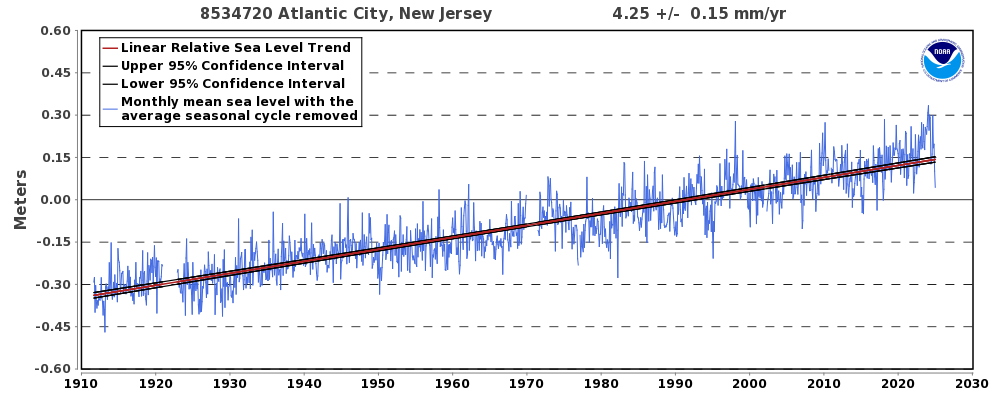
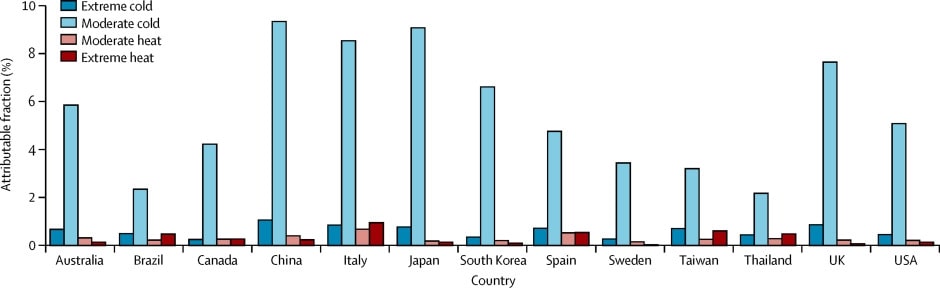
The image is based on a criticism of statisticians: “If my head is in the oven and my feet are in the freezer, my temperature may be on average normal.” UN Chief Guterres presumes to speak for the planet when he claims we are experiencing “Global Boiling.” Apparently, his feet are too numb to register any of the many cold temperatures in places around the world, so he is a victim fearing a runaway average warming. Let’s inform him and others similarly misled about the facts on the ground they are missing.
Australia
Why Is It So Cold Right Now? A Weather Expert Explains
Temperatures plummeted across southeast Australia this week, with Weatherzone reporting Canberra’s low of -7.2ºC was “its lowest temperature since 2018 and the lowest for June since 1986.”
Sydney experienced its coldest June morning today since 2010, with a temperature of 5.2ºC. In Victoria, temperatures of -7.2ºC were recorded.
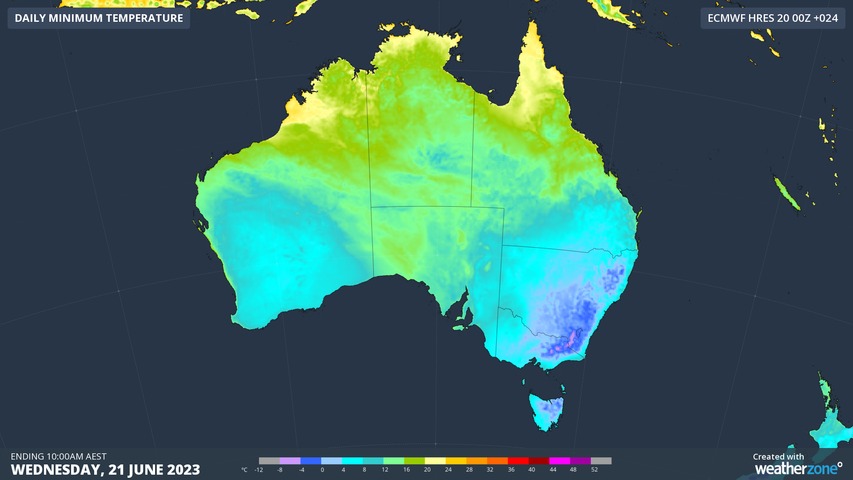
Australia just had one of its coolest and wettest summers of the last decade.
Snow settled on the Stirling Range in WA on Thursday morning after a frigid polar air mass travelled from Antarctica to Australia.
