The post below updates the UAH record of air temperatures over land and ocean. Each month and year exposes again the growing disconnect between the real world and the Zero Carbon zealots. It is as though the anti-hydrocarbon band wagon hopes to drown out the data contradicting their justification for the Great Energy Transition. Yes, there was warming from an El Nino buildup coincidental with North Atlantic warming, but no basis to blame it on CO2.
As an overview consider how recent rapid cooling completely overcame the warming from the last 3 El Ninos (1998, 2010 and 2016). The UAH record shows that the effects of the last one were gone as of April 2021, again in November 2021, and in February and June 2022 At year end 2022 and continuing into 2023 global temp anomaly matched or went lower than average since 1995, an ENSO neutral year. (UAH baseline is now 1991-2020). Then there was an usual El Nino warming spike of uncertain cause, unrelated to steadily rising CO2 and now dropping steadily.
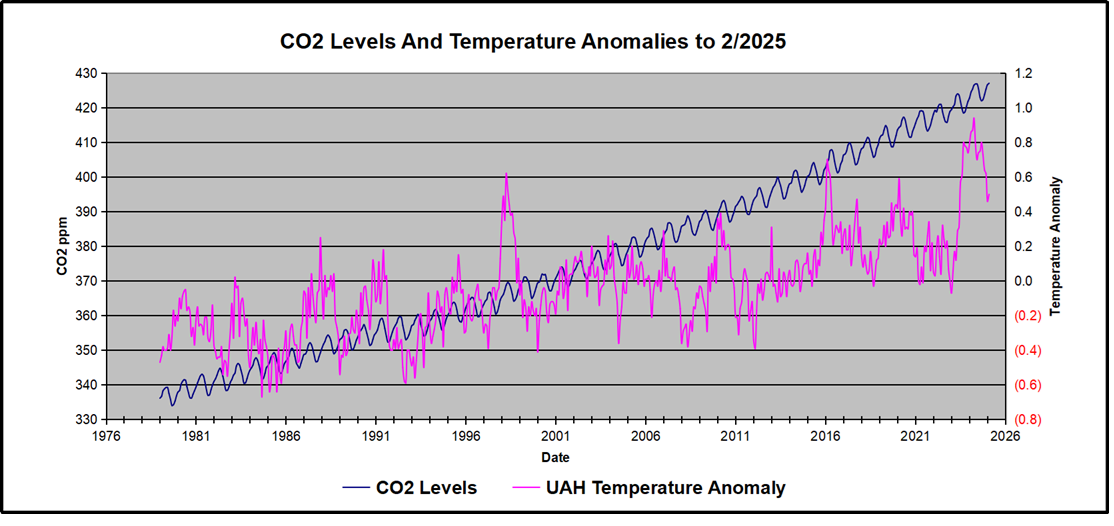
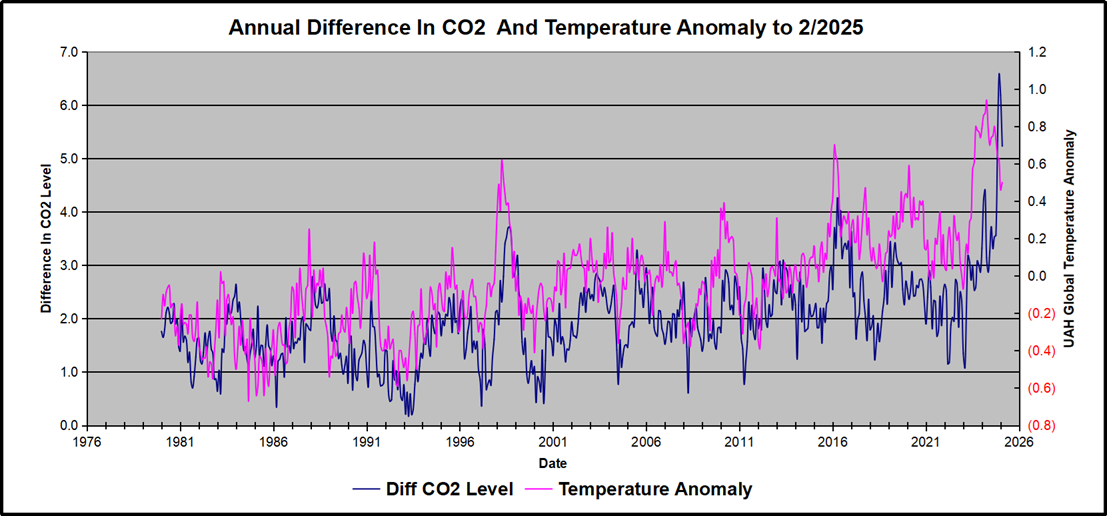
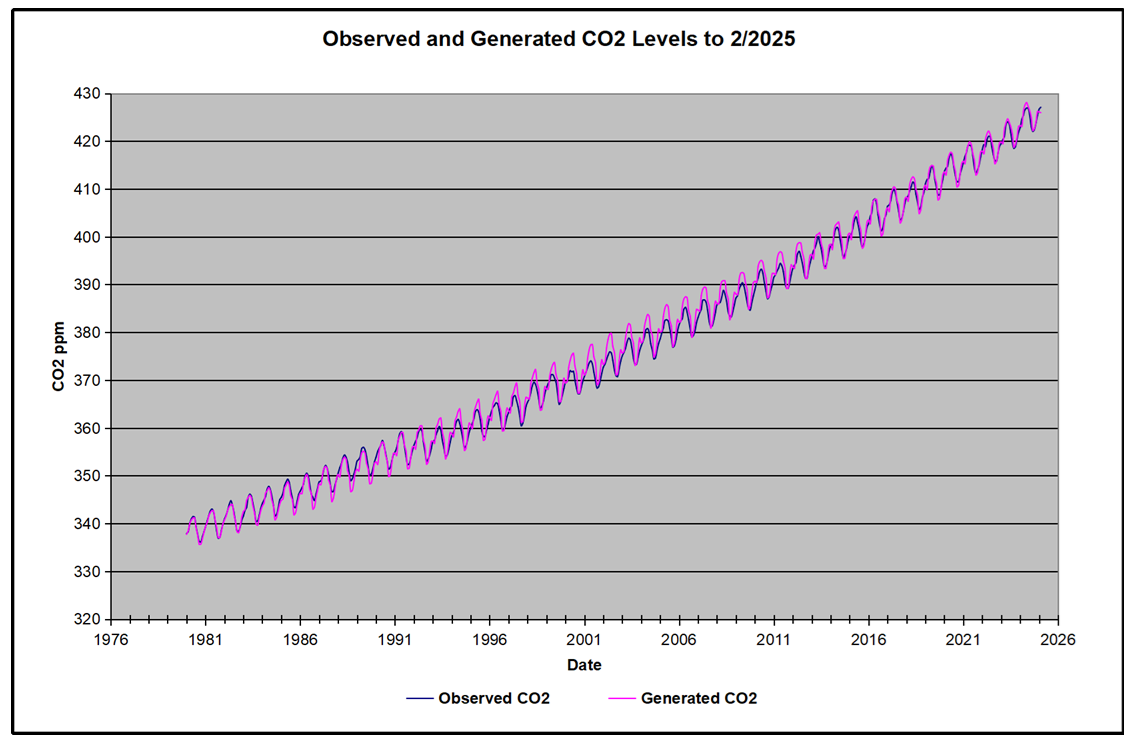
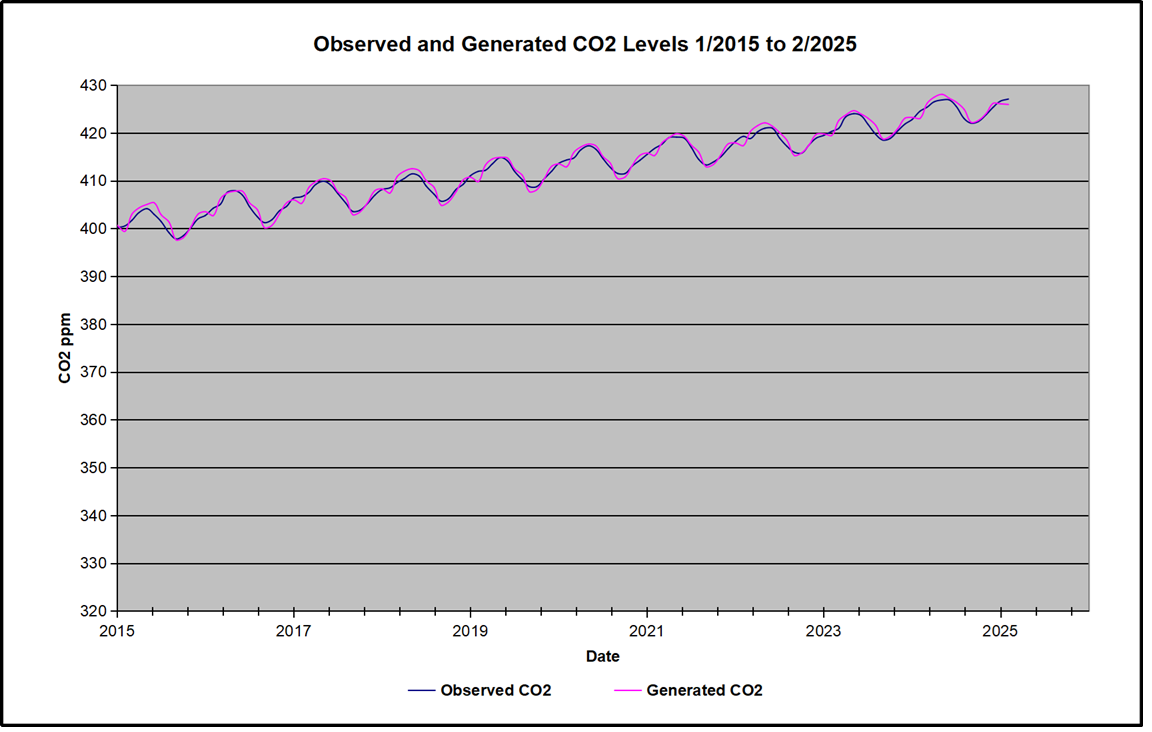
For reference I added an overlay of CO2 annual concentrations as measured at Mauna Loa. While temperatures fluctuated up and down ending flat, CO2 went up steadily by ~60 ppm, a 15% increase.
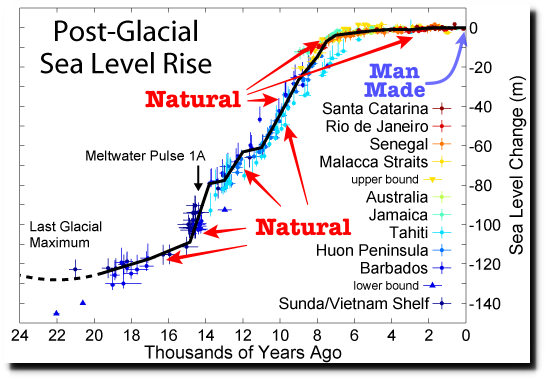
Furthermore, going back to previous warmings prior to the satellite record shows that the entire rise of 0.8C since 1947 is due to oceanic, not human activity.
