Why Fossil Fuels Still Rule
Kite & Key explain in their video, transcript in italics with my bolds and added images.
Tech executives. Heads of state. Brilliant scientists and engineers.
They’re some of the most talented and respected individuals in the world — and, in recent years, they’ve all come together behind a common purpose.
They’ve marshaled their talents — and trillions of dollars in cash — to move the world beyond the era of fossil fuels.
What can you accomplish when you have that much talent working towards a single goal?
Would you believe … almost nothing?
In recent years, the world has gone to extraordinary lengths to break its dependence on fossil fuels.
We’ve signed international treaties.
We’ve started enormous government programs.
We’ve launched corporate sustainability initiatives.
We’ve vandalized Stonehenge.

Not sure why that last one was necessary. Druids are about as low-carbon as they come.

Now, what do we have to show for all of these efforts to move beyond fossil fuels?
Well, it’s not nothing. But if you squint even just a little … it looks like nothing.
Here’s what we mean. Between 2015 and 2023, the world invested over $12 trillion in alternative energy. By the end of that period, we were investing nearly double as much in alternatives as we were in fossil fuels.i
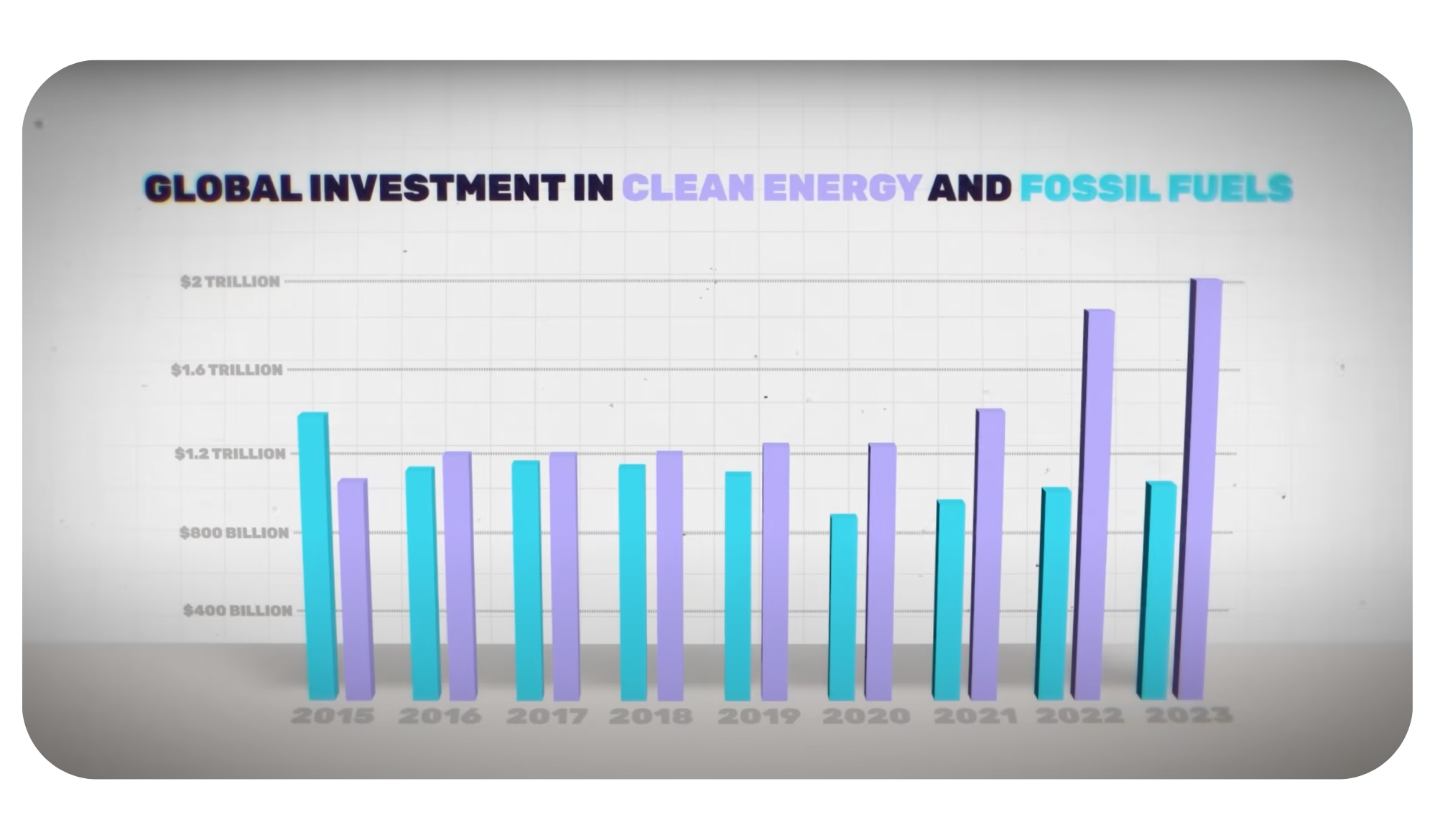
And the consequences of all that effort?