A long fetch of southerly winds has been blowing across the Southern Ocean during the past week, carrying polar air from the ice sheets of Antarctica into unusually low latitudes.
On Thursday morning, this Antarctic air mass reached the Stirling Range in WA and caused snow to settle on Bluff Knoll.
United Kingdom
Met Office explains why the weather is so miserable this May
‘High-pressure systems have been generally located over southern continental Europe and also to the far east of Europe’, they told Metro.co.uk.
The spokesperson continued: ‘As these high-pressure systems interacted through the season, the UK is positioned between them, leading to periods of cool, cloudy, and wet conditions for the UK. ‘These have generally either swept in from the Atlantic or slipped between the high-pressure systems to reach the UK.
‘Warmer-than-average sea temperatures also provided the necessary fuel for clouds to develop, which has been quite persistent in spring.’
Met Office meteorologist Clare Nasir said: ‘Showers over the next few days could be heavy with the risk of thunder and hail.’ She added that the risk of thunder and hail persist through Wednesday and Thursday.
Where has the UK summer gone
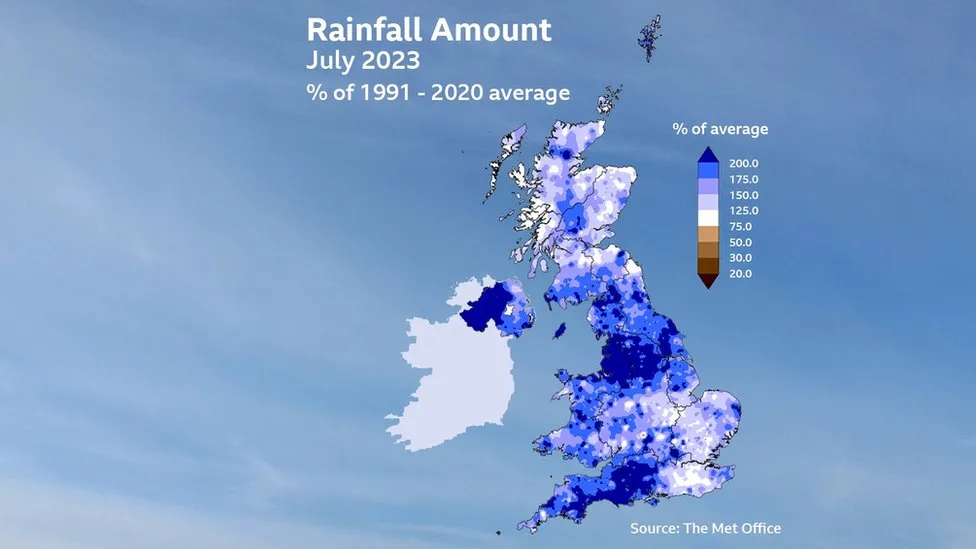
Summer 2023 so far has been one of contrasts – after the warmest June on record we had an exceptionally wet July. Northern Ireland and much of north-west England had their wettest July on record. Looking ahead there is no immediate end to the distinctly un-summery conditions. So what is going on?
Any spring warmth was hard to come by. After a cool April, very warm weather was distinctly lacking in May. Nowhere reached 24°C until the month was nearly over, on the 27th.
However, that theme changed dramatically in June. Temperatures soared to 32.2°C, with a heatwave being declared in many places and becoming the warmest June on record which, according to the Met Office, bears the “fingerprint of climate change”.
It was all change again in early July with low pressure setting in, and staying put. While much of Europe sweltered in a blistering heatwave the UK sat under cool, wet weather which looks set to stay for the first part of August too.
India
Is January 2023 going to be the coldest year in the 21st century?
There may be no relief from the ongoing spell of cold wave with minimum temperatures hovering below normal limits at most places, reports suggested. If a weather expert is believed, it has been predicted that temperatures in the plains are going to dip as far as -4 degrees Celsius next week.
Large parts of north India are still reeling under numbing cold with the mercury remaining below freezing point at most places in Jammu and Kashmir, while dense fog in the early hours of the morning hit road and rail traffic movement. Cold wave conditions abated in Delhi due to a fresh western disturbance affecting northwest India, even as a dense layer of fog lowered visibility to just 50 metres.
Northern India braces for coldest weather in years as dense fog, poor air quality linger

A new wave of cold weather is headed into northern India and could drop temperatures to levels not seen there in over three years, according to AccuWeather forecasters.
The cold weather shot will be the latest, and perhaps most significant, of many recent waves of chilly weather that have also led to travel-disrupting dense fog and poor air quality over parts of the Indian subcontinent since late December.