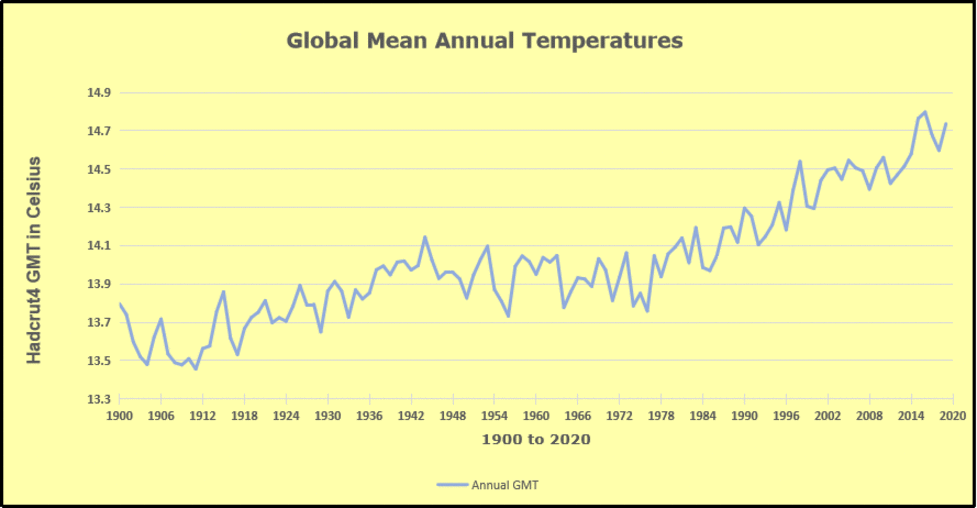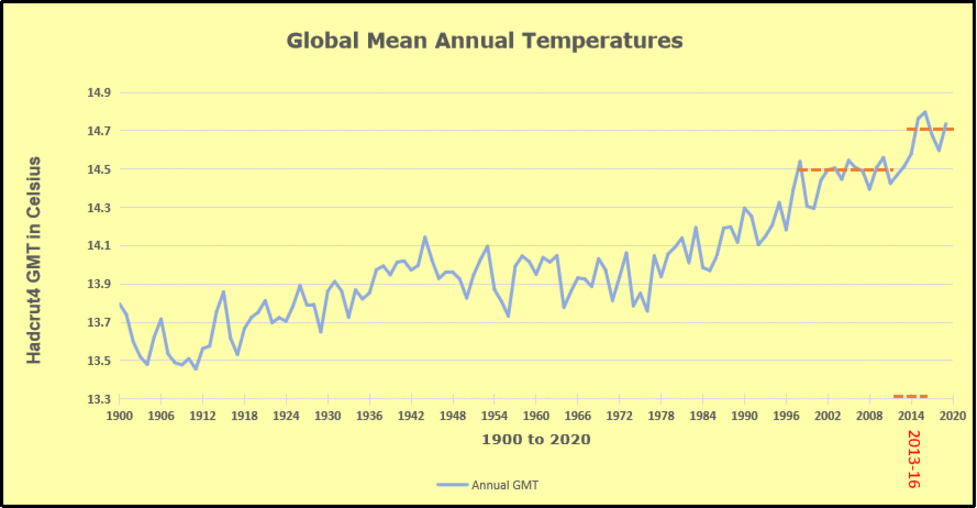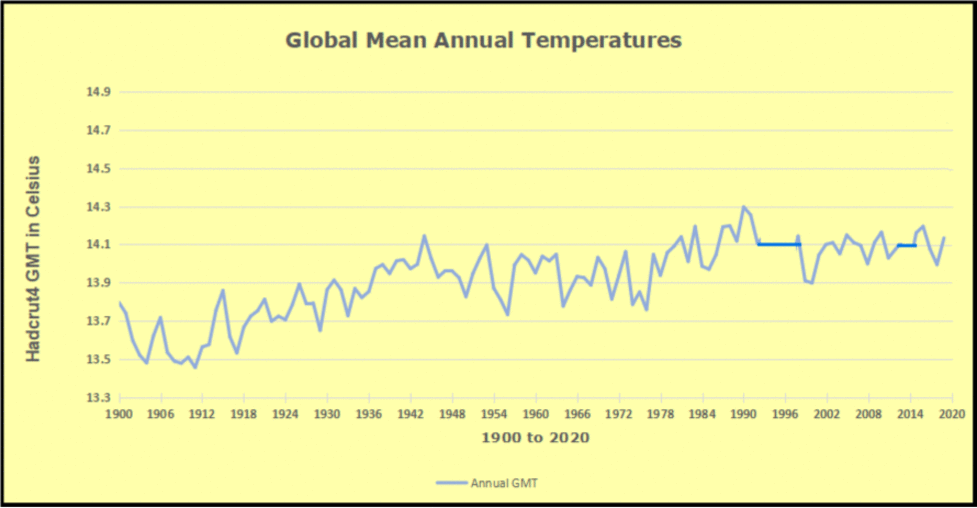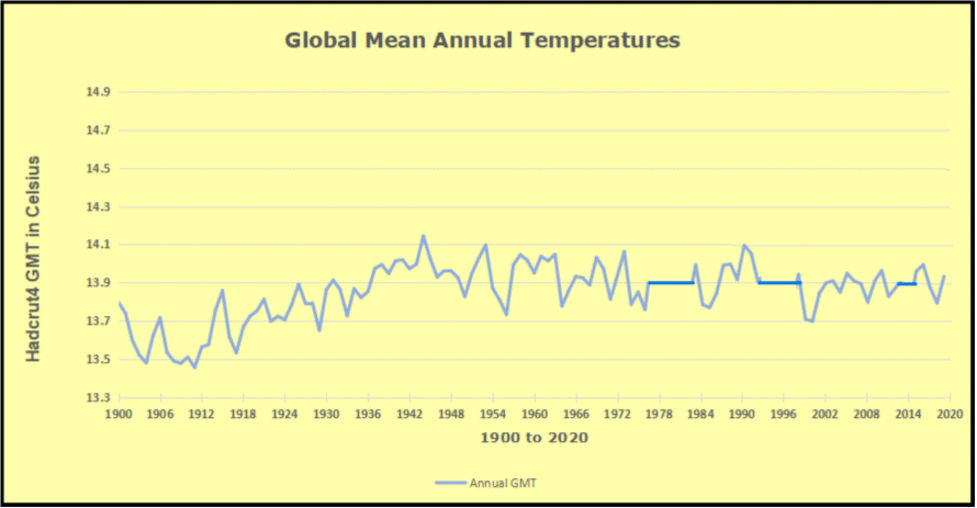
The animation is an update of a previous analysis from Dr. Murry Salby. These graphs use Hadcrut4 and include the 2016 El Nino warming event. The exhibit shows since 1947 GMT warmed by 0.8 C, from 13.9 to 14.7, as estimated by Hadcrut4. This resulted from three natural warming events involving ocean cycles. The most recent rise 2013-16 lifted temperatures by 0.2C. Previously the 1997-98 El Nino produced a plateau increase of 0.4C. Before that, a rise from 1977-81 added 0.2C to start the warming since 1947.