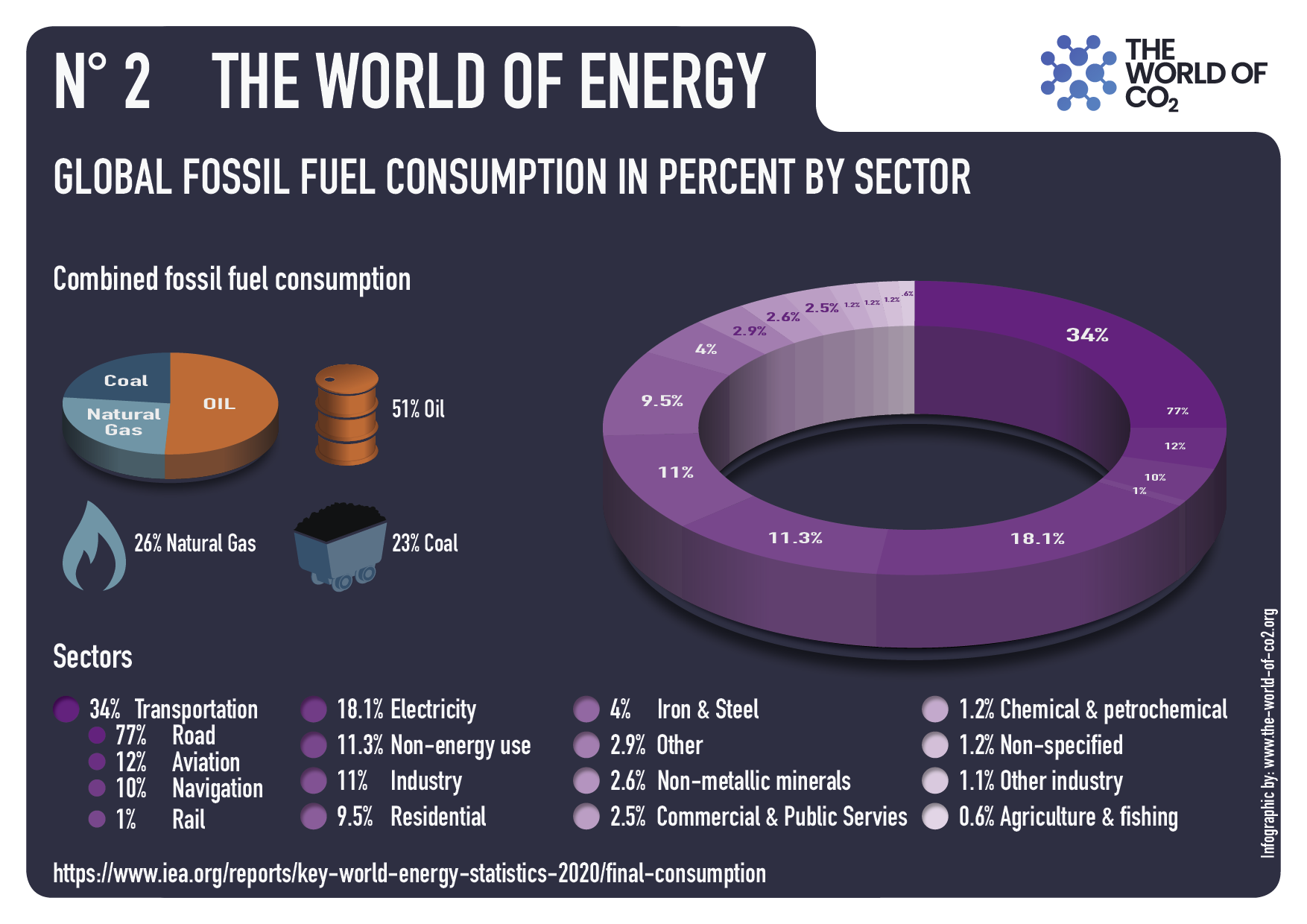
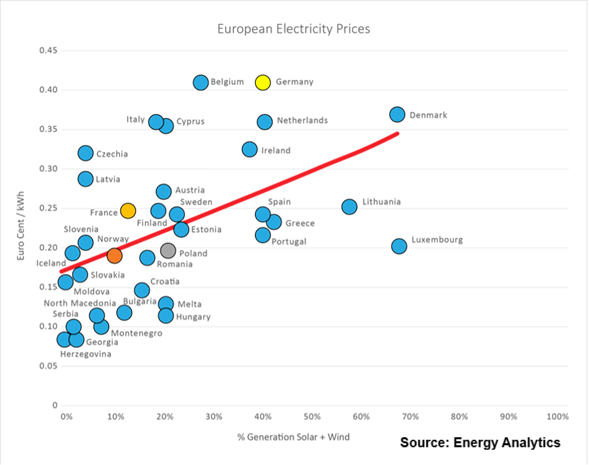
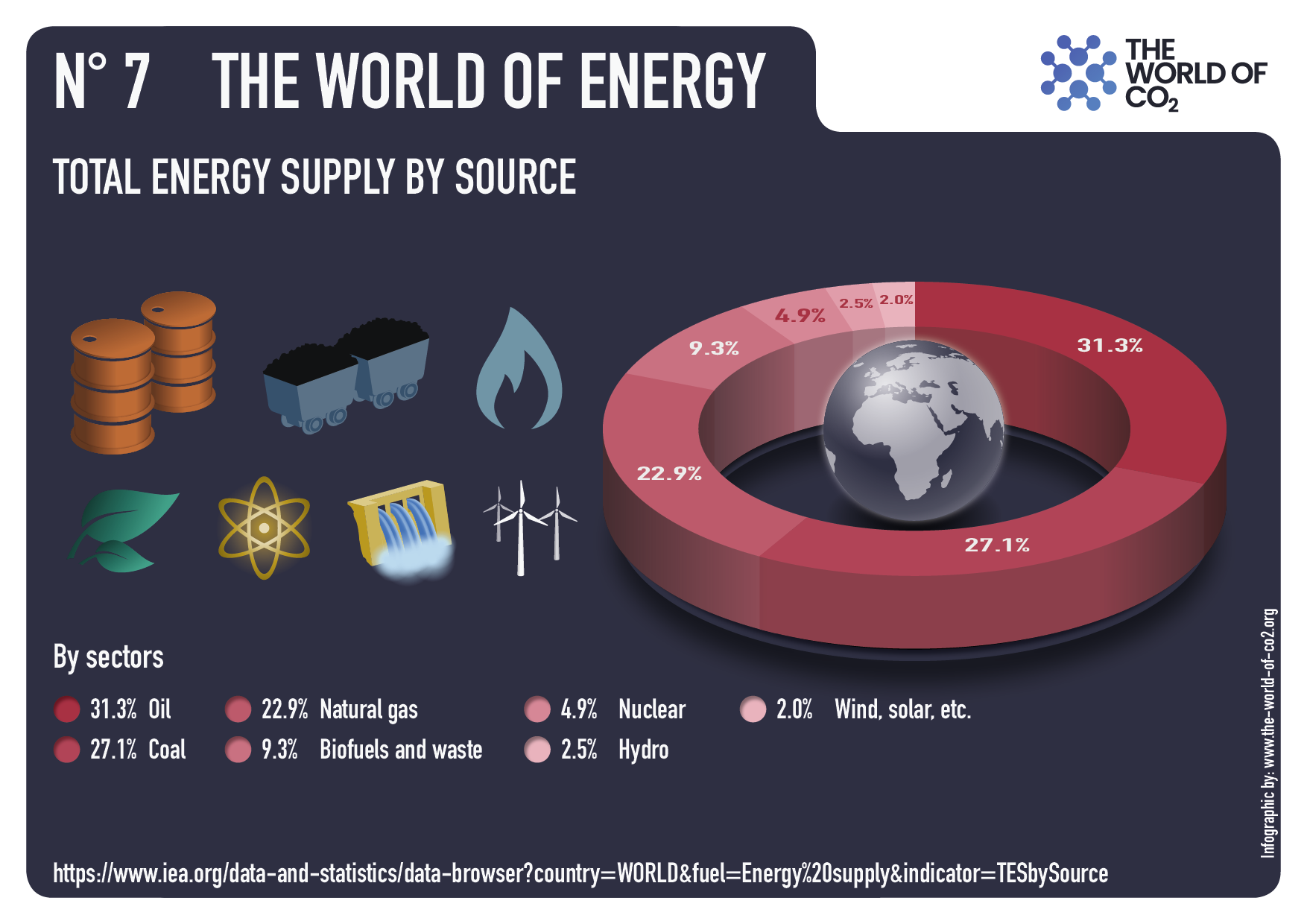
Well, according to the International Energy Agency, in the decade from 2013 to 2023 the percentage of global energy derived from fossil fuels declined from 82 percent … to 80 percent.ii

Since 1965 oil, gas and coal (FF, sometimes termed “Thermal”) averaged 88% of PE consumed, ranging from 93% in 1965 to 81% in 2024. Source: Energy Institute
Now, none of this is to make fun of these efforts. The people behind these initiatives are often very, very smart. Which ought to make us even more curious about why they’re still not able to move the needle much.
