be more advanced than peoples of the interior hinterlands in Africa or Asia.
Some disparities of course have their roots in discrimination. But the fatal mistake is to infer discrimination whenever the statistical disparities exceed what can be accounted for by random chance. Human beings are not random. They have very pronounced and complex cultural patterns. These patterns are not unchanging. But changing them for the better requires first acknowledging that “human capital” is crucial to economic advancement.
Those who make careers out of attributing disparities to the wickedness of other people
are an obstacle to the development of more human capital among the poor.
There was a time, as late as the mid-nineteenth century, when Japan lagged far behind the Western industrial nations because it was lacking in the kind of human capital needed in a modern economy. Importing Western technology was not enough, for the Japanese lacked the knowledge and experience required to operate it effectively.
Japanese workmen damaged or ruined machinery when they tried to use it. Fabrics were also ruined when the Japanese tried to dye them without understanding chemistry. Whole factories were badly designed and had to be reconstructed at great cost. What saved the Japanese was that they recognized their own backwardness—and worked for generations to overcome it.
They did not have cultural relativists to tell them that all cultures are equally valid
or political activists to tell them that their troubles were all somebody else’s fault.
Nor were there guilt-ridden outsiders offering them largess.
Affirmative action has been one of the great distractions from the real task of self-development. When it and the mindset that it represents passes from the scene, poorer minorities can become the biggest beneficiaries, if their attention and efforts turn toward improving themselves.
Unfortunately, a whole industry of civil rights activists, politicians and miscellaneous hustlers has every vested interest in promoting victimhood, resentment and paranoia instead.

Affirmative Action Around the World
While controversies rage over “affirmative action” policies in the United States, few Americans seem to notice the existence or relevance of similar policies in other countries around the world. Instead, the arguments pro and con both tend to invoke history and traditions that are distinctively American. Yet group preferences and quotas have existed in other countries with wholly different histories and traditions—and, in some countries, such policies have existed much longer than in the United States. What can the experiences of these other countries tell us? Are there common patterns, common rationales, common results? Or is the American situation unique?
Ironically, a claim or assumption of national uniqueness is one of the most common patterns found in numerous countries where group preferences and quotas have existed under a variety of names. The special situation of the Maoris in New Zealand, based on the 1840 Treaty of Waitangi, is invoked as passionately in defense of preferential treatment there as the unique position of untouchables in India or of blacks in the United States.
Despite how widespread affirmative action programs have become, even the promoters of such programs have seldom been bold enough to proclaim preferences and quotas to be desirable on principle or as permanent features of society. On the contrary, considerable effort has been made to depict such policies as “temporary,” even when in fact these preferences turn out not only to persist but to grow.
Official affirmative action or group preference policies must be distinguished from whatever purely subjective preferences or prejudices may exist among individuals and groups. These subjective feelings may of course influence policies, but the primary focus here is on concrete government policies and their empirical consequences—not on their rationales, hopes, or promises, though these latter considerations will not be wholly ignored. Fundamentally, however, this is a study of what actually happens, rather than a philosophical exploration of issues that have been amply—if not more than amply—explored elsewhere.

The resurgence of group preferences in societies committed to the equality of individuals before the law has been accompanied by claims not only that these preferences would be temporary, but also that they would be limited, rather than pervasive. That is, these programs would supposedly be limited not only in time but also in scope, with equal treatment policies prevailing outside the limited domain where members of particular groups would be given special help.
Similar reasoning was applied in the United States to both employment and admissions to colleges and universities. Initially, it was proposed that there would be special “outreach” efforts to contact minority individuals with information and encouragement to apply for jobs or college admissions in places where they might not have felt welcome before, but with the proviso that they would not be given special preferences throughout the whole subsequent processes of acceptance and advancement.
Similar policies and results have also been achieved in less blatant ways. During the era of the Soviet Union, professors were pressured to give preferential grading to Central Asian students and what has been called “affirmative grading” has also occurred in the United States, in order to prevent excessive failure rates among minority students admitted under lower academic standards. In India, such practices have been referred to as “grace marks.” Similar results can be achieved indirectly by providing ethnic studies courses that give easy grades and attract disproportionately the members of one ethnic group. This too is not peculiar to the United States. There are Maori studies programs in New Zealand and special studies for Malays in Singapore.
In the job market as well, the belief that special concerns for particular groups
could be confined to an initial stage proved untenable in practice.
Initially, the term “affirmative action” arose in the United States from an executive order by President John F. Kennedy, who called for “affirmative action to ensure that the applicants are employed, and that employees are treated during employment without regard to race, color, creed, or national origin.” In short, there were to be no preferences or quotas at all, just a special concern to make sure that those who had been discriminated against in the past would no longer be discriminated against in the future—and that concrete steps should be taken so that all and sundry would be made aware of this.
However, just as academic preferences initially limited in scope continued to expand,
so did the concept of affirmative action in the job market.
A later executive order by President Lyndon Johnson in 1968 contained the fateful expressions “goals and timetables” and “representation.” In December 1971, yet another Nixon executive order specified that “goals and timetables” were meant to “increase materially the utilization of minorities and women,” with “under-utilization” being spelled out as “having fewer minorities or women in a particular job classification than would reasonably be expected by their availability.” Affirmative action was now a numerical concept, whether called “goals” or “quotas.”
This confident pronouncement, however, presupposed a degree of control which has proved illusory in country after country. Moreover, “when and where there is social and economic inequality” encompasses virtually the entire world and virtually the entire history of the human race. A “temporary” program to eliminate a centuries-old condition is almost a contradiction in terms.
Equality of opportunity might be achieved within some feasible span of time,
but that is wholly different from eliminating inequalities of results.
Even an approximate equality of “representation” of different groups in different occupations, institutions or income levels has been a very rare—or non-existent—phenomenon, except where such numerical results have been imposed artificially by quotas. As a massive scholarly study of ethnic groups around the world put it, when discussing “proportional representation” of ethnic groups, “few, if any societies have ever approximated this description.”
In short, the even representation of groups that is taken as a norm is difficult or impossible to find anywhere, while the uneven representation that is regarded as a special deviation to be corrected is pervasive across the most disparate societies. People differ—and have for centuries. It is hard to imagine how they could not differ, given the enormous range of differing historical, cultural, geographic, demographic and other factors shaping the particular skills, habits, and attitudes of different groups.
Any “temporary” policy whose duration is defined by the goal of achieving something that has never been achieved before, anywhere in the world, could more fittingly be characterized as eternal.















































