Thomas Kolbe explains the sordid history in his American Thinker article Potsdam climate researchers under fire. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Critics of climate policy have long pointed to the problematic dominance of politics in climate science. A recent study from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), which systematically exaggerated the economic consequences of climate change, has reignited the debate over scientific standards and political manipulation in the field.
On April 17, 2024, the science journal Nature published a study by PIK researchers Maximilian Kotz, Anders Levermann, and Leonie Wenz. They calculated that global GDP would shrink by 19% by 2050 due to climate change, regardless whether future emissions were reduced. This projection corresponds to an annual output loss of around $38 trillion — an economic apocalypse, given that no society has the resilience to absorb such a dramatic collapse.

A Solution Delivered Alongside the Doom
The authors also provided a ready-made “solution”: according to their math, the costs of climate damage would be at least six times higher than the expenses required to keep global warming below 2°C. The implication is clear:
This was less a scientific exercise than a political directive for policymakers
to accelerate the fight against alleged man-made climate change.
A year later, the material was “corrected” and republished with slightly toned-down results. The timing was not coincidental: peer review — the scientific quality control process — loomed in the background and threatened to spark controversy.
Peer Review Delivers a Devastating Blow
That controversy soon arrived. Three U.S.-based scientists who reviewed the PIK paper identified serious methodological flaws and faulty data — problems that had been known for over a year. According to their report, PIK’s methodology had no scientific foundation. One reviewer wrote: “I have major concerns about the uncertainty and validity of the empirical model they built and used for the forecasts. It would help this study not to follow the often-exaggerated claims found in the literature.” From the Abstract of paper by Bearpark et al (link in red above):
Kotz, Levermann and Wenz1 (henceforth, KLW) analysed how subnational gross domestic product (GDP) growth responds to year-to-year changes in temperature and precipitation. They reported that if historical relationships continue to hold, global GDP would be lowered by roughly 62% (central estimate) in 2100 under the Representative Concentration Pathway 8.5 ‘high emissions’ scenario, an impact roughly 3 times larger than similar previous estimates,2,3. Here we show that (1) data anomalies arising from one country in KLW’s underlying GDP dataset, Uzbekistan, substantially bias their predicted impacts of climate change, (2) KLW underestimate statistical uncertainty in their future projections of climate impacts, and (3) additional data-quality concerns in KLW’s subnational GDP data warrant further investigation. When Uzbekistan’s data are removed and statistical uncertainty is corrected to account for spatial correlations, KLW’s central estimate aligns closely with previous literature and their results are no longer statistically distinguishable from mitigation costs at any time this century.
Such devastating words cast doubt not just on PIK’s work, but on the broader foundations of climate science itself. Yet papers like this are routinely used to justify green transformation policies, with their web of subsidies, NGOs, regulations, and deep intrusions into economic life.

Finance Dragged Into the Climate Matrix
The significance of this critique lies not only in the study’s flaws but also in the murky financing behind it. These alarmist reports are not just shaping public opinion; they are the cornerstone of a new “climate economy.” The goal is to channel capital flows so that state funds and private wealth are merged into politically favored projects — a carefully orchestrated fusion of financial power and ideology.

International organizations and political institutions amplify these narratives, embedding them into economic governance. The “Network for Greening the Financial System” (NGFS) — closely tied to PIK and consisting of central banks and regulators — projects future climate costs and uses them as a basis for political and financial decisions. The European Central Bank relies on such scenarios for stress tests on banks, forcing higher capital buffers and restricting lending — with direct consequences for growth.

Networks, Obfuscation, and Propaganda
Additional funding flows through organizations like Climate Works, which bankrolls both NGFS and PIK while paying for the calculation of key scenarios. This blurring of lines between sponsor and reviewer, between science and political agenda, opens the door to propaganda. Genuine public debate becomes nearly impossible under such conditions of institutionalized opacity.

The end result is soulless landscapes scarred by wind turbines, the shutdown of modern power plants, and intrusive state regulation extending into private households. The energy sector is sacrificed, home ownership turned into an ideological experiment — all justified by the apocalyptic narrative of man-made climate collapse.

The Origins of CO2 Politics
The roots of this orthodoxy can be traced back to 2009, when the Obama administration declared CO2 a “dangerous pollutant” via the EPA’s Endangerment Finding. This politically-driven decision, made without congressional approval, laid the groundwork for carbon pricing, emissions trading, and sweeping regulatory interventions.

Europe embraced the same model, perhaps even spearheaded it. As an energy-poor continent, the EU saw an opportunity: by making fossil fuels expensive and heavily regulated, it could level the playing field and prevent resource-rich competitors from exploiting their natural energy advantages.
Donald Trump briefly broke with this orthodoxy, scrapping central EPA rules, declassifying CO2 as an existential threat, and freeing coal, gas, and oil. It was a signal to the world: growth and sovereignty take precedence over panic-driven climate politics.

