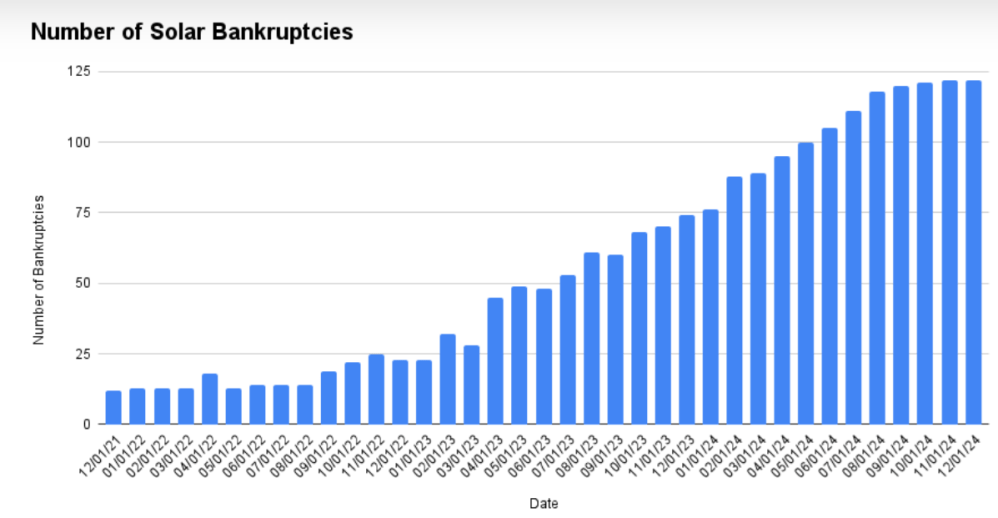
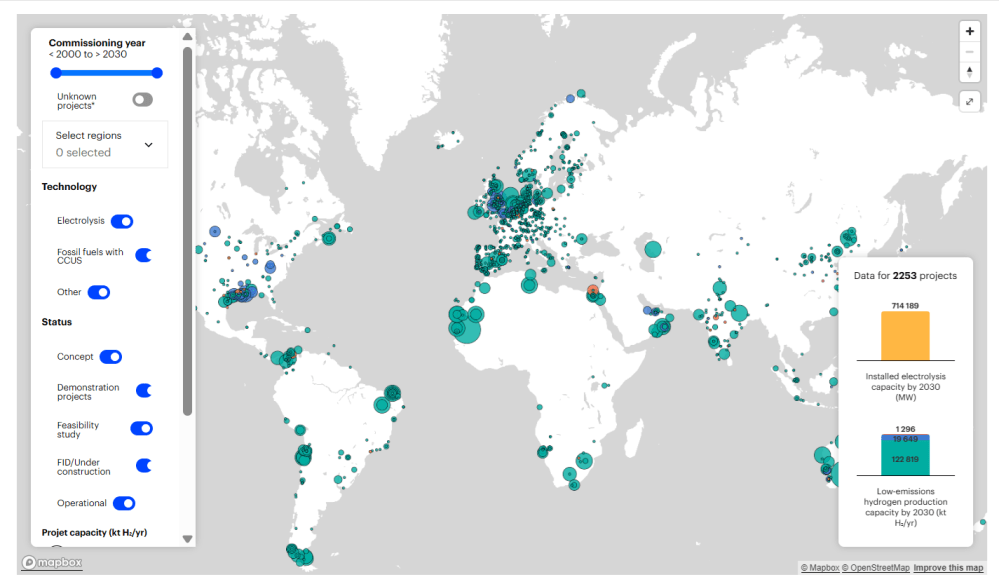
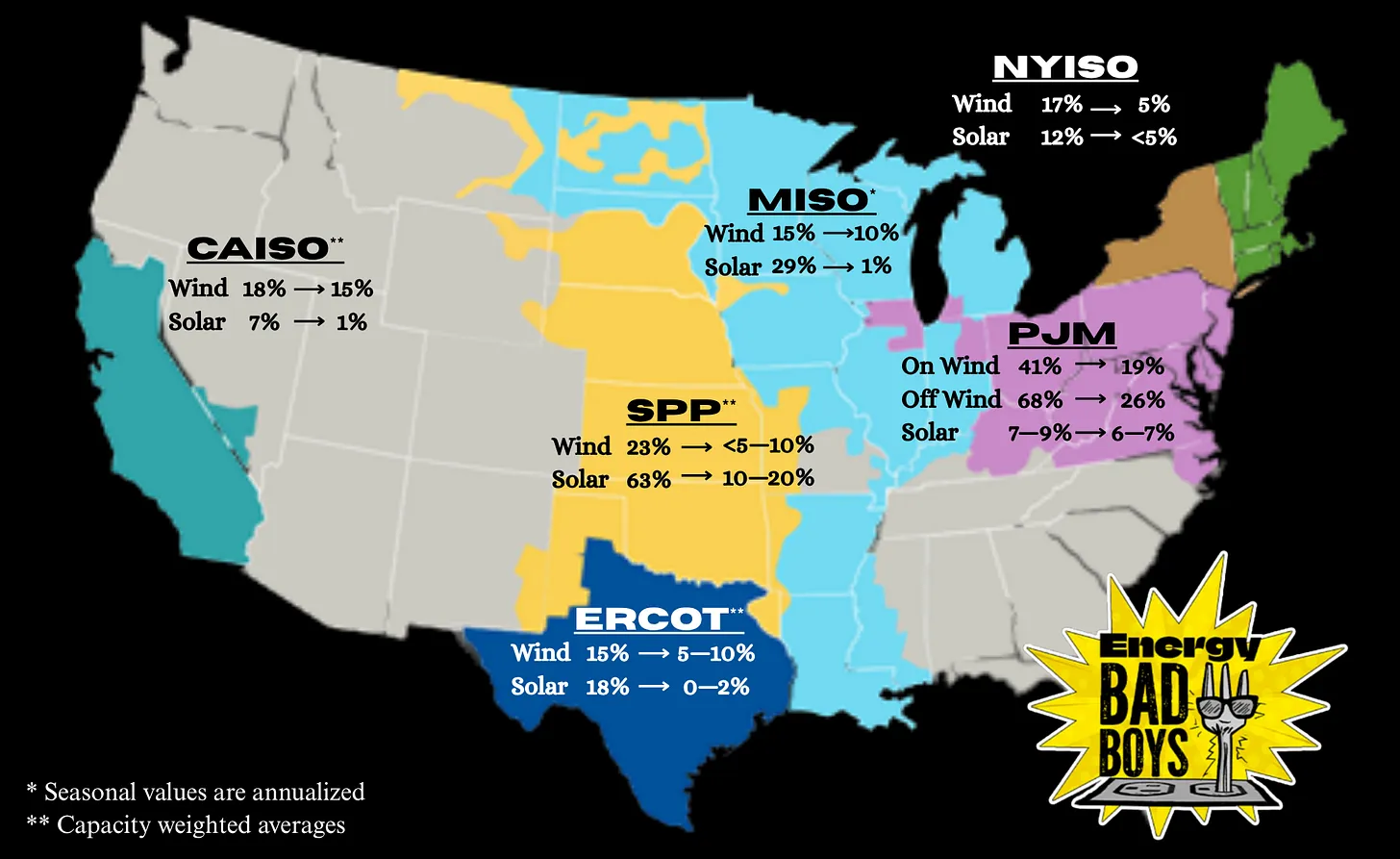
Net Zero Fails Science, Math and People
in the video above, Ron Barmby joins Angela Wheeler to discuss Sunset on Net Zero and the why green energy schemes fail. He questions the scientific, economic, and engineering basis of global net-zero policies. Drawing on physics, real-world observations, and decades of experience, he argues that CO2’s warming effect is small and diminishing. He also challenges climate models that rely on unverified assumptions. Barmby warns that many green energy solutions are impractical and that net-zero policies disproportionately harm the poor.
For those preferring to read, I provide below a lightly edited transcript in italics with added images. AW refers to Angela Wheeler and RB to Ron Barmby. H/T Climate Change Dispatch.
I think [Net Zero] is insane. It is pointless to pursue it because it will make no difference to the climate or to climate change. The climate will change as it wants to change, no matter how much CO2 we put in the air. So it’s a pointless thing to do. It is unachievable. And in the end, as always, it’s the poorest among us that will pay the highest price proportionally.
AW: This is Climate Debrief, brought to you by the CO2 Coalition. I’m Angela Wheeler. There’s a recently published book, Sunset on Net Zero, a heretics guide to the futile CO2 target. You’re going to hear from the author, CO2 Coalition member Ron Barmby. Ron is a professional engineer with a master’s degree from the University of Alberta and a four-decade career that’s taken him to over 40 countries across five continents. Ron’s adventures have shown him firsthand how societies really are adaptable to shifting climates.