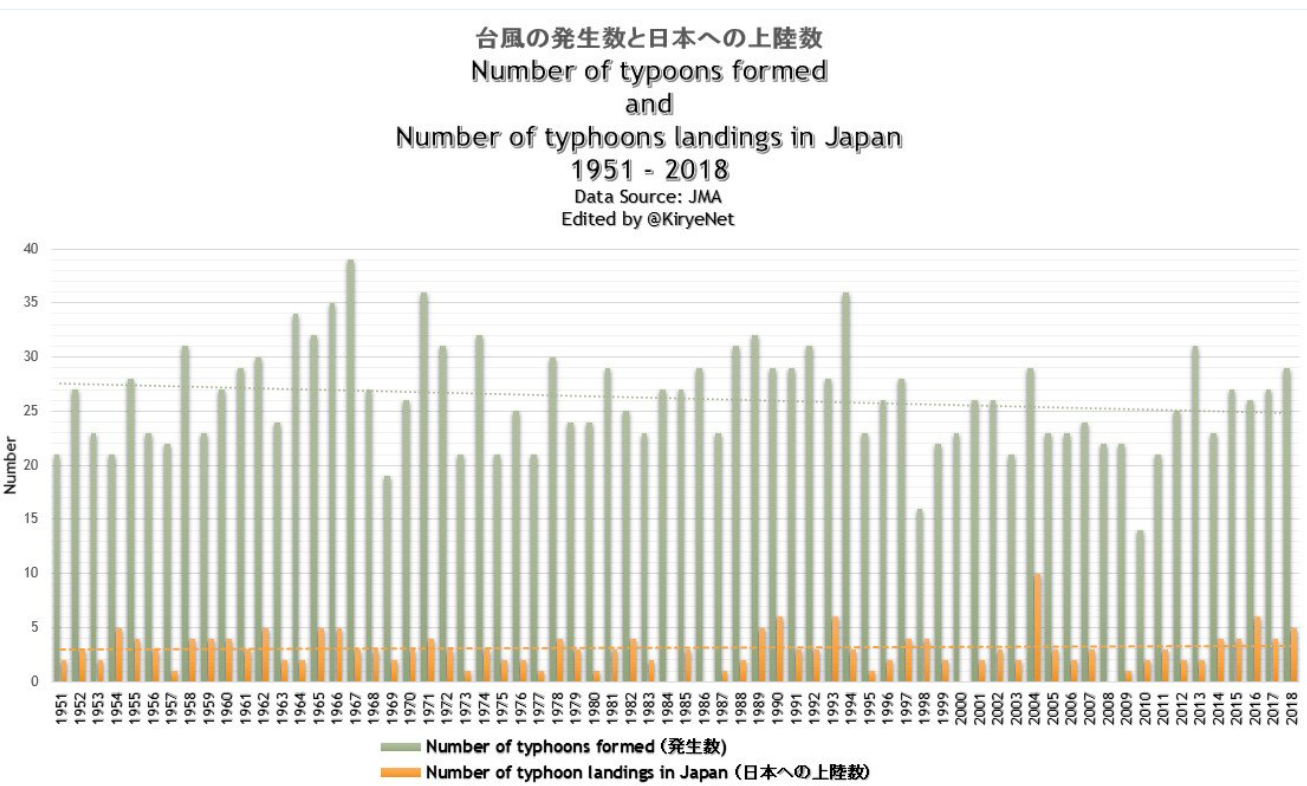






















 But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.
But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.