The temperature in New Delhi, the capital city of India and home to more than 18 million people, has the potential to drop as low as 2 degrees Celsius (35 degrees Fahrenheit) on Sunday night and Monday morning. While the record low for this coming Monday of 1.3 degrees Celsius below zero (29.7 degrees Fahrenheit) appears safe, it will be well below the average low of 6 degrees Celsius (42 degrees Fahrenheit) for the date.
Temperatures at this level would be the coldest readings in New Delhi since December 2019,” said Nicholls.
Ahead of the cold wave, the IMD has issued a cold wave warning for Sunday and Monday for the northern Indian states of Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh, Delhi and Rajasthan. The warning was issued to give residents advance notice of a level of cold that could adversely impact human health and property.
Canada
Spring forecast 2023: The La Nina Winter pattern is forecast to extend as we head into Spring despite the breakdown of the cold ocean anomalies
Spring season 2023 is nearing, with forecasts revealing the jet stream pattern over the North Pacific and the Atlantic to be influenced by the diminishing La Nina. A high-pressure system in the Pacific will define the weather patterns over North America, with a potential Stratospheric warming event playing a role early in the season.
The cold ocean phase in the equatorial Pacific is already in breakdown mode. It is expected to decline rapidly towards early Spring.
But, despite the breakdown of these cold ocean anomalies (La Nina), its influence can still persist in global weather circulation. Long-range weather calculations also see this, extending the La Nina jet stream pattern from Winter into Spring 2023.

Spring sits on the sidelines with Winter’s wild ride to the finish line

USA
Winter Forecast 2024: The Brrr Is Back
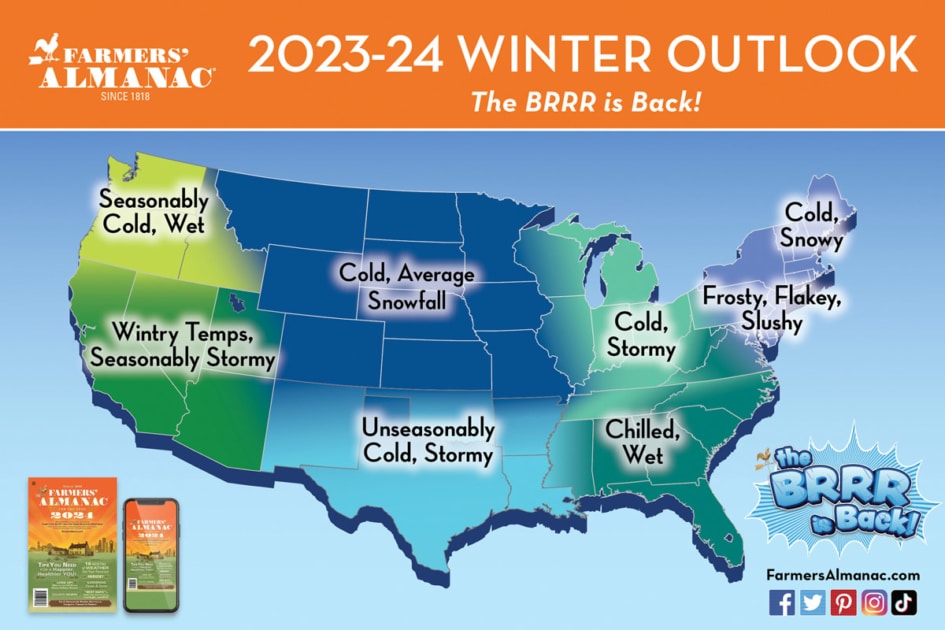
The Brrr is Back!
“After a weird and warm winter season last year, this winter should make cold weather fans rejoice—especially those in the Great Lakes, Midwest, and northern New England areas,” shares editor Pete Geiger, adding “the ‘brrr’ is coming back! We expect more snow and low temperatures nationwide.”
East Coast Snow?
Folks living along the I-95 corridor from Washington to Boston, who saw a lack of wintry precipitation last winter, should experience quite the opposite, with lots of rain/sleet and snowstorms to contend with.
Texans Beware!
According to Farmers’ Almanac 2024, Texans should prepare for an unseasonably cold and stormy winter season ahead
Frosts in Florida?
Winter will be wet in the Southeast region however a few frosts are forecast to bring the “brrrs” to Floridians and its snowbirds.
Asia
As Asian countries hit by extreme cold snap, here’s what life is like at -53C
An intense cold spell is gripping east Asia, with temperatures plunging and hazardous conditions reported across China, the Koreas and Japan.
On Monday one of China’s northern-most cities broke its lowest ever recorded temperature, with the mercury hitting -53C at 7am on the first day of the Lunar New Year in Mohe, Heilongjiang province.
Japan and the Korean peninsula have also issued warnings over freezing temperatures and gales that have killed at least one person, while at least 57 people have been reported dead in Afghanistan as the wintry conditions stretch across into central Asia.

