
Last week Ben Shapiro interviewed Chris Wright concerning the latest moves by realists against the climatists and what’s at stake in this power struggle over humankind’s energy platform, not only for U.S but for the world. For those who prefer reading, I provide a transcript lightly edited from the closed captions, text in italics with my bolds and added images.
Ben: One of the biggest moves that has been made in modern history in the regulatory state has happened this week. The Environmental Protection Agency on Tuesday, according to the Wall Street Journal, declared liberation day from Climate Imperialism by moving to repeal the 2009 so-called endangerment finding for greenhouse gas emissions. So basically, the Clean Air Act, which was put into place in the 1970s, authorized the EPA to regulate pollutants like ozone, particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and others that might reasonably be anticipated to endanger public health or welfare.
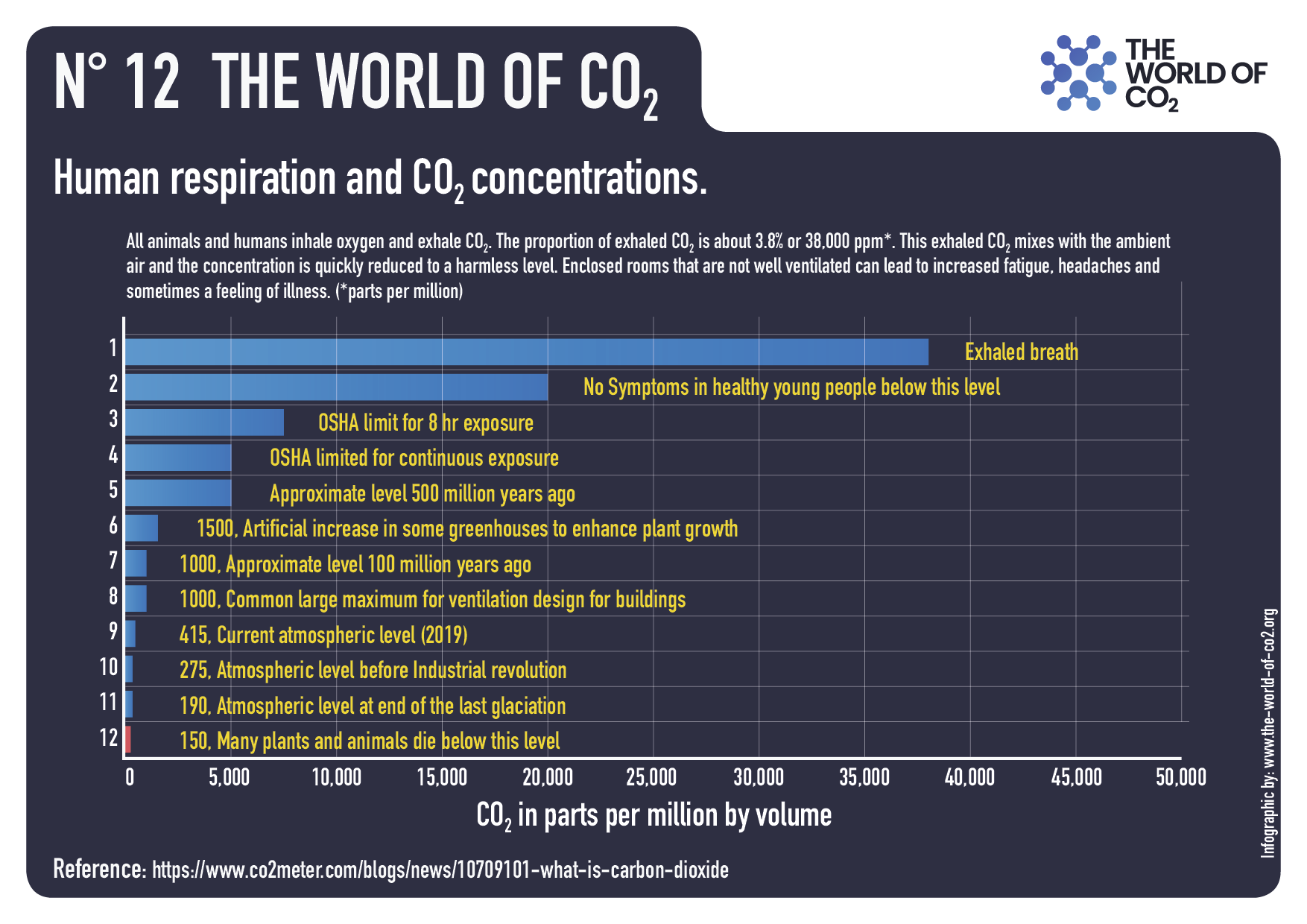
Well, the EPA suggested under Barack Obama that you could use the Clean Air Act in order to regulate carbon emissions, which is insane. That’s totally crazy. The kinds of stuff the Clean Air Act was meant to stop was again particulate matter. It was meant to stop ozone that was breaking down the ozone layer. It was not meant to deal with carbon and particularly carbon dioxide which is a thing that you know is a natural byproduct, for example breathing. Carbon dioxide in the environment is not a danger to human beings.