Why, despite all their efforts, do fossil fuels continue to be the world’s primary energy sources?
Well, here’s the thing: It’s not because of a lack of money or initiative.
It’s because of the way energy actually works.
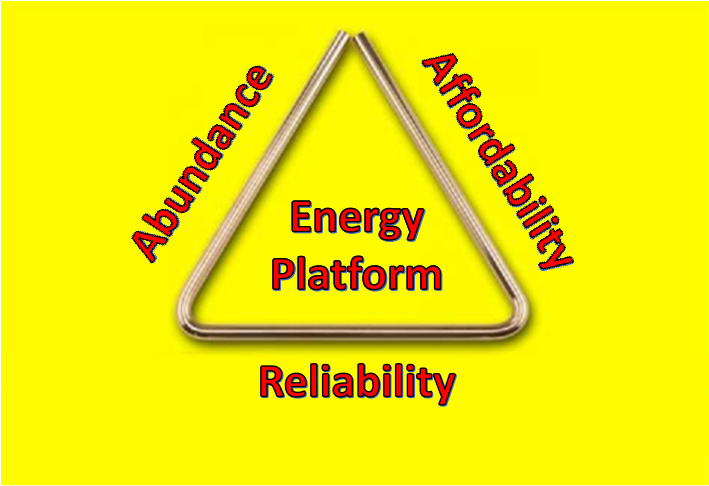
Because basically our entire existence — lighting and heating our homes, traveling to work, getting food onto the shelves of your grocery store — is dependent on energy, we need our power sources to be reliable, affordable, and abundant. And on that front … fossil fuels have proven hard to beat.
There are a lot of reasons for that, but here are three of the biggest ones.