Europe
Record-Challenging Cold Sweeps Europe
It’s been cold — ask a European, ask me…
We’ve enjoyed a ‘comfortably cool’ July here in Central Portugal (thus far), it’s been great. Same with my old haunt, the UK. July 2023 there is on course to be colder-than-average–and vs the historically cool 1961-1990 era that the Met Office still insist on using, no less.
Looking ahead, and particularly at central/eastern nations, those summer chills are about to take another step down.
As per the latest GFS run (shown below), ‘pinks’ and ‘purples’ are forecast to engulf the likes of Poland, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Albania, Belarus, Ukraine and Romania this week, sending temperatures crashing by as much as 18C below the seasonal norm.
Record summer lows are expected, an unbiased media would report on them (not holding my breath).

Russia
Extreme cold grips Siberia, as temperatures fall to lowest levels since 2002
The coldest air on Earth plunged into Siberia this week, dropping temperatures to as low as 80 degrees Fahrenheit below zero. An expansion of that cold is expected across eastern Asia into early next week and eventually North America, according to AccuWeather forecasters.
The bitter cold not only allowed temperature benchmarks that have not been hit in decades in some parts of Russia, but the extreme weather also created an icy spectacle as firefighters battled a fire in subzero temperatures on Jan. 8 in Ufa, Russia. Massive icicles clung to the home amid the anomalous cold.
The same Arctic blast dropped temperatures in Moscow to their lowest levels in years this past weekend, while even parts of northern India will get a taste of the cold beginning later this weekend.

Antarctica
Antarctica Plunges to -83.2C (-117.8F)–Earth’s Lowest Temperature Since 2017
While the media tricks the dumb and the gullible into believing the world is on fire –with poverty-inducing CO2 reductions their only savior– Antarctica is shivering through an extreme bout of cold, even by South Pole standards.
The Italian-French research station ‘Concordia’ posted a reading of -83.2C (-117.8F) on July 25. This ranks as the fifth coldest daily value in the operational life of the station, bested only by Aug 2010’s -84.7C; July 2010’s -84.6C; and June 2017’s -83.9C and -83.5C.
As discussed recently, Antarctic sea ice’s tough time of it in 2023 isn’t related to temperature, that correlation simply doesn’t exist. The Antarctic continent continues to cool, the data are very clear on that, yet ice is taking a proverbial beating this season.
South America
Fierce frosts have gripped areas of Argentina and Chile
Some of that aforementioned Antarctic cold has been spun northward over Southern Hemisphere land masses.
Fierce frosts have gripped areas of Argentina and Chile of late, as South America’s topsy–turvy ‘meridional jet stream‘-fueled winter drags on. Looking ahead, more of the same is on the cards, too, as we head into August:

Southern Africa
Southern Africa Freezes, Rare Snowfall Hits Johannesburg
Southern Africa is enduring fierce freeze this week as a blast of polar air engulfs the likes of SA, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, as well as Angola, Zambia and Malawi.
Coastal regions are struggling to climb above 10C (50F), while at higher-elevations and inland, frosts are proving widespread, with reports of rare snowfall coming out of some unusual spots such as Zimbabwe and South Africa, such as Johannesburg.

Several regions of South Africa are enduring a harsh winter this year, according to local media outlets, with this past weekend delivering an intensification. Sub-zero (C) lows struck Johannesburg and surrounding areas over the past few mornings, with daytime highs of just 4C (39.2F) noted–where the July average is closer to 17C (62.6F).
Temperatures also held low enough to keep the snow lying on the ground throughout the morning, bringing joyous scenes to many a school playground — this would have been the first time many children have seen snow (Prof David Viner take note).

