Kite & Key explains in above video Why the Odds Are Stacked Against Net Zero. For those preferring to read I provide a text from the captions, though the video is entertaining along with great images, some of which are included with the text in italics with my bolds.
Overview
Are we at the beginning of the end of fossil fuels? That’s the theory advanced by an international coalition of politicians who aim to get us to net zero carbon emissions by the year 2050. Just one problem: Research from the experts in their own governments suggests it’s a nearly impossible task. Enthusiasts for net zero often say we’re on the cusp of an “energy revolution.”
And that theory has a big problem: Energy revolutions don’t happen — at least not in the way that politicians often describe. While it’s true that technological and economic factors sometimes change the energy mix — countries that get wealthier become less dependent on wood, for example — the broader trend in the history of the world’s energy consumption can be defined by three words: more, more, more.
In a power-hungry world, we keep adding new energy sources. But there’s rarely any subtraction. And, with global energy demand expected to increase by about 35% by 2050, it’s nearly impossible that we can get all the power we need from carbon-free sources. For instance, meeting the net zero goals would require the construction of over 9,000 nuclear plants by 2050. The number currently being built around the world? 59.
So, what will the future of energy really look like? Our video explores.
Transcription
It doesn’t happen that often. But every once in a while, a single generation witnesses a technological breakthrough that will change the world forever.
The printing press.
The beginning of human flight.
And, for our generation, an inevitable full scale revolution in clean energy…
…that’s running a little behind schedule…
…Ok, way behind schedule.
“The beginning of the end of the fossil fuel era.” That’s how the United Nations referred to the outcome of a 2023 climate change summit held in…the United Arab Emirates. Which is sort of like having the Prohibition Conference in Vegas. Nevertheless, delegates from throughout the world left the gathering having pledged that the world would transition away from fossil fuels and get the world to net zero carbon emissions by the year 2050.
Now, the rationale for this is clear enough. Leaders from around the globe are worried that without a shift over to carbon-free energy sources like wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear the world will face significant problems as a result of climate change.
But, regardless of why they’re doing this, the more important question is whether they can do it. Because here’s the thing about energy revolutions: they don’t happen. At least not in the way that the UN is imagining. To understand why, it’s worth looking at the history of the world’s energy consumption – which looks like this.
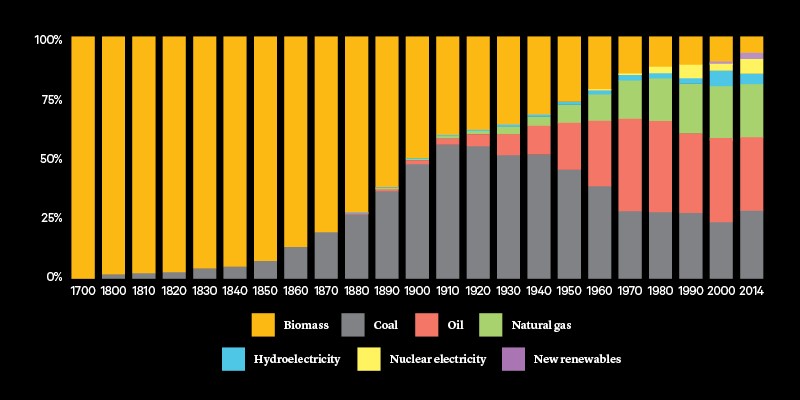
Go back a couple of centuries and the world basically ran on “traditional biomass”– -which is a fancy way of saying … wood. We burned a lot of wood and also … dung. Then in the mid 19th century, coal came into the picture in a big way. By the 20th century, we’re using tons of oil. And natural gas is a big factor too, especially as we cross into the 21st century, and fracking makes it both abundant and more affordable. As the years went by, we added low-carbon sources of energy as well, like nuclear, hydro, wind, and solar–though overall, they’re still a pretty small part of the picture.
Now, there are two important things to note about this chart. First, the history of the world’s energy consumption can be defined in three words: more, more, more. Which kind of makes sense. After all, pretty much everything that defines modern life involves a lot of energy. Between 1950 and 2022, for example, the population of the U.S. a little more than doubled. But in that same time period, our electricity use got 14 times larger.

And second, because of that “more and more, more” trend, the only things we’ve ever had that look like energy “revolutions” have been about adding new sources into the mix, not getting rid of existing ones as net zero goals propose.
Now, to be clear, that doesn’t mean that nothing ever changes. In wealthier nations, the rise of cheaper natural gas has led to less coal usage, especially in the U.S. And poorer countries usually abandoned traditional biomass as they get wealthier, because no advanced nation powers itself by burning wood. We use it for much more sophisticated purposes…like doing psychedelics in the Nevada desert.