Thank you for taking the time, Ron. Thank you for having me, Angela. Part one of your recent book is titled How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love Carbon Dioxide. Did you have a moment of clarity where this all made sense or did this happen over a period of time?
RB: It sort of happened over a period of time when the Al Gore movie came out. At first, I was impressed with it and I thought, well, this all makes sense. And then as other writers started pointing out the flaws in that movie, I decided I should look into this more too.

Al Gore with a version of the Hockey Stick graph in the 2006 movie An Inconvenient Truth
And as an engineer, I have a background in physics and I realized that a lot of the physical characteristics that Al Gore was talking about simply aren’t true. So it developed over time. And as it developed over time, some of my friends said, Ron, you should write this down. And so I did. And that was my first book. The second book, the one that you just mentioned, is sort of an update of what’s happened since 2020 when the first book was published.

AW: What is your analysis of this global effort to reach net zero?
RB: Well, I think it’s insane. That’s what I think. It is pointless to pursue it because it will make no difference to the climate or to climate change.
I now declare the Paris Agreement for Climate Change open for signature. More than 170 countries signed the Paris Agreement. They are pledging to take steps to limit the rise of global temperatures to well below two degrees Celsius.
–Ban Ki-moon, UN Secretary-General
The climate will change as it wants to change, no matter how much CO2 we put in the air. So it’s a pointless thing to do. The second part of it, it is unachievable.
And that’s where my engineering background comes in and many of the engineers that are part of the CO2 coalition. What they want to achieve simply can’t be done in a reasonable time frame at a reasonable cost, and it can’t be done globally. And the third thing about it is the whole thing is unfair because it punishes those that are trying to reduce CO2 emissions to the benefit of those who are only paying lip service to CO2 emissions. And in the end, as always, it’s the poorest among us that will pay the highest price proportionally.
AW: Your book sums it up well in stating that warming from future CO2 is too trivial and too gradual to justify drastic policy. Could you explain that?
RB: Well, there was a paper written in 2019 by two coalition members, Dr. Wijngaarden and Dr. Happer.
That paper explained from physicist to physicist how we can actually measure the amount of CO2 warming that has happened. And by measuring that amount, it confirmed the equations that would predict what would happen if we doubled the CO2 emissions again, or came to a complete doubling. And looking into that paper, I tried to explain in everyday terms how valid it is and what it means. And so in that investigation, I came to the conclusion that this is understandable by many, many people. And if we got the word out, that might help shift the view on the alarmism of carbon dioxide induced global warming.
[From Wijngaarden and Happer study: My synopsis is Climate Change and CO2 Not a Problem