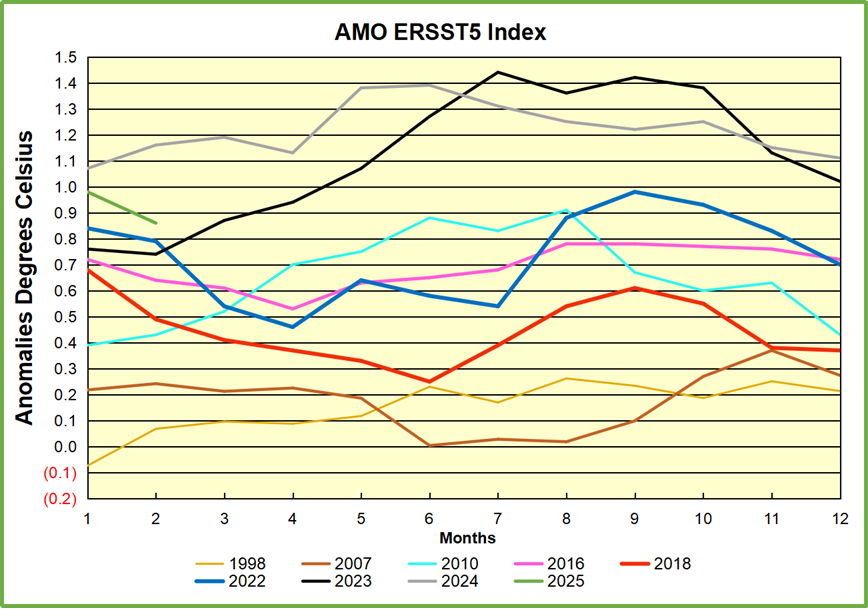
Importantly, the theory of human-caused global warming asserts that increasing CO2 in the atmosphere changes the baseline and causes systemic warming in our climate. On the contrary, all of the warming since 1947 was episodic, coming from three brief events associated with oceanic cycles. And in 2024 we saw an amazing episode with a temperature spike driven by ocean air warming in all regions, along with rising NH land temperatures, now dropping below its peak.
Chris Schoeneveld has produced a similar graph to the animation above, with a temperature series combining HadCRUT4 and UAH6. H/T WUWT
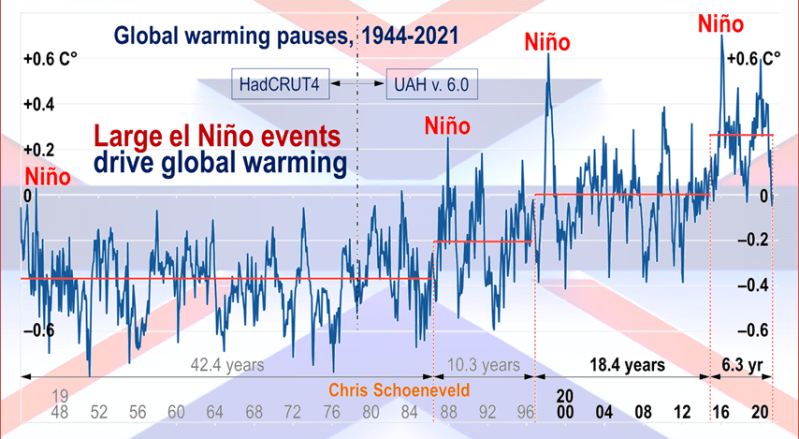
See Also Worst Threat: Greenhouse Gas or Quiet Sun?
March 2025 UAH Temps Yo-yo, Ocean First, Then Land 
With apologies to Paul Revere, this post is on the lookout for cooler weather with an eye on both the Land and the Sea. While you heard a lot about 2020-21 temperatures matching 2016 as the highest ever, that spin ignores how fast the cooling set in. The UAH data analyzed below shows that warming from the last El Nino had fully dissipated with chilly temperatures in all regions. After a warming blip in 2022, land and ocean temps dropped again with 2023 starting below the mean since 1995. Spring and Summer 2023 saw a series of warmings, continuing into 2024 peaking in April, then cooling off to the present.
UAH has updated their TLT (temperatures in lower troposphere) dataset for March 2025. Due to one satellite drifting more than can be corrected, the dataset has been recalibrated and retitled as version 6.1 Graphs here contain this updated 6.1 data. Posts on their reading of ocean air temps this month are ahead of the update from HadSST4. I posted recently on SSTs February 2025 Oceans Keep Cool. These posts have a separate graph of land air temps because the comparisons and contrasts are interesting as we contemplate possible cooling in coming months and years.
Sometimes air temps over land diverge from ocean air changes. In July 2024 all oceans were unchanged except for Tropical warming, while all land regions rose slightly. In August we saw a warming leap in SH land, slight Land cooling elsewhere, a dip in Tropical Ocean temp and slightly elsewhere. September showed a dramatic drop in SH land, overcome by a greater NH land increase. 2025 has shown a sharp contrast between land and sea, first with ocean air temps falling in January recovering in February. Then land air temps, especially NH, dropped in February and recovered in March.
Note: UAH has shifted their baseline from 1981-2010 to 1991-2020 beginning with January 2021. v6.1 data was recalibrated also starting with 2021. In the charts below, the trends and fluctuations remain the same but the anomaly values changed with the baseline reference shift.
