As Bloomberg reported, EU is attempting to force climate risk and ESG reporting on the whole world, not just its member nations.
As trans-Atlantic relations grow increasingly fraught, Europe’s ESG regulations are becoming yet another flashpoint that threatens to sour ties.
The American Chamber of Commerce to the European Union (AmCham EU) says proposed revisions to the bloc’s environmental, social and governance rules don’t adequately protect US interests. The complaint is part of a growing US response to Europe’s ESG framework. Republican lawmakers call the rules “hostile” and warn that America’s jurisdictional sovereignty is at stake, while Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick has said he’s willing to consider “trade tools” to retaliate.
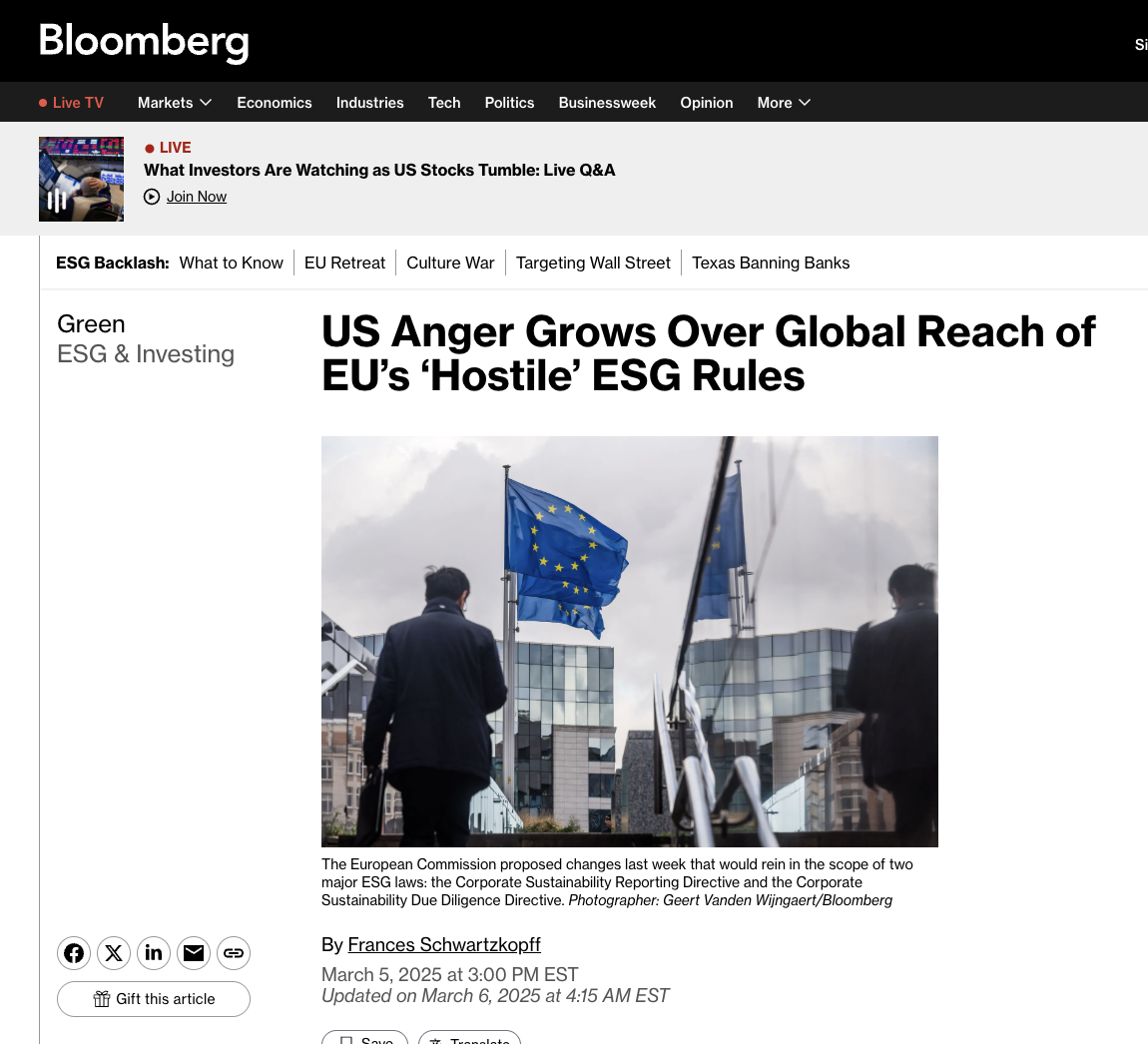
The European Commission proposed changes last week that would rein in the scope of two major ESG laws: the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive and the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive. However, big international companies with business in the EU would still have to comply.
The upshot is that non-EU companies risk being ensnared by the bloc’s ESG rules, even for products that aren’t sold in the EU, said Kim Watts, senior policy manager for AmCham EU, whose members include Ford Motor Co., Exxon Mobil Corp. and Amazon.com Inc.
AmCham is worried that the EU “is going too far on extraterritoriality,” she said in an interview.
It’s a complaint that’s being backed up in even stronger terms by GOP members of Congress. In a letter sent shortly after the European Commission published its proposed revisions to the bloc’s ESG rules, the US lawmakers wrote to Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and National Economic Council Director Kevin Hassett, warning of the “profound” implications of Europe’s due diligence directive for US businesses.
The lawmakers stated: “CSDDD imposes stringent due diligence requirements on in-scope companies, mandating the evaluation of supply chains to identify, mitigate, and eliminate human rights and environmental abuses as defined by United Nations (UN) and Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) principles.
“Furthermore, US firms will face increased litigation risks and potential enforcement actions from EU member states, with penalties under the Directive reaching up to 5% of a company’s global turnover.
“However, these principles have not been ratified by Congress, raising concerns about the legitimacy of EU enforcement against US companies based on these principles. Additionally, small businesses that supply larger companies will also be affected, even if their operations are solely within the US compliance efforts will require significant resource allocation, diverting funds away from critical areas such as research and development, talent acquisition, and investment.

One comment