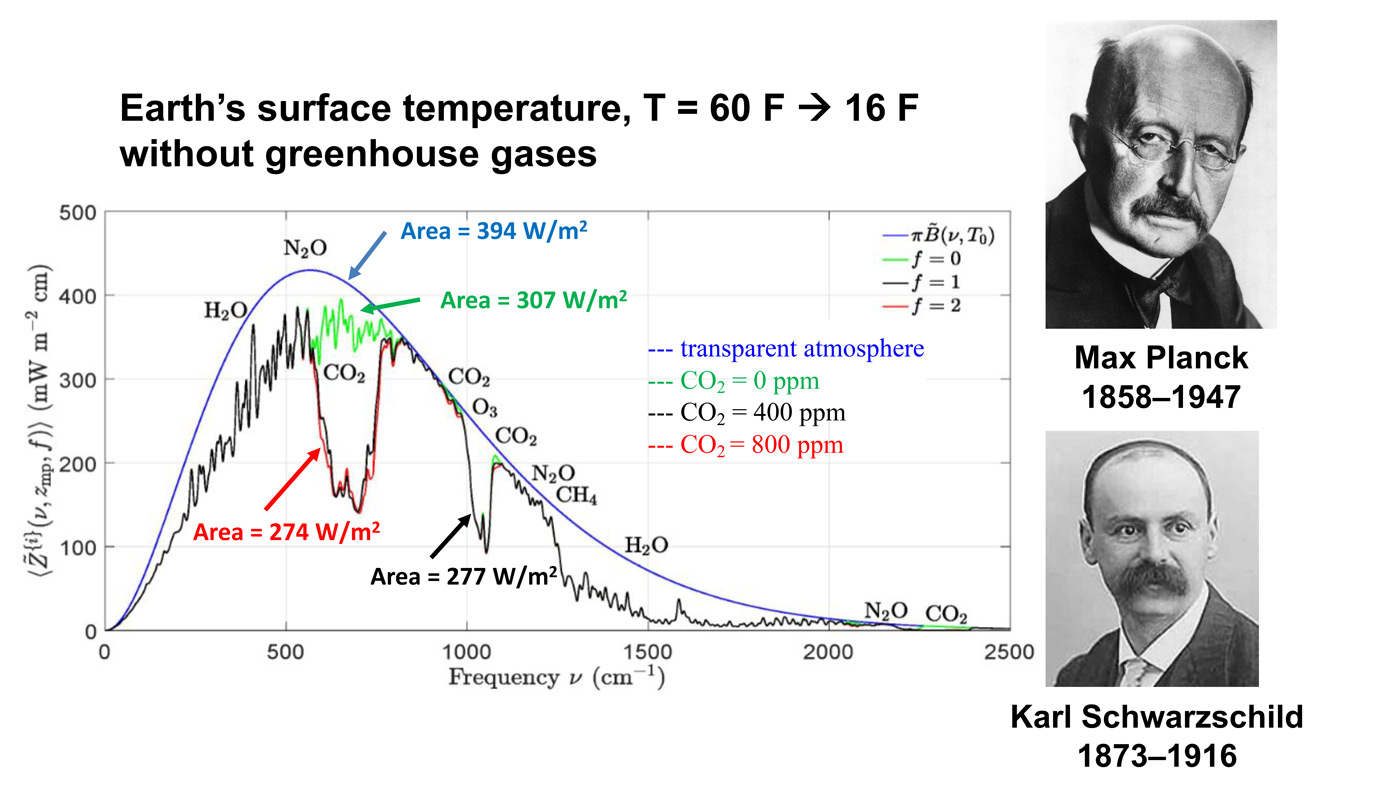
“Right in the middle of these curves, you can see a gap in spectrum. The gap is caused by CO2 absorbing radiation that would otherwise cool the Earth. If you double the amount of CO2, you don’t double the size of that gap. You just go from the black curve to the red curve, and you can barely see the difference. The gap hardly changes.”]
AW: Is it your position that the push for net zero stems from political exaggeration, followed by media amplification and not empirical science? Is that a fair assessment?
RB: I think that’s a fair assessment. And Margaret Thatcher is one person that I like to quote on that. Many people don’t realize that Margaret Thatcher was trained in Oxford as a chemist, as a research chemist. So she was one of the big people behind pushing for the Paris Agreement. And she wanted to reduce CO2 emissions because she was concerned. But she knew how the scientific method worked because she was trained in it. And when she saw the first reports come out, she changed her mind.
And she said, kind of paraphrasing Hamlet, that there isn’t method in their madness, there is actually madness in their method. And what Margaret Thatcher pointed out was that the desire to control CO2 emissions worldwide is something that would require a worldwide organization to organize and enforce. And so she saw it in that perspective, that it was a grand multinational global socialist effort to control the economy.
She was not far off. But I do think that on the other end of the spectrum, capitalists have found a way to exploit this energy transition and make money that they would otherwise not be able to make.
AW: Regarding net zero, your compelling argument cites the work of two other CO2 coalition members, our chairman, Dr. William Happer, and Dr. William Don Wingarden. Their work, as you mentioned, initially a series of academic papers by physicists for physicists, focuses on measuring thermal radiation transfer and had a truly profound effect because it undermines net zero. For one, they use real observations, not models. Can you please explain the difference and why is it worth noting?
RB: The scientific method is a way to make sure that we’re not fooling ourselves, that we think we understand something that we don’t really understand. And it was one thing that another CO2 member, Dr. Clauser, pointed out in his talk to Korean physicist students a couple of years ago. You have to go into science with an open mind and an unbiased mind. And you have to report faithfully what you observe. And it’s the observations of physical reality that is the link to truth in science.

So the computer models that the IPCC relies on aren’t based on observations that are linked to reality. They’re based on biases that the computer programmers put into their own models. And the brilliance behind the Van Wingarden and Happer study is that they found an existing public domain database that contained the observations needed to show that the effect of CO2 warming was very small and it’s diminishing rapidly. Another important thing to mention is that Dr. Happer and Dr. Van Wingarden’s math matches real world data from space. This follows the scientific method, observe, predict, test, repeat.