But using a little less coal or wood or relatively modest changes–and importantly are driven by cold, hard economic facts. By contrast, what the net zero goals entail is replacing all of this … with this … in just about 25 years. Based on little more than the fact that politicians just want it to happen.
To understand just how tall a task this is, it’s worth looking at what it would require to make it a reality. It’s estimated that meeting net zero goals would require deploying 2000 new wind turbines…
…every day … for the next 25 years. To give you some context for that, the U.S. builds about 3000 new wind turbines…
…a year.
Alternately, you could open one new nuclear plant every day for the next 25 years. For the record, that’s over 9,000 of them. And, also for the record, as of 2023, the number that were actually being built across the entire world was … 59. And here in the U.S. anyway, it generally takes over a decade to build them.
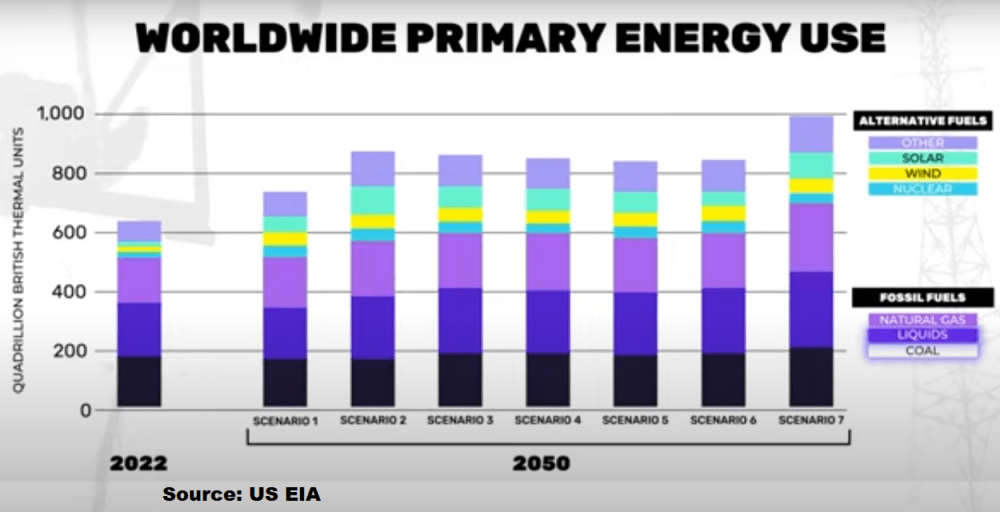
And those are some of the reasons why what politicians promise about net zero and what the experts in their own governments say…don’t exactly match up. The government’s U.S. Energy Information Administration, or EIA, projects that by the year 2050, far from seeing a revolution in energy, America will be a little less reliant on coal, a little more so on renewables…and the rest of the picture looks pretty much the same as today.
And in fact, this is true for the entire world. The EIA ran seven different scenarios for what the world’s energy consumption could look like in 2050, and while all of them showed a significant increase in renewables … they also all showed a world that continued to get most of its energy from things like coal, oil, and natural gas. Not exactly “the beginning of the end of the fossil fuel era.”
The reason for all of this: We simply can’t take enormous quantities of energy offline in a world where it’s predicted that we’re going to need almost 35% more of it by the year 2050. For one thing, there are a lot of poor countries around the world who are going to need dramatically more energy to bring themselves up to even a fraction of our standards of living.
And for another, the technologies of the future require vast amounts of power. By the year 2030, it’s estimated the computer usage around the world will take up as much as five times more of the world’s electricity production as it did even in 2020. The digital cloud we all use to store data already uses twice as much electricity as the entire nation of Japan. And with new energy-hungry technologies like AI on the way, things are only gonna move further in that direction.
Which means the real future of energy is probably: everything. Nuclear, natural gas, wind, and solar, oil, hydropower, coal. We’re going to need all of it. Probably not much wood though.
Except for these guys.



Just excellent!
The world will NEVER transition away from hydrocarbon fuels and hydrocarbon products.
NEVER.
The reasons are physics reality and physical reality. Life is carbon based, requiring carbon for life’s physical structures, and requiring the oxidation of carbon (carbohydrates, fats, proteins) to provide life’s energy.
For the same reasons that life utilizes carbon, the modern world utilizes the same physics and physical reality to utilize carbon…to provide energy–for fuels, for electricity generation, and hydrocarbons for the structures of the modern world’s products: plastics, fertilizers, cement, steel, basically every modern product.
The mass use of hydrocarbons in the modern world is simply mirroring the mass use of carbon in living creatures.
The pursuit of Net Zero is utterly insane and totally, completely, and inevitably, doomed to failure.
LikeLike
Thanks for your comment, and for reminding us our daily eating involves essential carbohydrates, like sugars and starches, that our bodies convert into energy that fuels our lives. Great analogy for how hydrocarbons fuel society as a whole.
LikeLike