Dearth of Green Jobs in UK
 Chris Morrison provides the analysis in his Daily Sceptic article ONS Reveals the Pitiful Number of New Green Jobs Being Created in the U.K. Economy. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Chris Morrison provides the analysis in his Daily Sceptic article ONS Reveals the Pitiful Number of New Green Jobs Being Created in the U.K. Economy. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
The problem with the green U.K. economy, and its associated destruction of the hydrocarbon environment, is that there are very few jobs being created. The few remaining ‘workers’ in the ruling Labour party are starting to rumble all the luxury boondoggles that are set to further decimate well-paid jobs in their communities. The figures compiled by the Office for National Statistics (ONS), trying to estimate the actual number of green jobs, are always a highly creative hoot, and the latest batch are no exception. Many jobs identified are simply displacement activity, with one repair or maintenance occupation taking over from another. Around 6% of the total are to be found in ‘environmental charities’, an interesting way to describe elite billionaire political funding to push the Net Zero fantasy. Such is the seeming desperation to rustle up a green job, the ONS even includes repairing home appliances, controlling forest fires and separating hydrogen by carbon dioxide-producing electrolysis.

The latest ‘estimates’ from the ONS cover 2021 and 2022, and they are said to show an increase in both years. But as the graph below reveals, the rises are pitiful over a decade, and the 2022 estimate of 639,000 is less than 2% of jobs in the economy as a whole.

As can be seen, environmental charities employ 40,000 people, almost as many as the 47,000 that work in renewable energy. But the charities figure does not include all those make-work jobs in environmental consultancy and education or what is described as in-house environmental activities. If all the displacement, invented or re-badged jobs in repair, electric vehicles, waste disposal, water treatment, energy efficiency, Net Zero promotion, teaching and the ubiquitous bureaucracy are rightly ignored, it is unlikely that more than 150,000 new jobs have been created.
 Fairly small pickings, it might be thought, from all the cash sprayed at subsidy-hunting chancers over at least two decades. Even worse, any new jobs are easily offset by the occupations being destroyed in steel making, refining hydrocarbons, coal mining and oil and gas exploration. Fracking for gas would transform a number of deprived areas in the U.K. at little environmental cost, as it has done in the U.S. Energy security would likely be achieved, and the tax take would be considerable. But fracking is anathema to the major political parties in the U.K., except the emerging Reform party.
Fairly small pickings, it might be thought, from all the cash sprayed at subsidy-hunting chancers over at least two decades. Even worse, any new jobs are easily offset by the occupations being destroyed in steel making, refining hydrocarbons, coal mining and oil and gas exploration. Fracking for gas would transform a number of deprived areas in the U.K. at little environmental cost, as it has done in the U.S. Energy security would likely be achieved, and the tax take would be considerable. But fracking is anathema to the major political parties in the U.K., except the emerging Reform party. Last week saw some real push back on the madness of Net Zero and the so-called green economy. The boss of GMB, the third largest trade union in the country, told the annual Labour party conference that its plans to decarbonise the energy network by 2030 will cost up to one million jobs, decimate working communities and push up bills for the poorest. According to Smith, Government’s plans for Net Zero were “bonkers” and “fundamentally dishonest”. In a week when it was revealed that British consumers, both industrial and private, had some of the highest electricity prices in the developed world, he charged that current energy policy amounted to virtue signalling by politicians. He accused them of exporting jobs and importing virtue because the jobs were being created abroad rather than in the U.K.
Last week saw some real push back on the madness of Net Zero and the so-called green economy. The boss of GMB, the third largest trade union in the country, told the annual Labour party conference that its plans to decarbonise the energy network by 2030 will cost up to one million jobs, decimate working communities and push up bills for the poorest. According to Smith, Government’s plans for Net Zero were “bonkers” and “fundamentally dishonest”. In a week when it was revealed that British consumers, both industrial and private, had some of the highest electricity prices in the developed world, he charged that current energy policy amounted to virtue signalling by politicians. He accused them of exporting jobs and importing virtue because the jobs were being created abroad rather than in the U.K.