Footnote: Climate is Dynamic: Hot Today, Cold Tomorrow
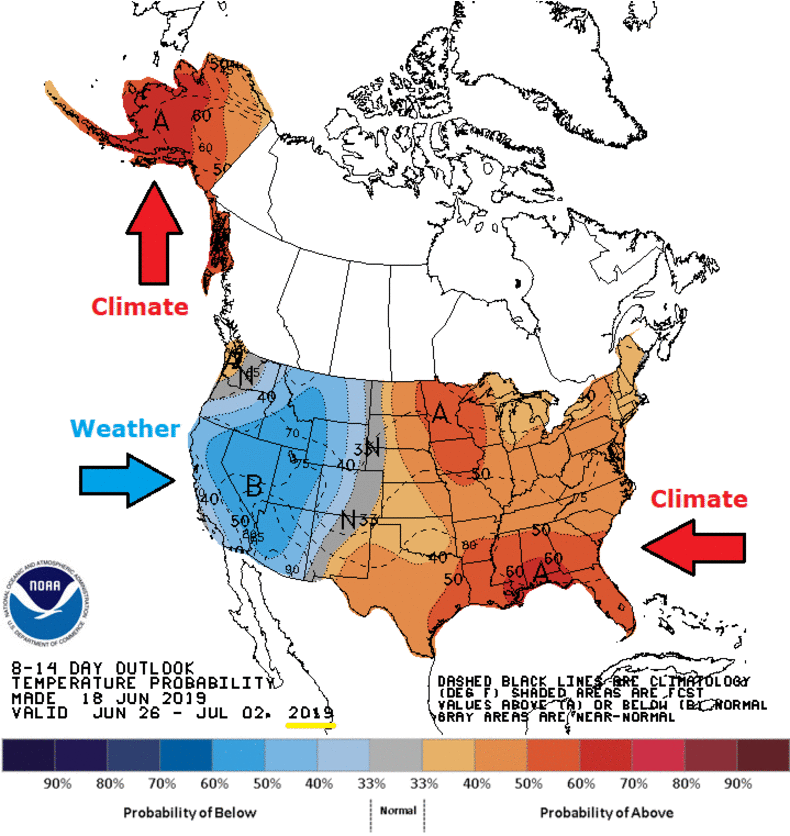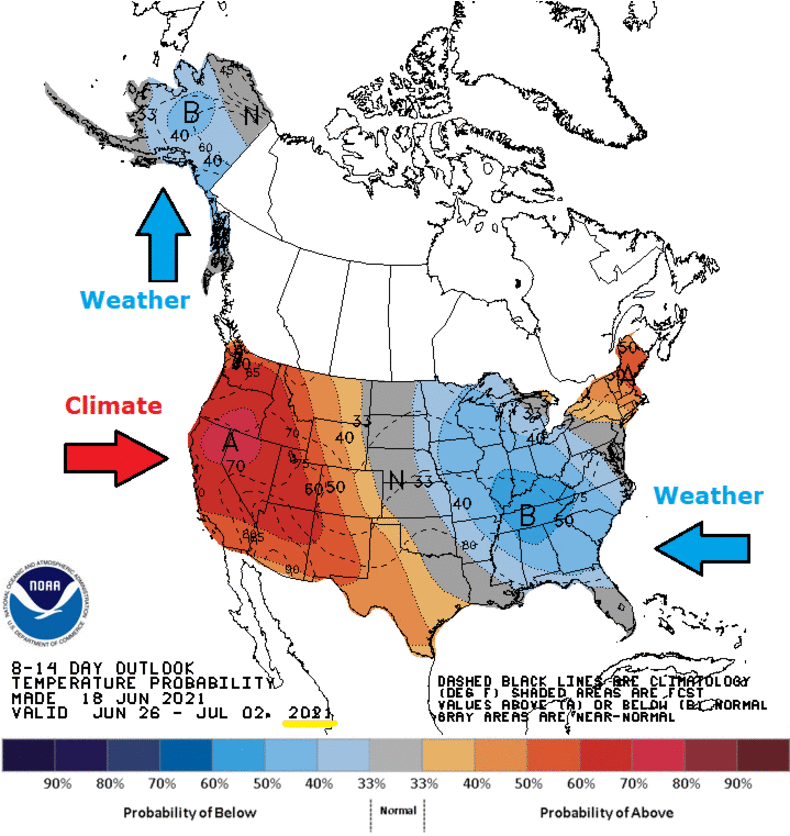