First: efficiency. Fossil fuels allow you to get a lot of energy out of very little material.
For example, to generate as much energy as you get from just one oil well in the Permian Basin of West Texas you’d need to build 10 windmills, each about 330 feet high.iii And because demand is only going up — the world uses 40 percent more energy now than it did just 20 years agoiv — we’re deeply dependent on whichever sources can give us the most bang for our buck.
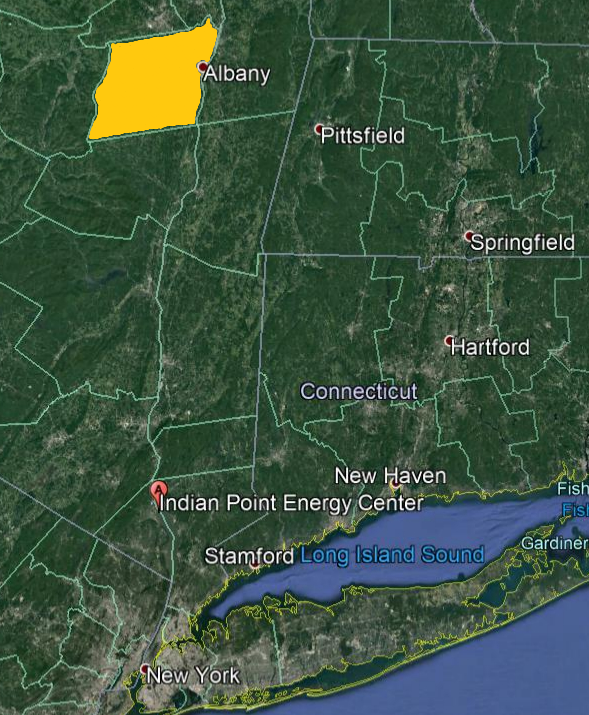
To replace the electricity from now closed Indian Point nuclear plant would require covering Albany County with wind turbines.