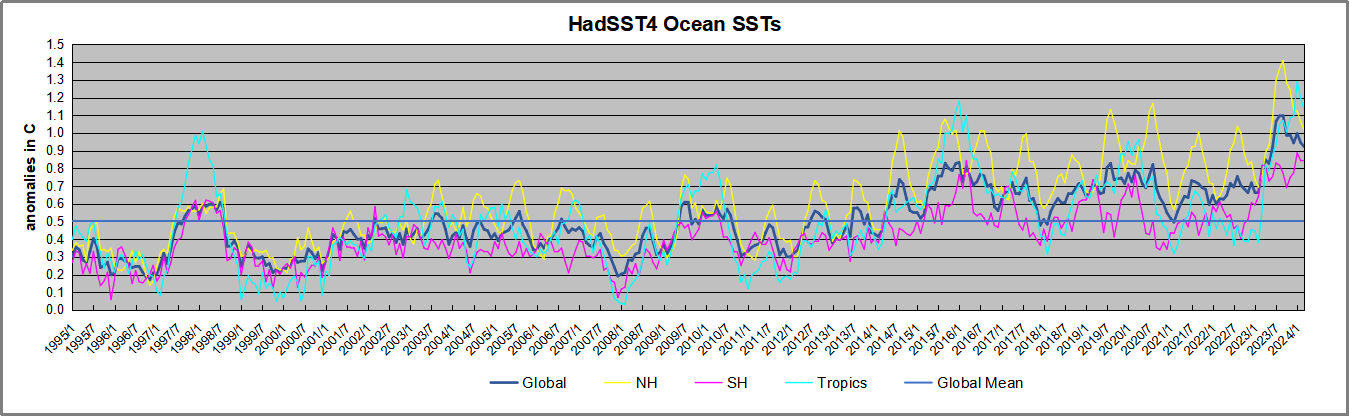
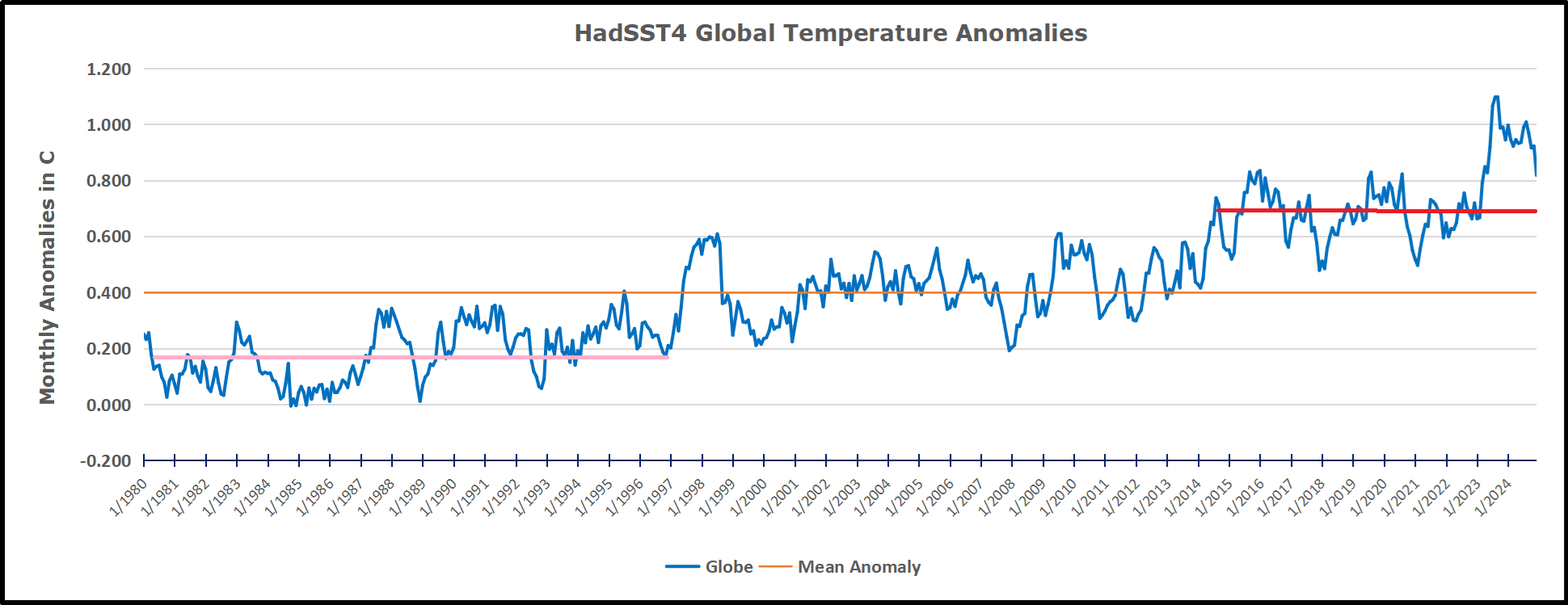
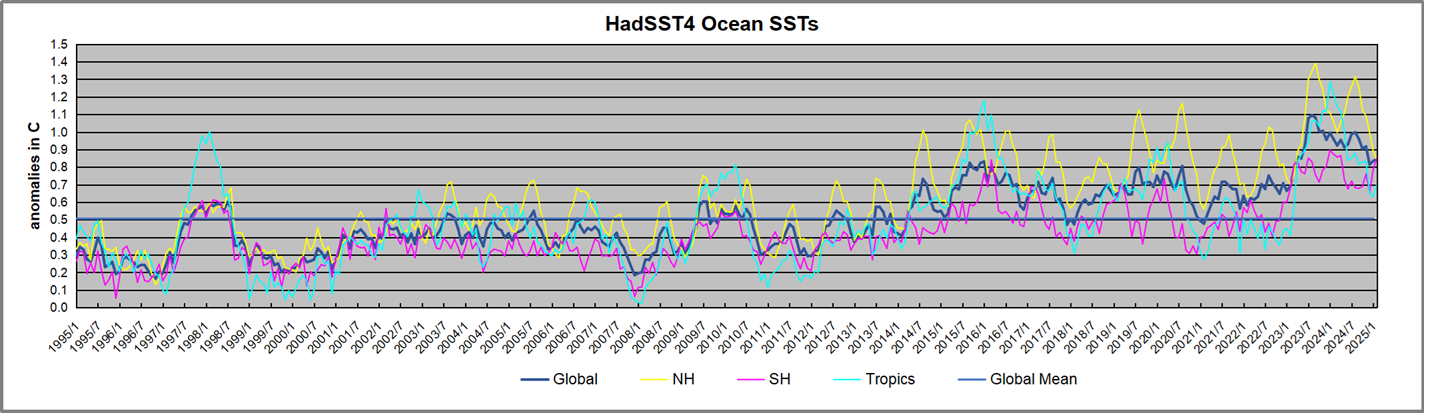
Presently sea surface temperatures (SST) are the best available indicator of heat content gained or lost from earth’s climate system. Enthalpy is the thermodynamic term for total heat content in a system, and humidity differences in air parcels affect enthalpy. Measuring water temperature directly avoids distorted impressions from air measurements. In addition, ocean covers 71% of the planet surface and thus dominates surface temperature estimates. Eventually we will likely have reliable means of recording water temperatures at depth.
Recently, Dr. Ole Humlum reported from his research that air temperatures lag 2-3 months behind changes in SST. Thus cooling oceans portend cooling land air temperatures to follow. He also observed that changes in CO2 atmospheric concentrations lag behind SST by 11-12 months. This latter point is addressed in a previous post Who to Blame for Rising CO2?