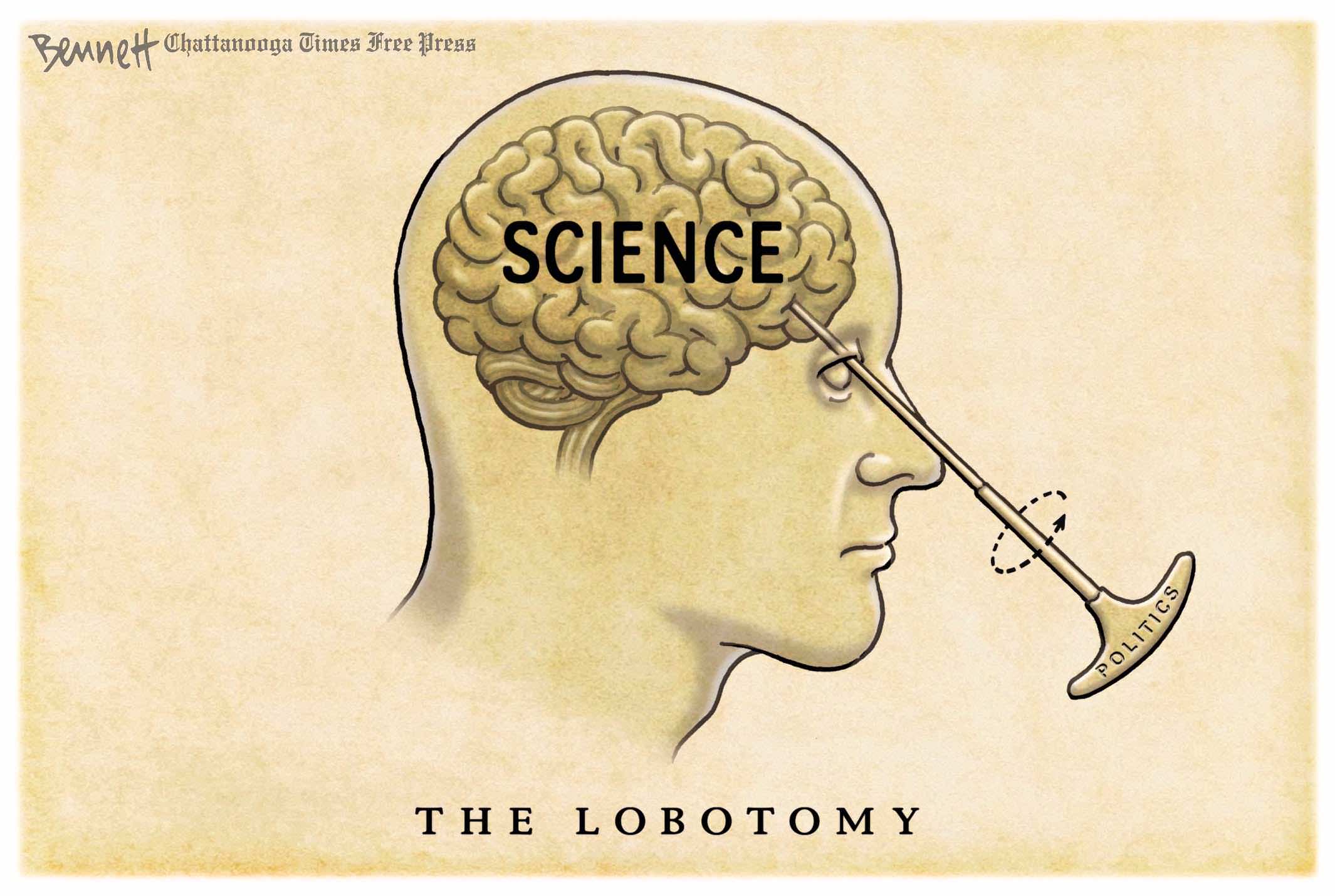
Politicized Science
The PIK case highlights the dangers of academia’s fusion with state agendas. The old saying applies: “Whose bread I eat, his song I sing.” It was only a matter of time before such politically tailored studies surfaced.

Just as with government-influenced modeling during the COVID crisis, climate research now faces the urgent task of disentangling politics from science. On the back of the man-made climate narrative, an entire apparatus of subsidies, NGOs, and Brussels bureaucracy has entrenched itself. Untangling this nexus is no longer just a scientific issue — it is a historic necessity.

Footnote On the Failings of PIK GDP Study
Climate study from Potsdam – how questionable forecasts misled politics and business
A controversial climate study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is one of the biggest scientific scandals of recent years. Media outlets like “Tagesschau” and “Spiegel” made it headlines in 2024. “Scientifically completely invalid,” economist Richard Rosen declared. However, politicians and the financial world made far-reaching decisions based on the PIK study. The alleged annual economic damage of $38 trillion shaped global debates. (welt: 25.08.25)
The publication of the PIK study by “Nature” lent its brilliance. But internal documents show that all four reviewers reported serious deficiencies. One expert wrote: “The statistical methodology … [has] no scientific basis whatsoever.” Another emphasized that the forecasts seemed “unintuitively large.”
Roger Pielke Jr. calls it a scandal. Incorrect figures have been known for over a year, yet they continue to shape climate policy and financial decisions. Weinkle criticizes that “Nature” has “turned into a doormat.” This is how science loses credibility.
Just a few weeks after publication, Christof Schötz of the Technical University of Munich presented a detailed critique. He made it clear that the results “do not provide the robust empirical evidence required for climate policy.” Nevertheless, Nature suppressed the analysis for months.
Other researchers from Princeton and the Bank Policy Institute responded. Gregory Hopper describes his unsuccessful attempts to submit comments. Rosen described the PIK study as “completely scientifically invalid.” It has since become clear that while the criticism was suppressed, the NGFS continued to use the data. This resulted in massive economic and political damage.
Under pressure, the PIK researchers published a new version. In this “preprint,” they claimed their core findings remained intact. However, they had to swap methods to produce similar results. For Pielke, this is “a tacit admission… that the original analysis is no longer valid.”
Hopper is even more critical of the new version. “The revised climate damage model is even more flawed,” he explains. The statistical problems persist. This demonstrates that science is serving politics here rather than providing objective results.