You may not like what it does in terms of global climate change, but the idea that the EPA has authority under the Clean Air Act is wrong. If Congress wants to give the EPA that authority, then it certainly could, but it never did. The Supreme Court found in 2007 that greenhouse gases could qualify as pollutants under an extraordinarily broad misreading of the law.
But now the EPA is walking that back. And the EPA is suggesting that this is not correct. The Supreme Court and the EPA under their 2009 ruling said, “There is some evidence that elevated carbon dioxide concentrations and climate changes can lead to changes in aeroallergens that could increase the potential for allergenic illnesses.” Well, the Energy Department has now walked that back. They published a comprehensive analysis of climate science and its uncertainties by five outside scientists. One of those is Steven Koonin, who served in the Obama administration.
The crucial point is that CO2 is different from the pollutants Congress expressly authorized the EPA to regulate. Those pollutants are “subject to regulatory control because they cause local problems depending on concentrations including nuisances, damages to plants, and at high enough exposure levels, toxic effects on humans. In contrast, CO2 is odorless, does not affect visibility, and it has no toxicological effects at ambient levels. So, you’re not going to get sick from CO2 in the air.
And so, the EPA administrator Lee Zeldin and Energy Secretary Chris Wright are taking this on. They have said in our interpretation the Clean Air Act no longer applies to greenhouse gases. Well, what does that mean? It means something extraordinary for the American economy, among other things, which is under a massive deregulatory environment.
The alleged cost of regulating greenhouse gas emissions under the Clean Air Act amounts to something like 54 billion per year. So if you multiply that out over the course of the last decade and a half, you’re talking about a cost of in excess of $800 billion based again on a regulatory agency radically exceeding its boundaries.
Well, joining us online to discuss this massive move by the Trump administration is the energy secretary Chris Wright. Secretary, thanks so much for taking the time. Really appreciate it. Thanks for having me, Ben.
Ben: So, first of all, why don’t we discuss what the EPA just did, what that actually means, how’s the energy department involved, and and what does it mean for sort of the future of things like energy developments in the United States?

The Poisonous Tree: Massachusetts v. EPA and the 2009 endangerment finding
Chris: Well, the endangerment finding, 2007 Supreme Court decision, Massachusetts and a bunch of environmental groups sued the EPA and said, “You must regulate greenhouse gas emissions.” Climate activists, basically. Unfortunately the Supreme Court decided five to four in 2007 that greenhouse gases could become endangerments, and if they were the EPA had the option but not the compulsion to regulate greenhouse gases. In 2009, as soon as the Obama administration came in, they did a tortured kind of process to say greenhouse gases endanger the lives of Americans. And that gave the regulatory state, the EPA, the ability to regulate greenhouse gases that the Obama administration and others had failed to pass through Congress. If you pass a law through the House and the Senate and the president signs it, then you can do that. But they just made it up. They just did it through a regulatory backdoor.
And now those those regulations just infuse everything we do, maybe most famously automobiles, the EV mandates, the continual increasing of fuel economy standards that brought us the SUV and everyone buying trucks because they don’t want to buy small cars. But it’s regulating your appliances and power plants and your and home hair dryers and outdoor heaters. So, it’s just been a huge entanglement into American life.
Big brother climate regulations from the government. They don’t do anything meaningful for global greenhouse gas emissions. They don’t change any health outcomes for Americans, but they massively grow the government. They increase costs and they grow the reach of the government. So, Administrator Lee Zeldin is reviewing that and saying, ” We don’t believe that greenhouse gases are a significant endangerment to the American public and they shouldn’t be regulated by the EPA. The EPA does not have authority to regulate them because Congress never passed such a law.