After a change in priorities, updates are now exclusive to HadSST4. For comparison we can also look at lower troposphere temperatures (TLT) from UAHv6.1 which are now posted for March 2025. The temperature record is derived from microwave sounding units (MSU) on board satellites like the one pictured above. Recently there was a change in UAH processing of satellite drift corrections, including dropping one platform which can no longer be corrected. The graphs below are taken from the revised and current dataset.
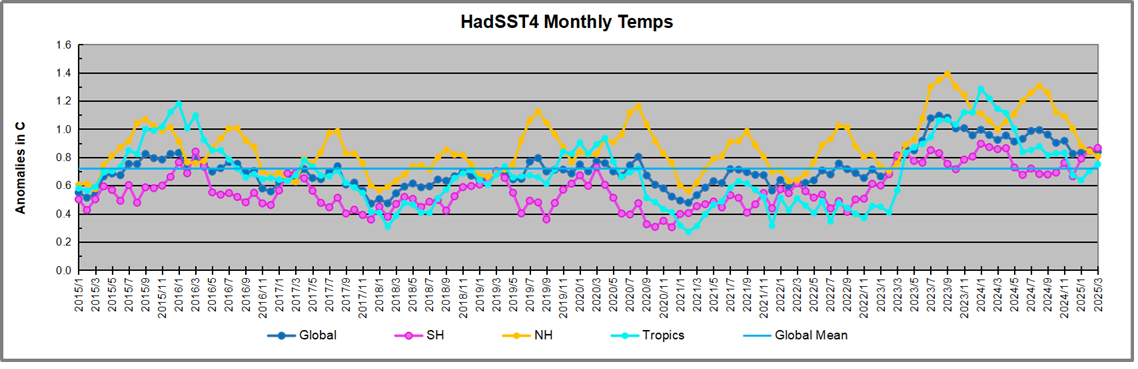
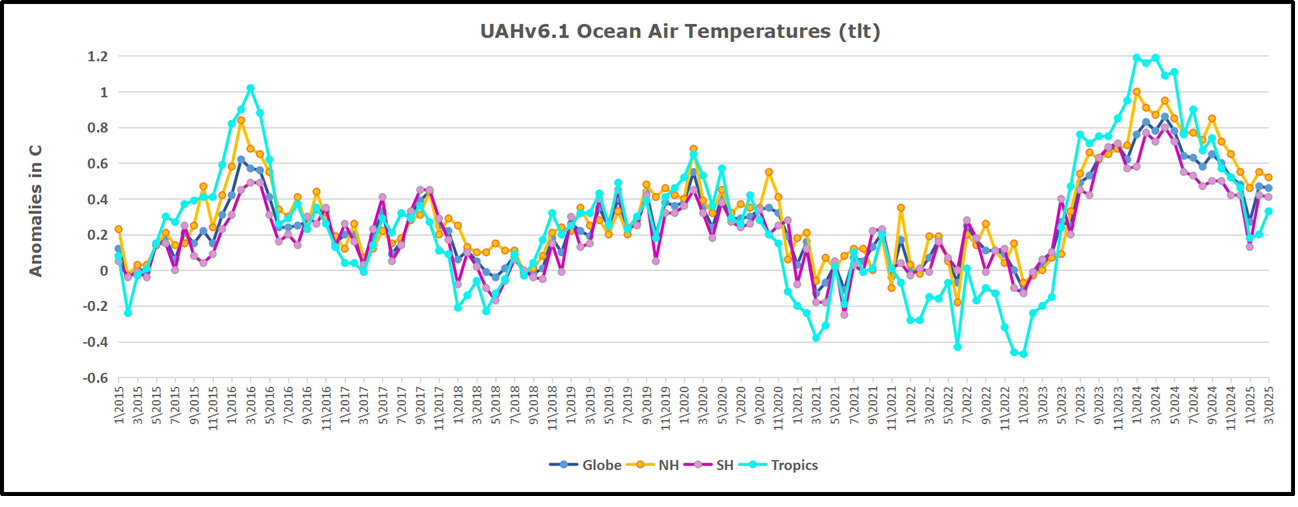
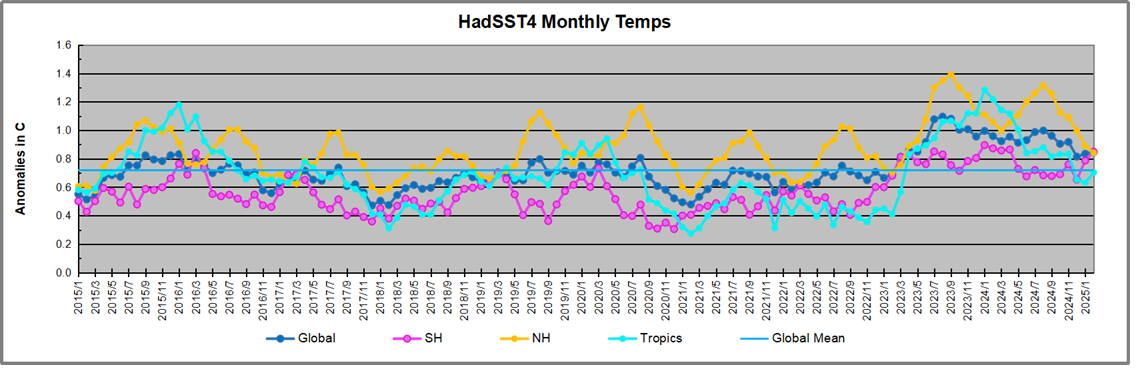
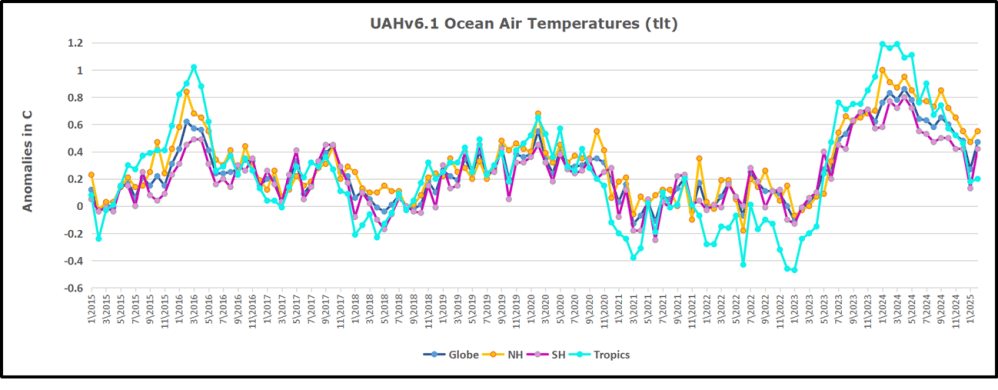
The UAH dataset includes temperature results for air above the oceans, and thus should be most comparable to the SSTs. There is the additional feature that ocean air temps avoid Urban Heat Islands (UHI). The graph below shows monthly anomalies for ocean air temps since January 2015.