AW: What you’re saying, and especially in your book, that the scientific method is so important, do you feel it is being neglected and perhaps not followed at the university level today?
RB: Unfortunately, I think, Angela, it’s worse than that. It’s not followed, maybe not at the university level, but I think it’s the elementary, junior high, and high school level where it needs to be brought back into the curriculum and taught. It’s when 10 and 12 year old students come home and they’re convinced that CO2 is something to be afraid of. That’s where the problem starts. And I think that’s where the problem has to be fixed.
AW: Regarding the paper by Dr. Happer and Dr. Van Wingarden, they didn’t just claim CO2 impact is small. They measured it, verified it, and anyone can check their data. They replaced alarmist models with hard, observable facts. How can anyone argue that?
RB: Angela, I don’t think anyone has argued with that. I think the mainstream media and the IPCC have simply ignored it. They haven’t addressed it. Coming out in the United States is a presidential directive that all science backed by the federal government must meet the scientific method standards. And I think that’s going to be a huge change worldwide when organizations, both federal and international organizations, when they are held to the standard of the scientific method, I think their karmic alarmism is just going to melt away.
AW: As a former teacher and also as a mother and now a GG, I was gratified to see your chapter Stop Scaring the Children. What compelled you to write this chapter?
RB: I’m a grandfather, and my grandkids are very concerned about CO2. And so it takes me a long time to explain to them that there’s nothing to worry about. And unfortunately, in a more of a millennial generation, there’s been a lot of extreme anxiety among that generation about climate change. And unfortunately, there’s been some tragedies that have resulted because of that. So I think it’s important to stop scaring the children. If you want to deal with a scientific methodology or a proposition you want to promote, bring it forward to trained people who can discuss it intelligently with you. Don’t bring it into the classroom of an elementary school and scare children with it.

AW: Ron, the second part of your book is Engineering 101 is the doomsday book for net zero. Why is that?
RB: Well, because there are all of the green energy sources and the green machines that run on them, and many of them just simply fail when you try to build them. And I think I quote in my book, it was James Michener who said scientists dream of great things, but engineers build them. Well, you can have great dreams. You can dream of creating a solar guidance star like Dr. Hapur did, but it’s up to the engineers to build them. And everyone is crossing their fingers until the thing actually works.
And a lot of the propositions that are out in the mainstream media, how we can avoid or reduce our CO2 emissions are either uneconomic or they hurt the environment more than they help, or they simply don’t work. And that’s my engineering perspective coming into play.
AW: I see. And that makes me think of models, climate models. For example, you can create the model, but from an engineering standpoint, and with regard to net zero, is it impossible to come up with the conclusions that they do with models?
RB: In the case of climate, yes, it is. Now in engineering we use models for a number of things, because we have verified that the equations we’ve put into the model are correct, and they can predict what might happen. And you can see that in flight simulators.
In my own background, reservoir engineering models are based on the Darcy equation, and they’re quite good at predicting what will happen, because those equations stand up to the scientific method. And so when your equations can predict what happens in the future, and it actually happens, then you verified the equation, then you verified the model. The IPCC models, they have equations in there and assumptions that simply aren’t verified, and they don’t predict accurately.
One thing that came out of the Van Wintergaarden and Happer paper, and other papers that are associated with members of the CO2, is that the CO2 warming from the IPCC models has to be at least doubled, and some would claim quadrupled, in order to get the alarmist levels of warming that they predict. And so that factor of two or four just thrown in to cause more anxiety, that’s not science, that’s scare tactics. And it’s important to point out that the IPCC is a government organization, it’s not a science organization.
AW: And the other thing is, they say carbon dioxide is the control knob for temperature, and that’s not the case, correct?
RB: You’re absolutely correct. We run on an energy balance, and that energy balance coming from the sun has part to do with the climate on earth. And as Gregory Wrightstone pointed out in his book, 90% of the global warming effect of CO2 is already behind us. So the next 10% is going to be minimal. So the next 10% is not the control knob of temperature on earth. Now, if there was no CO2 on earth, as there is no CO2 on the moon, the first amounts of CO2 added would have a dramatic effect on temperature. But that’s way, way behind us.
AW: Well, in concluding our conversation, I would like to let our viewers and listeners know that they can get your new book, Sunset on Net Zero, A Heretic’s Guide to the Futile CO2 Target at Amazon. Ron, there are many excellent points in your book we didn’t get to. I hope you will join us again soon on Climate Debrief. I’d love to, Angela. Thank you very much.




