At the Department of Energy, sorry for the long answer, what we did was to reach out to five prestigious climate scientists that are real scientists in my mind; meaning they follow the data wherever it leads, not only if it aligns with their politics or their views otherwise. And we published a long critical overview of climate science and its impact on Americans. And that was released yesterday on the DOE website. I highly recommend everyone to give it a read in synopsis since it’s a big report obviously.
Ben: What are the biggest findings from that report that you commissioned at the Department of Energy with regard to this stuff?
Chris: Maybe the single biggest one that everyone should be aware of is: The ceaseless repeating that climate change is making storms more frequent and more severe and more dangerous is just nonsense. That’s never been in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports. It’s just not true. But media and politicians and activists just keep repeating it. And in fact, I saw The Hill had a piece right away when when our press release went out yesterday morning:
Despite decades of data and scientific consensus that climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of storms, the EPA has reversed the endangerment finding.
Even the headlines are just wrong. One of my goals for 20 years, Ben, is for people to be just a little more knowledgeable of what is actually true with climate change, and what actually are the tradeoffs between trying to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by top- down government actions and what does that mean for the energy system?
We’ve driven up the price of energy, reduced choice to American consumers,
without meaningfully moving global greenhouse gas emissions at all.
And when I talk to activists or politicians about it, they’re not even that concerned about it. They don’t act as if their real goal is to incrementally reduce greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Their real goal is for the government and them, you know, a small number of people to decide what’s appropriate behavior for all Americans.
Just creepy, top-down control sold in the name of protecting the future of the planet. If it was really about that, they’d know a little bit more about climate change, but they almost never do.
Ben: Well, this is the part that’s always astonishing to me. I get in a room with with climate scientists from places like MIT or Caltech, and we’ll discuss what exactly is going on. These are people who believe that there is anthropogenic climate change, that human activity is causing some sort of market impact on the climate. But when you discuss with them, okay, so what are the solutions? The solutions that that are proposed are never in line with the the kind of risk that they seek to prevent. I mean, the Nobel Prize winning economist William Nordhaus has made the point that there are certain things you could do economically that would totally destroy your economy and might save you an incremental amount of climate change on the other end. And then there are the things that we actually could do that are practical–things like building seawalls, things like hardening an infrastructure, moving toward nuclear energy would be a big one.
And to me, the litmus test of whether somebody is serious or not about climate change is what their feelings are about nuclear energy. If they’re anti-uclear energy, but somehow want to curb climate change, then you know, one of those things is false. It cannot be that you wish to oppose nuclear energy development, also your chief goal is to lower carbon emissions. That’s just a lie.
Chris: Exactly. I mean the biggest driver of reduced greenhouse gas emissions in the US by far has been natural gas displacing coal in the power sector. It’s about 60% of all the US reduction in emissions. But they hate natural gas, you know, because again they’re against hydrocarbons in order to move toward a society that somehow they think is better.
It is helping that more on the left become pro-nuclear. So, I’ll view that as one of the positive side effects of the climate movement and probably is going to help nuclear energy start going again. Of course, there are plenty that are anti-nuclear and climate crazies. So, there’s plenty of them still left. But, as you just mentioned, Nordhaus said in his lecture we should do the things where the benefits are greater than the cost. Sort of common sense. And in his proposed optimal scenario, you know, we reduce the warming through this century by about 20%. Not net zero, because that means you spend hundred trillion dollars and maybe you get $10 trillion of benefits. You know, that’s not good, and then people tell me, well, it’s an admirable goal. It’s aspirational. I’m saying, turning dollars into dimes is not aspirational. It’s human impoverishing.
And we can look over to the United Kingdom. They very proudly announced that they have the largest percent reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, 40%. They don’t tell you they’ve had an almost 30% reduction in energy consumption in the United Kingdom. So their dominant mechanism to drive down their greenhouse gas emissions is simply to consume less energy in England. That comes from two factors. The biggest one is their energy intensive industry is shut down in the country and all those jobs have gone overseas.
That stuff is now made in China, loaded on a diesel-powered ship,
shipped back to the United Kingdom, and they call that green.
And the other mechanism is they made energy so expensive that people don’t heat their houses as warm in the winter. They don’t travel as much. They don’t cool their houses as much in the hot summer days. They’ve impoverished their people so they can’t afford needed energy. This isn’t victory and this isn’t changing the global future of the world. We just need back some common sense around energy and climate change.