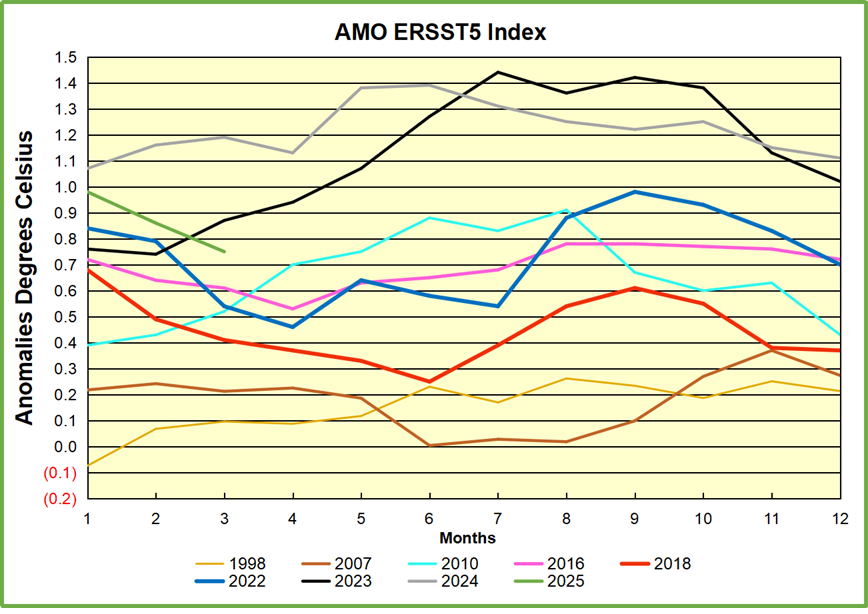
In 2021-22, SH and NH showed spikes up and down while the Tropics cooled dramatically, with some ups and downs, but hitting a new low in January 2023. At that point all regions were more or less in negative territory.
After sharp cooling everywhere in January 2023, there was a remarkable spiking of Tropical ocean temps from -0.5C up to + 1.2C in January 2024. The rise was matched by other regions in 2024, such that the Global anomaly peaked at 0.86C in April. Since then all regions have cooled down sharply to a low of 0.27C in January. In February 2025, SH rose from 0.1C to 0.4C pulling the Global ocean air anomaly up to 0.47C, where it stayed in March.
Land Air Temperatures Tracking in Seesaw Pattern
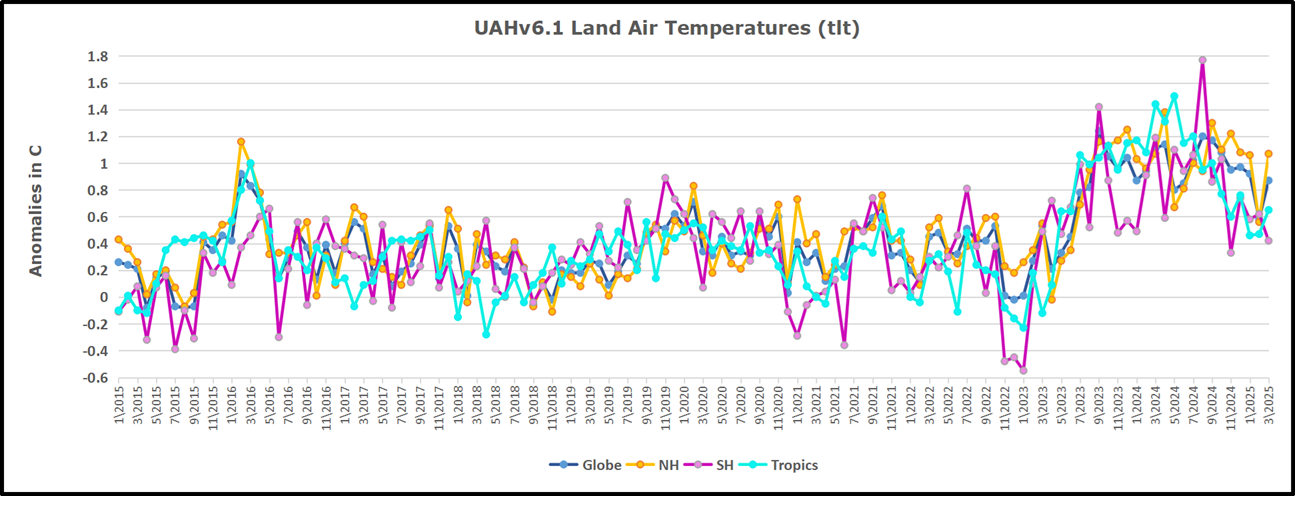
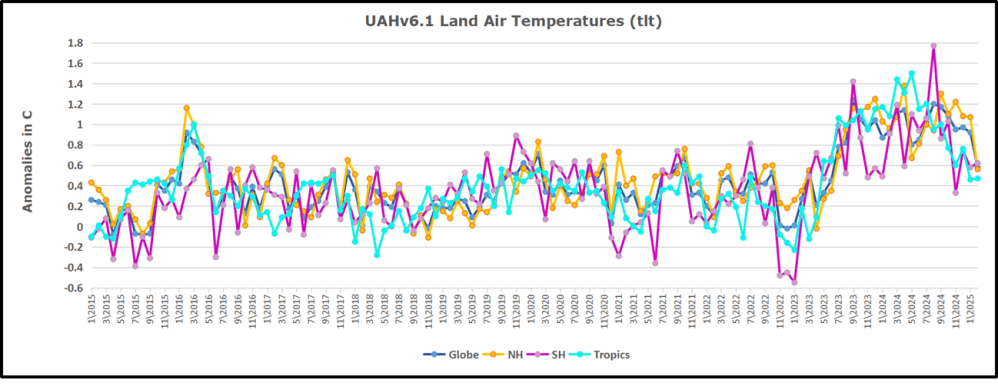
We sometimes overlook that in climate temperature records, while the oceans are measured directly with SSTs, land temps are measured only indirectly. The land temperature records at surface stations sample air temps at 2 meters above ground. UAH gives tlt anomalies for air over land separately from ocean air temps. The graph updated for March is below.