Meanwhile, a recent paper published in Science came to a damning conclusion that will not surprise sceptics, namely that 96% of climate policies over the last 25 years, ultimately designed to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, have been a waste of money. “That’s where green spin has got us,” writes George Monbiot, although these days the Guardian’s extremist-in-chief seems to have given up on all life enhancing processes that run the risk of disturbing anything on the planet. “Finally, 15 years and a trillion dollars too late, George Monbiot says what sceptics have been saying all along,” observes the sceptical journalist Jo Nova. “Nearly every single carbon reduction scheme is a useless make-work machination that creates the illusion that the government is doing something,” she says.
As we can see, the ONS survey is full of these make-work schemes providing jobs that can only exist by rigging free markets and providing eye-watering subsidies from consumers and taxpayers. As the more concerned trade unionists can see, much of the cost of these fantasy ventures falls on the poorest members of society forced to pay higher prices for many of the basic essentials of life. In addition, as we have observed, most green schemes make mugs of the wider investing public, with the RENIXX, a stock capitalisation global index of the 30 largest renewable industrial companies, showing near zero growth since it was started in 2006. None of this matters, of course, to the Mad Miliband and his weird wonks at the U.K. Department of Energy, who are ramping up ideological plans to hose cash at daft ideas like carbon capture, battery energy storage and hydrogen production.
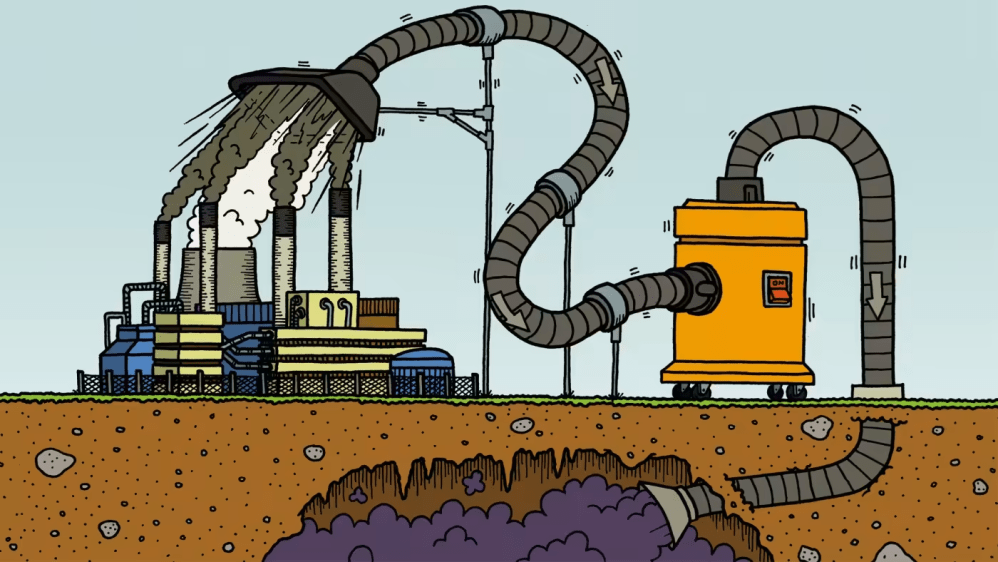
Not only is CO2 Capture and Storage wildly impractical, its aim is to deprive the biosphere of plant food.
But all is not lost on the jobs front – opportunities must be taken when they occur. Earlier this year, Gary Smith was able to point to some new employment clearing away the animal casualties of wind farm blades. “It’s usually a man in a rowing boat, sweeping up the dead birds,” he observed.
Footnote Q & A:
Q: What is the difference between Golf and Government?
A: In Government you can always improve your lie.
–Anonymous Source