That’s where the Trump administration is headed across the administration, not just administer Zeldin and myself, but everyone in the administration. We just want Americans to have a government that follows basic common sense.

Ben: Now, Secretary Wright, we were discussing a little bit earlier on in the show this this excellent second quarter GDP number, some of which is being driven certainly by mass investment in technologies like AI. If you talk to folks who are in the capital intensive arenas, pretty much all the money right now is going into AI. That’s a race the United States must win. And one of the huge components there is the energy that is going to be necessary in order to pursue the sorts of processing that AI is going to require. The gigantic data centers that are now being built are going to require inordinate amounts of energy. Everybody knows and acknowledges this. China is producing energy at a rate that far outstrips the United States at this point. So if we wish to actually win the AI race, we have to unleash an all of the above strategy with regard to energy production. That’s obviously something you’re very focused on. And if we don’t win the AI race, in all likelihood China becomes the dominant economic power on planet Earth. So how important is AI to this? And what does it mean for the energy sector?
Chris: It’s massively important. As you just said, it’s what I called it Manhattan Project 2.0. Because in the Manhattan project when we developed an atomic bomb in World War II, we could not have come in second. If Nazi Germany had developed an atomic weapon before us, we would live in a different world now. It’s a similar risk here if China gets a meaningful lead on the US in artificial intelligence.
Because it’s not just economics and science, it’s national defense, it’s the military. Now we are under serious threat from China and we go into a very different world. We must lead in this area. We have the leading scientists. We have businesses. We have the ability to invest these huge amounts of capital again from private markets and private businesses, which a free market capitalist like myself loves.
The biggest limiter as you set up is electricity. The highest form and most expensive type of energy there is turning primary energy into electricity. And as you just said, China’s been growing their electricity production massively. Ours has barely grown in the last 20 years. In fact, it grew like two or 3% in the Obama years, but then during the Biden years, they got prices up over 25%. You could say they helped elect President Trump by just doing everything wrong on energy. And they certainly weren’t into all of the above. They were all about wind, solar, and batteries. And congratulations, they got them to about 3% of total US energy at the end of the Biden years.

The graph shows that global Primary Energy (PE) consumption from all sources has grown continuously over nearly 6 decades. Since 1965 oil, gas and coal (FF, sometimes termed “Thermal”) averaged 88% of PE consumed, ranging from 93% in 1965 to 81% in 2024. Source: Energy Institute
Hydrocarbons went from 82% in 2019, when Biden promised and guaranteed he would end fossil fuels, to 82% his last year in office. Zero change in market share. So they just believe and cling to too many silly things about energy. So today in the United States, the biggest source of electricity by far is natural gas. That will be the dominant growth that will enable us to build all these tens of gigawatts of data centers. It’s abundant, it’s affordable, and it works all the time. I’ve never been an all of the above guy because subsidizing wind and solar is problematic. You know, globally, a few trillions of dollars have gone into it, and if you get high penetration, the main result is expensive electricity and a less stable grid.
That’s not good. The crazy amount of money the United States government spent on wind and solar hasn’t grown our electricity production because they’re not there at peak demand time. Texas has the biggest penetration of wind and second biggest penetration of solar, 35% of the capacity on the Texas grid. But at peak demand with these cold or warm high-pressure systems the wind is gone. Peak demand time is after the sun goes down and you get almost nothing from wind and solar.
Parasites is what they really are. Just in the middle of the day when demand is low, and all the power
plants that are needed to supply at peak demand just all have to turn down. And then the sun goes behind a cloud and they got to turn up again. And then when peak demand comes, when it’s very cold at in the evening, all the existing thermal capacity and nuclear capacity has to run and drive the grid.
So if you don’t add to reliable production at peak demand time,
you’re not adding to the capacity of the grid. You’re
just adding to the complexity and cost of the grid.
I mean, if Harris had won the election, we would not only have no chance to win the AI race against China. We would have increasing blackouts and brownouts today, let alone with the the extra demand, some extra demand that would have come from AI, even if they had won the race. But because President Trump won, common sense came back in spades, and we’re allowing American businesses to invest and lead in AI, we’re in a very different trajectory.
Ben: A very different trajectory. Well, that’s US Energy Secretary Chris Wright doing a fantastic job over there. One of the big reasons that the Trump economy continues to churn along. Secretary Wright, really appreciate the time and the insight. Thanks so much for having me, Ben. Appreciate all you do.














