
A recent international analysis of 1500 climate policies around the world concluded that 63 or 4% of them were successful in reducing emissions. The paper is Climate policies that achieved major emission reductions: Global evidence from two decades published at Science.org. Excerpts in italics with my bolds.
Abstract
Meeting the Paris Agreement’s climate targets necessitates better knowledge about which climate policies work in reducing emissions at the necessary scale. We provide a global, systematic ex post evaluation to identify policy combinations that have led to large emission reductions out of 1500 climate policies implemented between 1998 and 2022 across 41 countries from six continents. Our approachintegrates a comprehensive climate policy database with a machine learning–based extension ofthe common difference-in-differences approach. We identified 63 successful policy interventions with total emission reductions between 0.6 billion and 1.8 billion metric tonnes CO2 . Our insights on effective but rarely studied policy combinations highlight the important role of price-based instruments in well-designed policy mixes and the policy efforts necessary for closing the emissions gap.
Context
(1). Although the [Paris] agreement seeks to limit global average temperature increase to “well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C,” its success critically hinges on the implementation of effective climate policies at the national level. However, scenarios from global integrated assessment models suggest that the aggregated mitigation efforts communicated through nationally determined contributions (NDCs) fall short of the required emission reductions.
(2)The United Nations (UN) estimates quantify a median emission gap of 23 billion metric tonnes(Gt) carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-eq) by 2030
(3). The persistence of this emissions gap is not only caused by an ambition gap but also a gap in the outcomes that adopted policies achieve in terms of emission reductions.
(4). This raises the fundamental question as to which types of policy measures are successfully causing meaningful emission reductions. Despite more than two decades of experience with thousands of diverse climate policy measures gained around the world, there is consensus in neither science nor policy on this question.
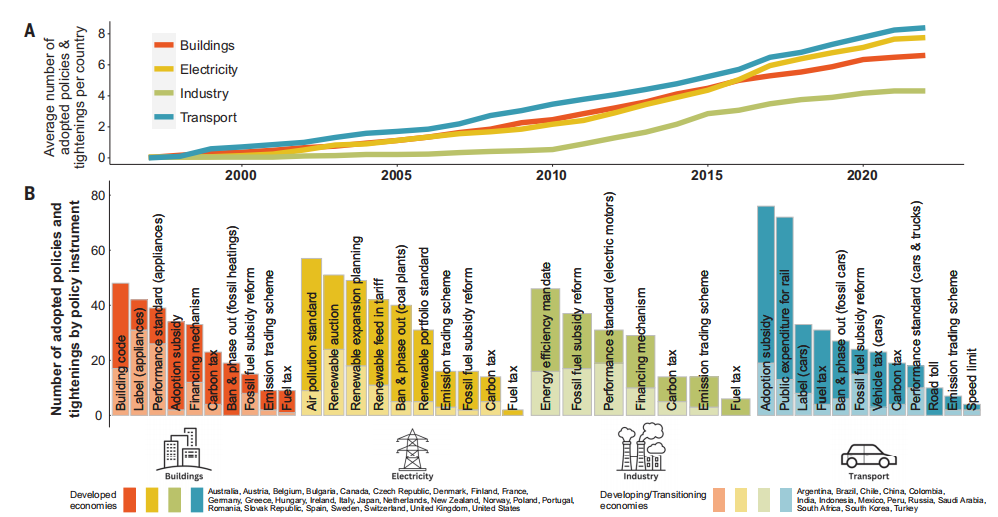
The exhibit above shows the scope and complexity of the analysis. But the bottom line is that 96% of the effort and trillions of $$$ were spent to no avail. It is estimated that on the order of 1.2 Billion tonnes of CO2 were prevented over the last 20 years, with an additional 23 Billion tonnes to be erased by 2030.
Any enterprise with that performance would be liquidated.
That is an epic failure in fact.
And recommending mixing of policies including subsidies and regulations along with pricing goes against economic theory and fails in practice. Ross McKitrick explains the dangers of making climate policies willy-nilly in his Financial Post article Economists’ letter misses the point about the carbon tax revolt. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Yes, the carbon tax works great in a ‘first-best’ world where it’s the
only carbon policy. In the real world, carbon policies are piled high.
An open letter is circulating online among my economist colleagues aiming to promote sound thinking on carbon taxes. It makes some valid points and will probably get waved around in the House of Commons before long. But it’s conspicuously selective in its focus, to the point of ignoring the main problems with Canadian climate policy as a whole.