Second: reliability. Energy buffs like to talk about something called the capacity factor, which in plain English means the amount of time a power source can generate its maximum amount of power. For solar, it’s less than 25 percent of the time. For wind, it’s about 34 percent. By contrast, coal is at over 42 percent and natural gas is at essentially 60 percent.v
Third: storage. Fossil fuels are easy and cheap to store, which is necessary to make sure you’ve got enough supply to know the lights will stay on.
How cheap? The costs of storing a barrel of oil or the equivalent amount of natural gas is about $1 a month. For coal, it’s even cheaper.vi To store the same amount of energy from wind or solar — which would require a lithium battery — costs 30 times as much.vii
All of which is to say that when you look at the physics and the economics
— you can start to see why America still gets more than
80 percent of its energy from fossil fuels.viii
Which, by the way, is pretty standard for wealthy countries: They talk a lot about renewables, but when it comes right down to it?
The U.K. gets about 75 percent of its energy from fossil fuels. As does Germany. In Japan it’s over 83 percent. In Australia it’s 85 percent.ix Not because they aren’t trying to move away from fossil fuels, but because they’re coming up against the reality that fossil fuels are the only sources that can give them as much power as their countries need.
There is, however, at least one noteworthy counterexample: France, which, as of 2023, relies on fossil fuels for less than 50 percent of its energy needs.x How do they do that? Well, here’s the catch: It’s not because of things like wind and solar. France gets over 1/3 of its power from nuclear, a carbon-free energy source that can run at full power over 92 percent of the time.xi
Which is an interesting idea … that the world’s wealthy democracies are largely ignoring. In fact, of the 61 new nuclear reactors currently being built around the world, 29 of them are in China.xii And many of the rest are in places like Bangladesh, Turkey, and Egypt.
But there’s one other factor we have to take into consideration when we think about why fossil fuels have endured — and it’s a big one. When we talk about energy, many of us think in terms of electricity. But in reality, America’s single largest use of energy is for transportation. And nearly 90 percent of that energy comes from oil.xiii
Why? Well, for a clarifying example, think about the journey of a package that you buy online. Maybe it comes from overseas on a cargo ship or, if you’re really fancy, a plane. It gets sent to a warehouse, loaded onto a truck, sent off to a series of processing centers, and then arrives seamlessly … on your neighbor’s porch, for some reason.
Now, this process is invisible to most of us, but if we tried to dramatically change the fuel sources involved … well, let’s just say we’d notice.
Want that package to come on an electric plane? Given the current limits of the technology, it could travel a distance of about 30 miles.xiv
Want it to cross the ocean on a battery-powered cargo ship? The journeys those vessels take can run anywhere from 15 to 50 days.xv The biggest battery available could get you … one day of power.xvi Which would ensure your package was speedily delivered to the bottom of the Western Pacific.
Want an electric big rig to move your package across the country? Because they can travel less than half as far as a normal truck before they have to recharge, are three times as expensive to buy, and would require trucking companies to roughly double their number of both drivers and vehicles, your package would arrive much later and be way more expensive.xvii
In fact, it’s estimated that moving to all-electric trucking would be so costly that on its own it’d create a one percent increase in inflation for the entire country.xviii
Bottom line: The decisions as to which energy sources we rely on aren’t arbitrary.
The world as we know it is powered by reliable fuel sources like
natural gas, oil, and — when we’ll allow it — nuclear.
Plenty of people would like to move beyond those sources in theory. But when they experienced what the world actually looks like without them — higher prices, slower travel, less reliable electricity — chances are there’d be a lot fewer takers.
Except the Druids. These dudes would be fine.