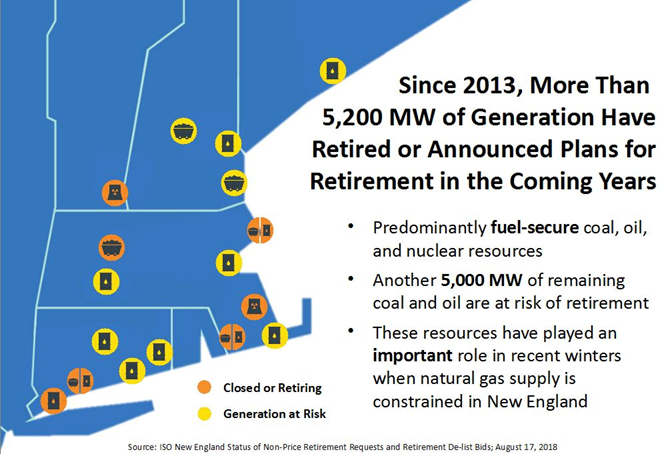
 The system is under strain even without electrification
The system is under strain even without electrification











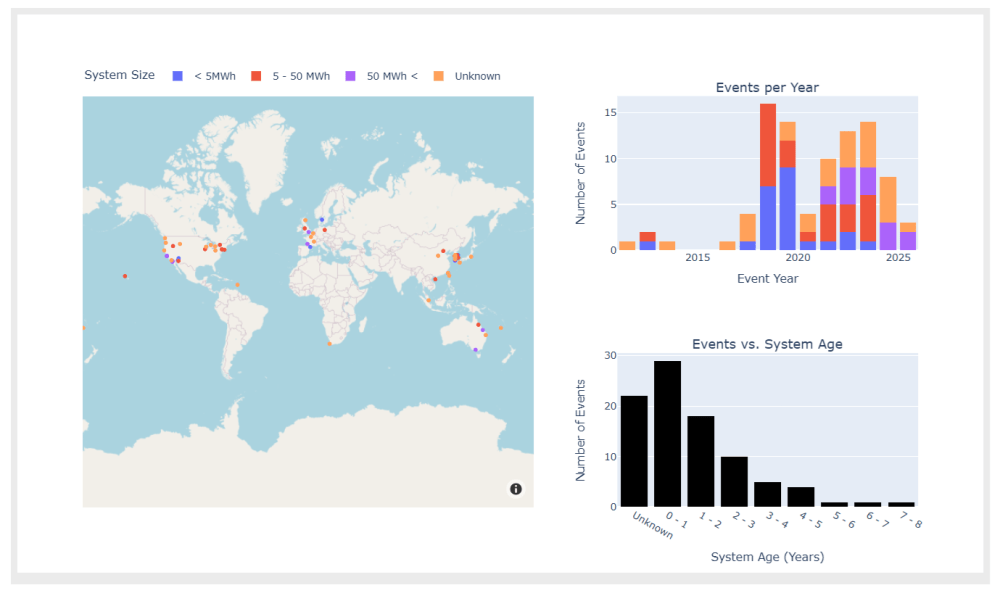
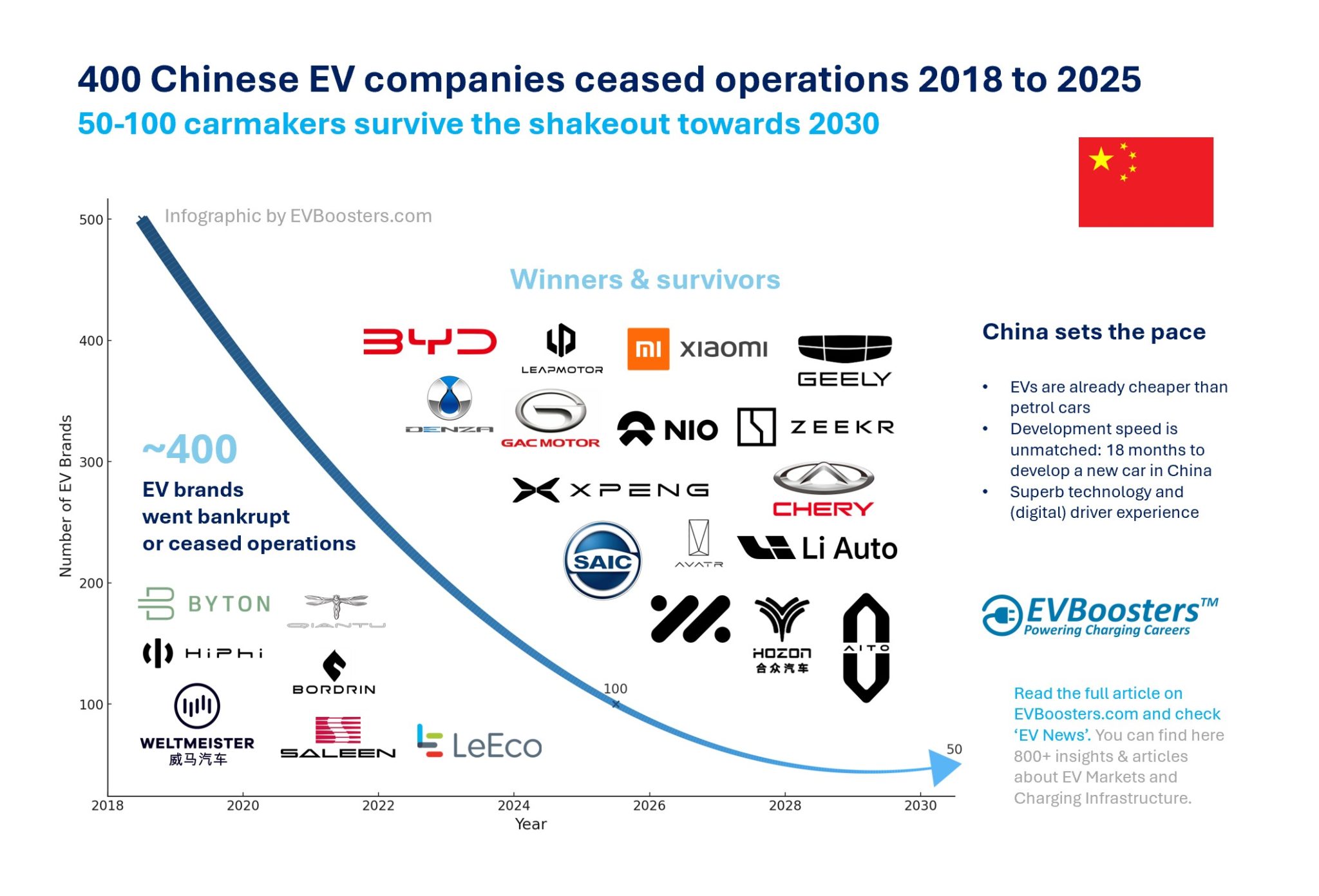 The Chinese electric vehicle (EV) boom has turned into a dramatic shakeout. Around 2018, China had more than 500 EV startups registered. These included everything from serious automotive disruptors to local government-backed ventures that never made it past the prototype phase. What do we mean by “EV startup”? In this context, it includes any newly registered Chinese company involved in the design, development, or production of new energy vehicles (NEVs) — including electric, plug-in hybrid and hydrogen cars. Many were speculative projects, created quickly to benefit from generous state subsidies, often with minimal automotive expertise. While a few had serious ambitions and advanced prototypes, the vast majority never got a vehicle on the road. By 2025, only around 100 of these brands remain active. Analysts from McKinsey predict that by 2030, fewer than 50 Chinese EV companies will survive. This is not just a story of collapse, but also of market maturation, consolidation, and strategic realignment.
The Chinese electric vehicle (EV) boom has turned into a dramatic shakeout. Around 2018, China had more than 500 EV startups registered. These included everything from serious automotive disruptors to local government-backed ventures that never made it past the prototype phase. What do we mean by “EV startup”? In this context, it includes any newly registered Chinese company involved in the design, development, or production of new energy vehicles (NEVs) — including electric, plug-in hybrid and hydrogen cars. Many were speculative projects, created quickly to benefit from generous state subsidies, often with minimal automotive expertise. While a few had serious ambitions and advanced prototypes, the vast majority never got a vehicle on the road. By 2025, only around 100 of these brands remain active. Analysts from McKinsey predict that by 2030, fewer than 50 Chinese EV companies will survive. This is not just a story of collapse, but also of market maturation, consolidation, and strategic realignment.