And the same goes for precipitation:
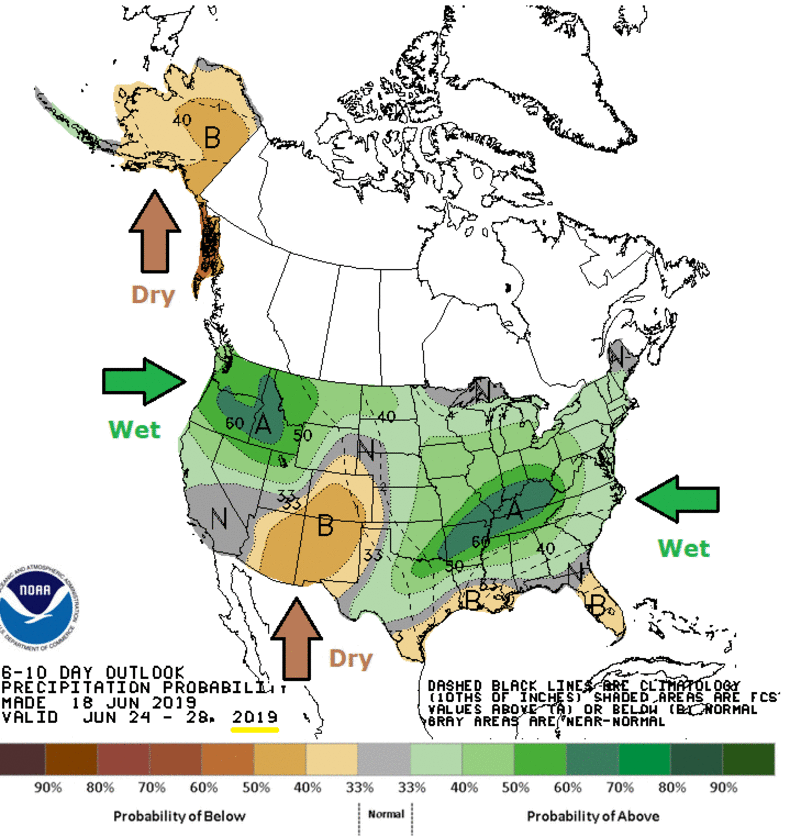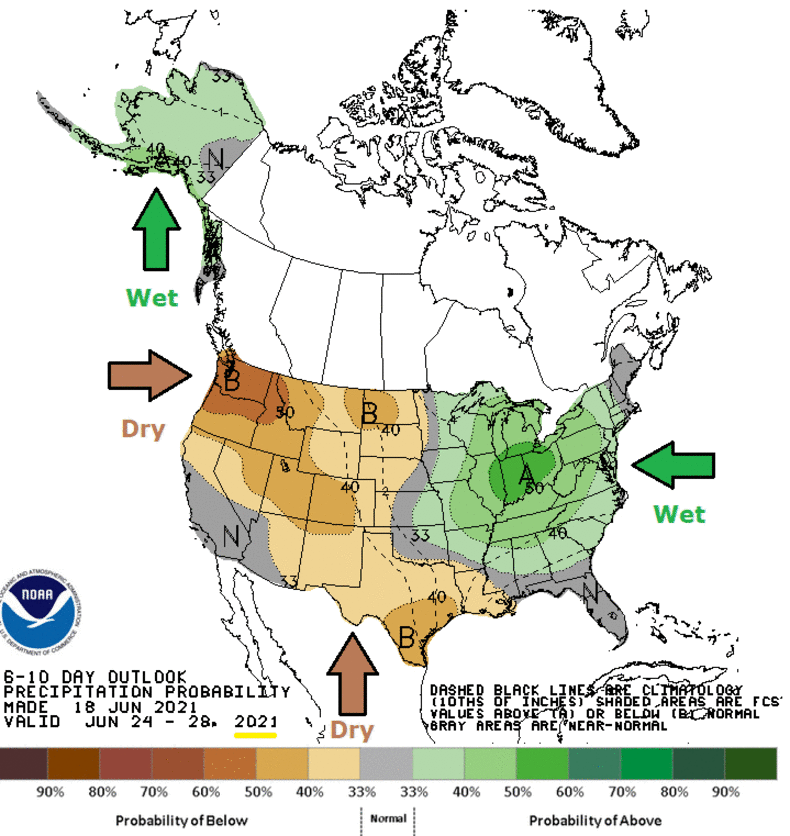






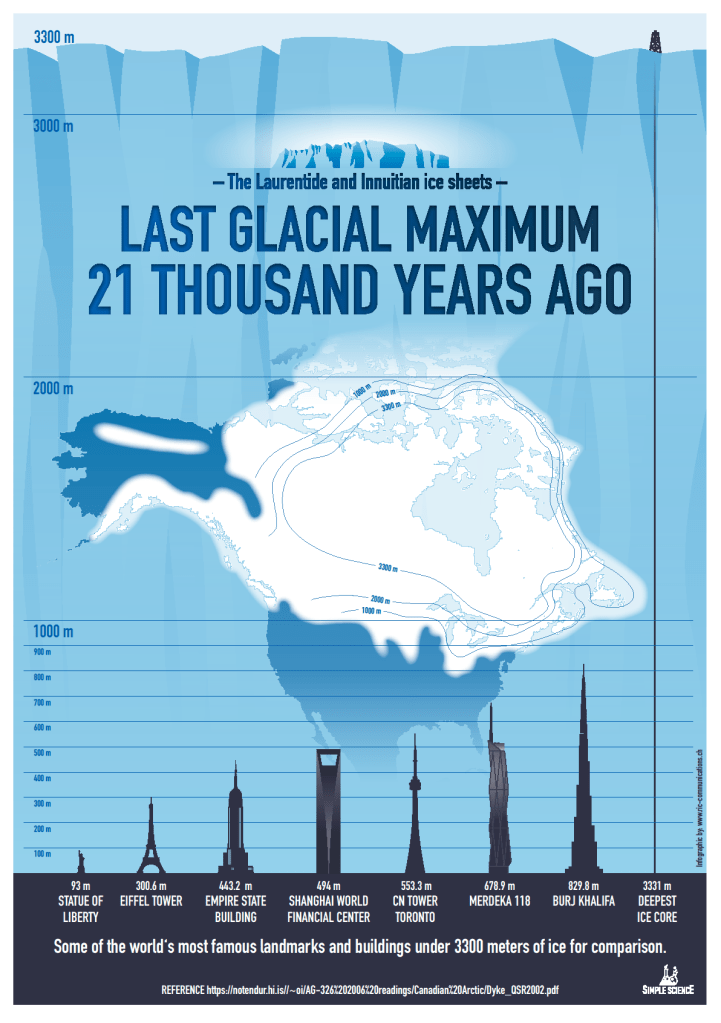

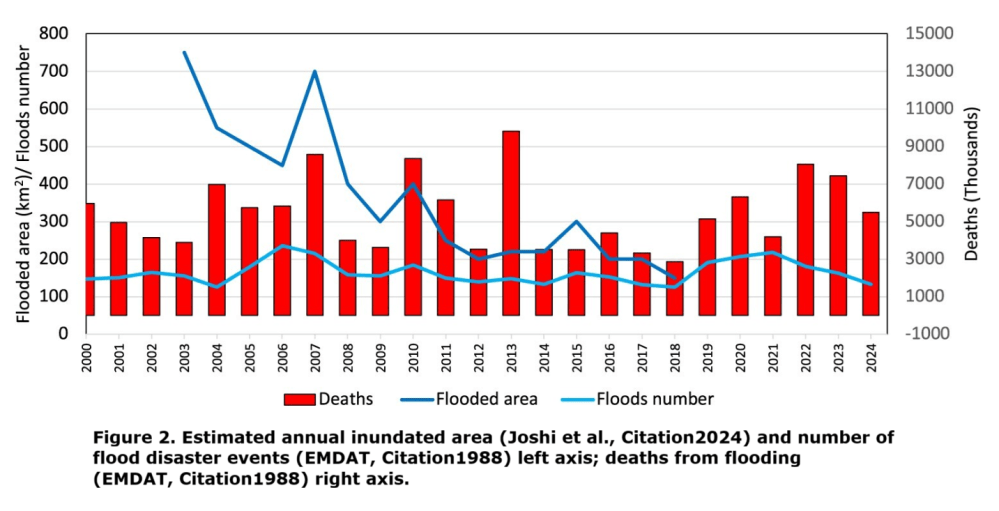
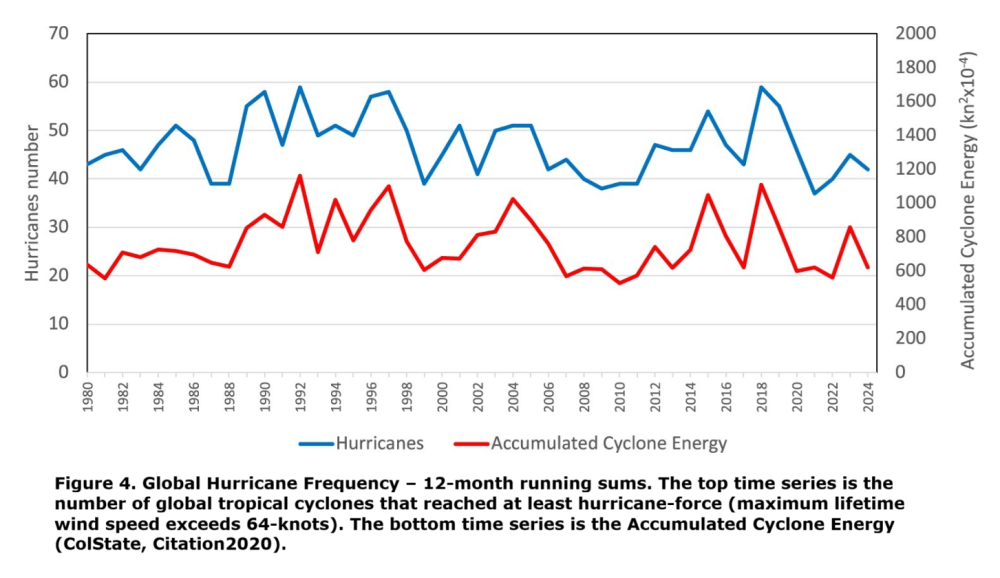
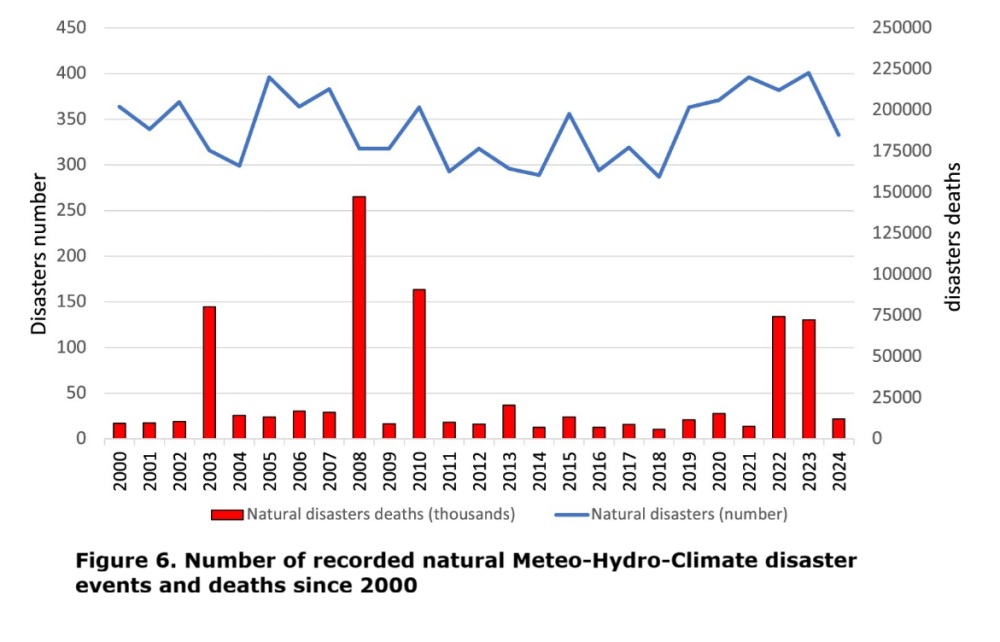
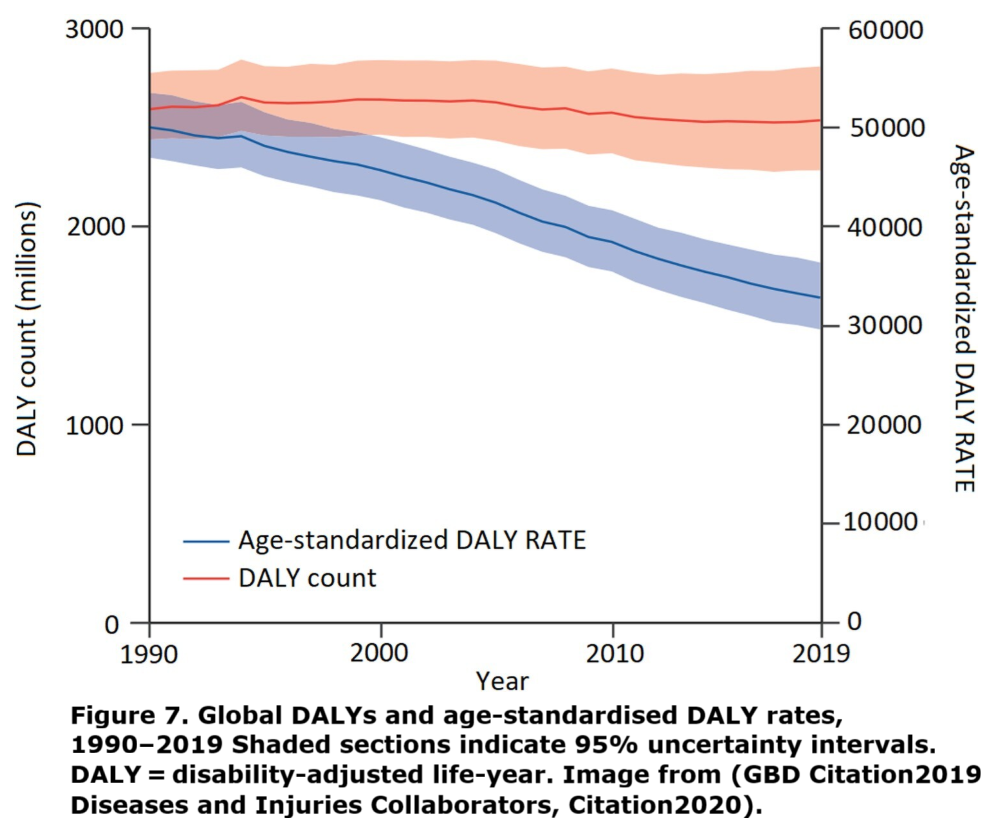
 From Inside Climate News comes this example,
From Inside Climate News comes this example,