The overturning of the EPA CO2 endangerment finding is very good news for those who believe in rational policy. But the interview misses a key issue. CO2 and other greenhouse gases are (to use a term from Hansen et al 1988) well-mixed. It is irrelevant where in the world the gas is emitted or even if the emissions are natural or human-caused. Any impacts on atmospheric trace gas levels is the same. That means effective regulation of emissions needs to be at the global level.
But global emissions regulation of CO2 etc was never going to happen. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), adopted in March 1994, distinguishes between Annex I countries (referred to as “developed” countries) and non-Annex I countries(referred to as “developing” countries). With the US now out the picture, the Annex 1 developed countries account for just 15% of global CO2 emissions. The major policy countries are the EU, Japan, Canada, UK and Australia. That means global emissions are being predominantly driven by countries without aggressive GHG reduction policies.
For comparison, consider smoke from the burning of coal in the UK in say 1950. There most houses used coal for heating. If a particular town compelled the use of low smoke, or smokeless, coal it would make a significant difference in that town. The UK-wide switch away from coal to gas produced from coal, then gas extracted from the ground got rid of nearly all the coal-smoke problem in the UK. Coal-burning in China and India does not impact the coal-smoke in the UK. But the CO2 produced in China and India does impact the British CO2 levels just as much as the Chinese and Indian CO2 levels.
Two things arise.
Attempts to sue Western Big Oil for the emissions resulting from their production are unfair, as the combined amount results in less than 3% of GHG emissions measured in CO2 equivalents. The Big 4 Russian Oil & Gas companies “produce” more CO2, Aramco about the same and China Coal maybe 5 times more.
The Stern Review 2006 claimed that future global warming costs would be 5% of global GDP or more, against 1% spent globally on efficiently reducing emissions by about 80% by 2050. For the UK alone the 5:1 ratio becomes worse than 1:100, whilst being stuck with nearly of those warming costs anyway. Without a consistent efficient global policy, emissions reductions are far from worthwhile. Even with such a policy, reductions in growth for developing countries means costs are huge. The best emissions reduction (climate mitigation) policy is no policy. Climate science is irrelevant.
I am currently working on two articles covering the marginal impact of some countries policies and the policy costs v climate costs.
LikeLike
Kevin, I think your premise is mistaken.

LikeLike
Ron,
My argument makes climate science irrelevant to successfully controlling emissions. If a few countries follow the 1.5C pathway (which in AR6 WG3 SPM means net negative emissions after net zero), 2100 emissions will be mostly determined by countries without such aggressive emissions reduction policies. Those modelling policy make the false assumption that the world acts as one. In reality, nations only have control over their own territory. Using the AR6 figures, if all countries had constant emissions 2020-2100 I estimate 3.5C of warming in 2100. The current Annex 1 countries following the 1.5C pathway, would give 3.18C. If Canada unilaterally followed the lead of the US, and and joined the global majority global temperatures would be around 0.05C higher. The UK doing the same would make just 0.02C of difference.
I hope to publish with more details in a few days.
LikeLike
Kevin, I don’t believe the AR6 numbers. The weather and climate will warm and cool as it has always done unaffected by humans burning hydrocarbons.
LikeLike
Ron,
The AR6 numbers are simply rubbish. On a deeper level, it is an extreme case of undetermination. They can’t disprove an alternative set of assumptions – both empirical or structural – that might say 2 °C is already built in, or that unmitigated human-caused emissions will result in less than 2 °C of anthropogenic warming by 2100 relative to 1850.
But this is outside of my argument. That is that IPCC AR6 1.5 °C and 2 °C global emission pathways will never be remotely achieved, as only a few countries are getting anywhere near those pathways. For the next few decades global emissions will be mostly determined by the rest of the world. Climate science is pushing useless and harmful policies regardless of whether St Greta of Thunberg is right about a coming climate apocalypse, or President Trump is right about it being a complete hoax.
Climate activists don’t recognise their limited power to change things as they desire, nor the adverse consequences of the policies they advocate.
LikeLike
Agree Kevin. Their numbers come from models presuming a direct warming from more CO2 tripled by a supposed H2O positive feedback. All of it is hypothetical. The whole ghg emissions budget and accounting regime is akin to the medieval theologians calculating the number of angels on the head of a pin.
I refer you to my post on the ICJ ruling calling for nations to achieve net zero.
https://rclutz.com/2025/07/23/icj-issues-biased-advice-on-climate-change/
LikeLike