EV charging sign Electric-vehicle mandates and subsidies are among the mountain of climate policies that have been piled on top of Canada’s carbon tax. PHOTO BY JOSHUA A. BICKEL/THE ASSOCIATED PRESS
There’s a massive pile of boulders blocking the road to efficient policy, including:
-
- clean fuel regulations,
- the oil-and-gas-sector emissions cap,
- the electricity sector coal phase-out,
- strict energy efficiency rules for new and existing buildings,
- new performance mandates for natural gas-fired generation plants,
- the regulatory blockade against liquified natural gas export facilities,
- new motor vehicle fuel economy standards,
- caps on fertilizer use on farms,
- provincial ethanol production subsidies,
- electric vehicle mandates and subsidies,
- provincial renewable electricity mandates,
- grid-scale battery storage experiments,
- the Green Infrastructure Fund,
- carbon capture and underground storage mandates,
- subsidies for electric buses and emergency vehicles in Canadian cities,
- new aviation and rail sector emission limits,
and many more.
Not one of these occasioned a letter of protest from Canadian economists.

Beside that mountain of boulders there’s a twig labelled “overstated objections to carbon pricing.” At the sight of it, hundreds of economists have rushed forward to sweep it off the road. What a help!
To my well-meaning colleagues I say: the pile of regulatory boulders
long ago made the economic case for carbon pricing irrelevant.
Layering a carbon tax on top of current and planned command-and-control regulations does not yield an efficient outcome, it just raises the overall cost to consumers. Which is why I can’t get excited about and certainly won’t sign the carbon-pricing letter. That’s not where the heavy lifting is needed.
My colleagues object to exaggerated claims about the cost of carbon taxes. Fair enough. But far worse are exaggerated claims about both the benefits of reducing carbon dioxide emissions and the economic opportunities associated with the so-called “energy transition.” Exaggeration about the benefits of emission reduction is traceable to poor-quality academic research, such as continued use of climate models known to have large, persistent warming biases and of the RCP8.5 emissions scenario, long since shown in the academic literature to be grossly exaggerated.
But a lot of it is simply groundless rhetoric. Climate activists, politicians and journalists have spent years blaming Canadians’ fossil fuel use for every bad weather event that comes along and shutting down rational debate with polemical cudgels such as “climate emergency” declarations. Again, none of this occasioned a cautionary letter from economists.

There’s another big issue on which the letter was silent. Suppose we did clear all the regulatory boulders along with the carbon-pricing-costs-too-much twig. How high should the carbon tax be? A few of the letter’s signatories are former students of mine so I expect they remember the formula for an optimal emissions tax in the presence of an existing tax system. If not, they can take their copy of Economic Analysis of Environmental Policy by Prof. McKitrick off the shelf, blow off the thick layer of dust and look it up. Or they can consult any of the half-dozen or so journal articles published since the 1970s that derive it. But I suspect most of the other signatories have never seen the formula and don’t even know it exists.
To be technical for a moment, the optimal carbon tax rate varies inversely with the marginal cost of the overall tax system. The higher the tax burden — and with our heavy reliance on income taxes our burden is high — the costlier it is at the margin to provide any public good, including emissions reductions. Economists call this a “second-best problem”: inefficiencies in one place, like the tax system, cause inefficiencies in other policy areas, yielding in this case a higher optimal level of emissions and a lower optimal carbon tax rate.

Based on reasonable estimates of the social cost of carbon and the marginal costs of our tax system, our carbon price is already high enough. In fact, it may well be too high. I say this as one of the only Canadian economists who has published on all aspects of the question. Believing in mainstream climate science and economics, as I do, does not oblige you to dismiss public complaints that the carbon tax is too costly.
Which raises my final point: the age of mass academic letter-writing has long since passed. Academia has become too politically one-sided. Universities don’t get to spend years filling their ranks with staff drawn from one side of the political spectrum and then expect to be viewed as neutral arbiters of public policy issues. The more signatories there are on a letter like this, the less impact it will have. People nowadays will make up their own minds, thank you very much, and a well-argued essay by an individual willing to stand alone may even carry more weight.

Online conversations today are about rising living costs, stagnant real wages and deindustrialization. Even if carbon pricing isn’t the main cause of all this, climate policy is playing a growing role and people can be excused for lumping it all together. The public would welcome insight from economists about how to deal with these challenges. A mass letter enthusing about carbon taxes doesn’t provide it.
Postscript: All the Pain for No Gain is Unnecessary
There is no charge for content on this site, nor for subscribers to receive email notifications of postings.



4 comments