Here we have fresh evidence of the greater volatility of the Land temperatures, along with extraordinary departures by SH land. The seesaw pattern in Land temps is similar to ocean temps 2021-22, except that SH is the outlier, hitting bottom in January 2023. Then exceptionally SH goes from -0.6C up to 1.4C in September 2023 and 1.8C in August 2024, with a large drop in between. In November, SH and the Tropics pulled the Global Land anomaly further down despite a bump in NH land temps. February showed a sharp drop in NH land air temps from 1.07C down to 0.56C, pulling the Global land anomaly downward from 0.9C to 0.6C. Now that drop is reversed in March with both NH and Global land back to January values, despite another drop in SH land air temps.
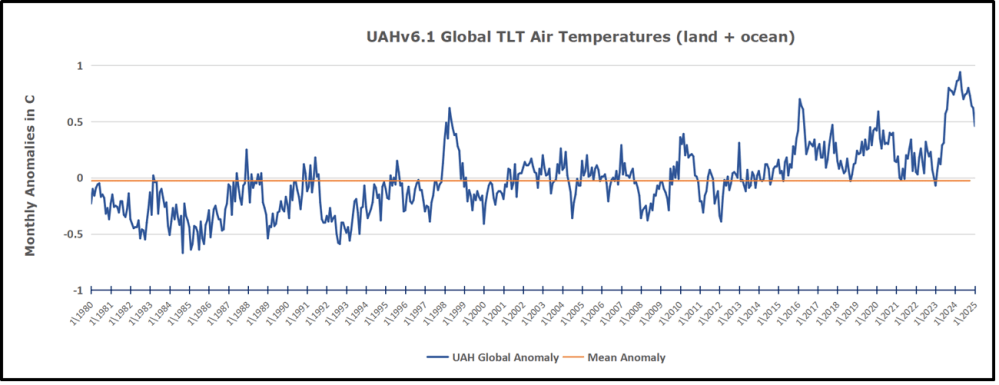
The Bigger Picture UAH Global Since 1980
The chart shows monthly Global Land and Ocean anomalies starting 01/1980 to present. The average monthly anomaly is -0.03, for this period of more than four decades. The graph shows the 1998 El Nino after which the mean resumed, and again after the smaller 2010 event. The 2016 El Nino matched 1998 peak and in addition NH after effects lasted longer, followed by the NH warming 2019-20. An upward bump in 2021 was reversed with temps having returned close to the mean as of 2/2022. March and April brought warmer Global temps, later reversed
With the sharp drops in Nov., Dec. and January 2023 temps, there was no increase over 1980. Then in 2023 the buildup to the October/November peak exceeded the sharp April peak of the El Nino 1998 event. It also surpassed the February peak in 2016. In 2024 March and April took the Global anomaly to a new peak of 0.94C. The cool down started with May dropping to 0.9C, and in June a further decline to 0.8C. October went down to 0.7C, November and December dropped to 0.6C. February went down to 0.5C, now back up to 0.6C driven by the bounce in NH land air temps.
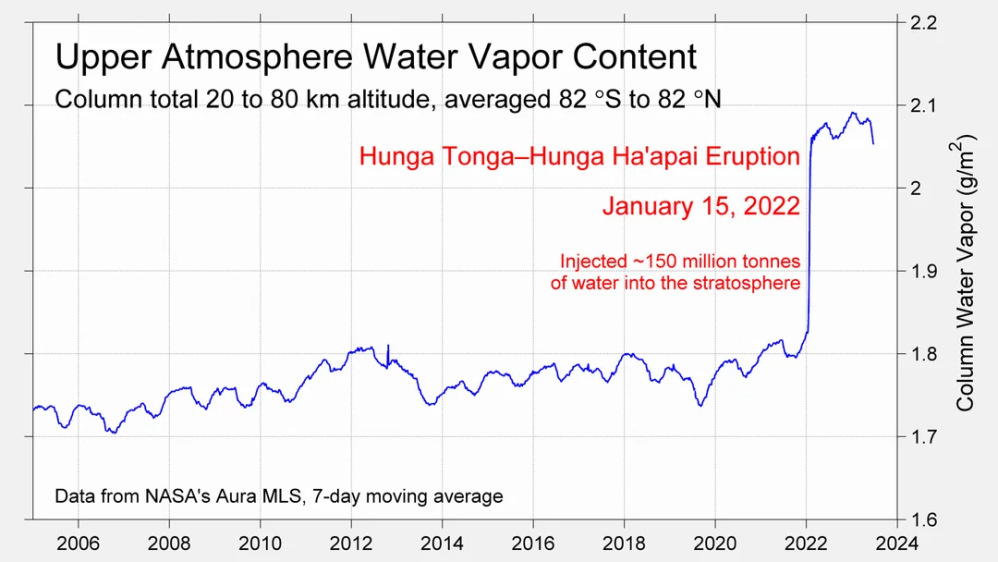
The graph reminds of another chart showing the abrupt ejection of humid air from Hunga Tonga eruption.
TLTs include mixing above the oceans and probably some influence from nearby more volatile land temps. Clearly NH and Global land temps have been dropping in a seesaw pattern, nearly 1C lower than the 2016 peak. Since the ocean has 1000 times the heat capacity as the atmosphere, that cooling is a significant driving force. TLT measures started the recent cooling later than SSTs from HadSST4, but are now showing the same pattern. Despite the three El Ninos, their warming had not persisted prior to 2023, and without them it would probably have cooled since 1995. Of course, the future has not yet been written.
 The best context for understanding decadal temperature changes comes from the world’s sea surface temperatures (SST), for several reasons:
The best context for understanding decadal temperature changes comes from the world’s sea surface temperatures (SST), for several reasons: