Advance Briefing for COP29 Baku 2024
Overview from CFR. COP29 Summit in Baku: What to Expect Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Negotiators from across the globe will gather in Baku, Azerbaijan, for the twenty-ninth annual UN climate change conference on November 11. COP29 marks the midpoint of the “COP Presidencies Troika,” a collaborative effort between the United Arab Emirates (UAE, host to COP28) and Brazil (host to COP30 in 2025) aimed at accelerating progress toward the 1.5°C goal. Unlike COP28 in Dubai last year, which hosted a record hundred thousand attendees, COP29 will be smaller, with Baku expected to host around fifty thousand participants.
The selection of Azerbaijan as the host country has raised concerns about the credibility and integrity of the COP process. COP29 marks the third time a significant fossil fuel-producing country has hosted the conference, and the second time in two years. Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev has announced plans to increase gas production in part to satisfy European Union (EU) demands and referred to the country’s oil and gas reserves as “a gift from God.”
What’s on the Agenda–Three Pledges Are Proposed
Reducing emissions and increasing green energy. The presidency has put forward a series of commitments for investing in renewable energy, such as a Global Energy Storage and Grids Pledge, which aims to enhance energy infrastructure and storage capabilities worldwide, an ambitious Hydrogen Declaration, and a Declaration on Reducing Methane from Organic Waste. With the Green Digital Action Declaration, COP29 leadership seeks to reduce emissions in the information and communication sectors. The agenda, however, makes no direct mention of a transition from fossil fuels.
Building climate resilience. The COP presidency has put forth a climate initiative for farmers and a declaration calling for integrated approaches to combating climate threats to water basins and ecosystems. Additionally, Baku aims to present the Initiative on Human Development for Climate Resilience, which focuses on education, skills, health, and well-being, and the COP29 Multisectoral Actions Pathways (MAP) Declaration that aims to enhance urban climate resilience.
New climate finance targets. Nations are expected to replace the previous $100 billion annual commitment to developing countries from the 2009 Copenhagen Accord. The new target, known as the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG), will be under discussion at November’s COP and is intended to take effect from 2025 onwards. A 2022 report [PDF] by the Independent High-level Expert Group on Climate Finance found that developing countries need around $1 trillion per year by 2025, and $2.4 trillion by 2030 to meet their climate finance needs. Among the most contentious issues that remain are how much money developed nations will provide, and who should provide climate finance.

Yes, those are Trillions of US$ they are projecting to spend.
My Comments
Since there is a big push on climate funding, maybe they could get to the bottom of this:
Maybe donors are put off by no one knowing who gets the money and for what it is spent. And while they are investigating, how about understanding Energy Return on Investment (EROI): you know, the notion that an energy project is worth doing if the energy produced is greater than energy spent. The windmills in the logo at the top reminded me of this:
Why a COP Briefing?
Actually, climate hysteria is like a seasonal sickness. Each year a contagion of anxiety and fear is created by disinformation going viral in both legacy and social media in the run up to the annual autumnal COP. Since the climatists have put themselves at the controls of the formidable US federal government, we can expect the public will be hugely hosed with alarms over the next few weeks. Before the distress signals go full tilt, individuals need to inoculate themselves against the false claims, in order to build some herd immunity against the nonsense the media will promulgate. This post is offered as a means to that end.

Media Climate Hype is a Cover Up
Back in 2015 in the run up to Paris COP, French mathematicians published a thorough critique of the raison d’etre of the whole crusade. They said:
Fighting Global Warming is Absurd, Costly and Pointless.
- Absurd because of no reliable evidence that anything unusual is happening in our climate.
- Costly because trillions of dollars are wasted on immature, inefficient technologies that serve only to make cheap, reliable energy expensive and intermittent.
- Pointless because we do not control the weather anyway.
The prestigious Société de Calcul Mathématique (Society for Mathematical Calculation) issued a detailed 195-page White Paper presenting a blistering point-by-point critique of the key dogmas of global warming. The synopsis with links to the entire document is at COP Briefing for Realists
Even without attending to their documentation, you can tell they are right because all the media climate hype is concentrated against those three points.
Finding: Nothing unusual is happening with our weather and climate.
Hype: Every metric or weather event is “unprecedented,” or “worse than we thought.”
Finding: Proposed solutions will cost many trillions of dollars for little effect or benefit.
Hype: Zero carbon will lead the world to do the right thing. Anyway, the planet must be saved at any cost.
Finding: Nature operates without caring what humans do or think.
Hype: Any destructive natural event is blamed on humans burning fossil fuels.
How the Media Throws Up Flak to Defend False Suppositions
The Absurd Media: Climate is Dangerous Today, Yesterday It was Ideal.
Billions of dollars have been spent researching any and all negative effects from a warming world: Everything from Acne to Zika virus. A recent Climate Report repeats the usual litany of calamities to be feared and avoided by submitting to IPCC demands. The evidence does not support these claims. An example:
It is scientifically established that human activities produce GHG emissions, which accumulate in the atmosphere and the oceans, resulting in warming of Earth’s surface and the oceans, acidification of the oceans, increased variability of climate, with a higher incidence of extreme weather events, and other changes in the climate.
Moreover, leading experts believe that there is already more than enough excess heat in the climate system to do severe damage and that 2C of warming would have very significant adverse effects, including resulting in multi-meter sea level rise.
Experts have observed an increased incidence of climate-related extreme weather events, including increased frequency and intensity of extreme heat and heavy precipitation events and more severe droughts and associated heatwaves. Experts have also observed an increased incidence of large forest fires; and reduced snowpack affecting water resources in the western U.S. The most recent National Climate Assessment projects these climate impacts will continue to worsen in the future as global temperatures increase.
Alarming Weather and Wildfires
But: Weather is not more extreme.

And Wildfires were worse in the past. But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.
But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.

Litany of Changes
Seven of the ten hottest years on record have occurred within the last decade; wildfires are at an all-time high, while Arctic Sea ice is rapidly diminishing.
We are seeing one-in-a-thousand-year floods with astonishing frequency.
When it rains really hard, it’s harder than ever.
We’re seeing glaciers melting, sea level rising.
The length and the intensity of heatwaves has gone up dramatically.
Plants and trees are flowering earlier in the year. Birds are moving polewards.
We’re seeing more intense storms.
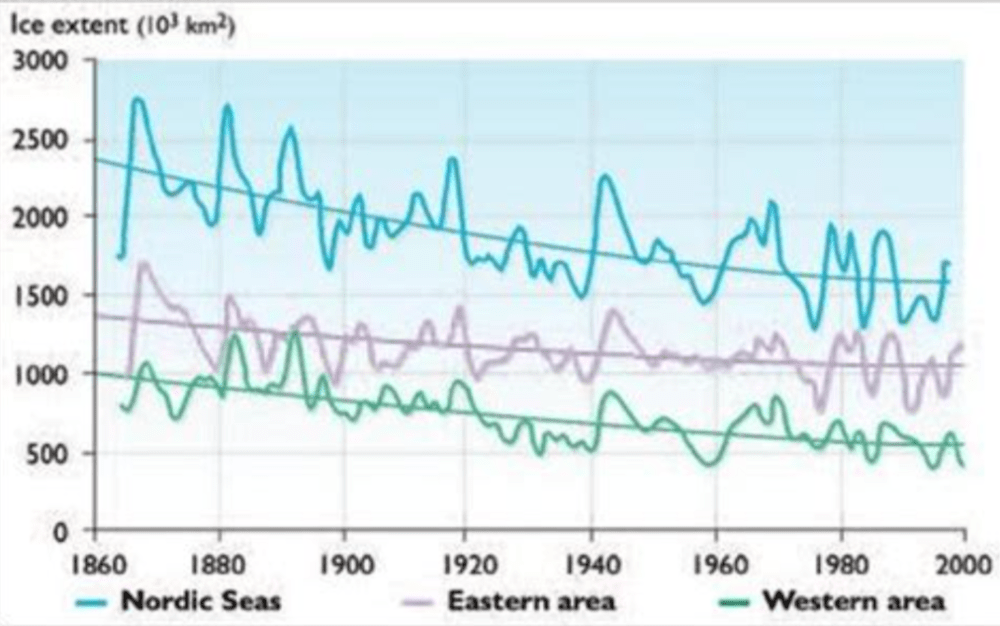
But: Arctic Ice has not declined since 2007.
But: All of these are within the range of past variability. In fact our climate is remarkably stable, compared to the range of daily temperatures during a year where I live.
In fact our climate is remarkably stable, compared to the range of daily temperatures during a year where I live.
And many aspects follow quasi-60 year cycles.
The Impractical Media: Money is No Object in Saving the Planet.
Here it is blithely assumed that the UN can rule the seas to stop rising, heat waves to cease, and Arctic ice to grow (though why we would want that is debatable). All this will be achieved by leaving fossil fuels in the ground and powering civilization with windmills and solar panels. While admitting that our way of life depends on fossil fuels, they ignore the inadequacy of renewable energy sources at their present immaturity.

An Example:
The choice between incurring manageable costs now and the incalculable, perhaps even irreparable, burden Youth Plaintiffs and Affected Children will face if Defendants fail to rapidly transition to a non-fossil fuel economy is clear. While the full costs of the climate damages that would result from maintaining a fossil fuel-based economy may be incalculable, there is already ample evidence concerning the lower bound of such costs, and with these minimum estimates, it is already clear that the cost of transitioning to a low/no carbon economy are far less than the benefits of such a transition. No rational calculus could come to an alternative conclusion. Defendants must act with all deliberate speed and immediately cease the subsidization of fossil fuels and any new fossil fuel projects, and implement policies to rapidly transition the U.S. economy away from fossil fuels.
But CO2 relation to Temperature is Inconsistent.
But: The planet is greener because of rising CO2.
But: Modern nations (G20) depend on fossil fuels for nearly 90% of their energy.
But: Renewables are not ready for prime time.
People need to know that adding renewables to an electrical grid presents both technical and economic challenges. Experience shows that adding intermittent power more than 10% of the baseload makes precarious the reliability of the supply. South Australia is demonstrating this with a series of blackouts when the grid cannot be balanced. Germany got to a higher % by dumping its excess renewable generation onto neighboring countries until the EU finally woke up and stopped them. Texas got up to 29% by dumping onto neighboring states, and some like Georgia are having problems.
But more dangerous is the way renewables destroy the economics of electrical power. Seasoned energy analyst Gail Tverberg writes:
In fact, I have come to the rather astounding conclusion that even if wind turbines and solar PV could be built at zero cost, it would not make sense to continue to add them to the electric grid in the absence of very much better and cheaper electricity storage than we have today. There are too many costs outside building the devices themselves. It is these secondary costs that are problematic. Also, the presence of intermittent electricity disrupts competitive prices, leading to electricity prices that are far too low for other electricity providers, including those providing electricity using nuclear or natural gas. The tiny contribution of wind and solar to grid electricity cannot make up for the loss of more traditional electricity sources due to low prices.
These issues are discussed in more detail in the post Climateers Tilting at Windmills
The Irrational Media: Whatever Happens in Nature is Our Fault.
An Example:
Other potential examples include agricultural losses. Whether or not insurance
reimburses farmers for their crops, there can be food shortages that lead to higher food
prices (that will be borne by consumers, that is, Youth Plaintiffs and Affected Children).
There is a further risk that as our climate and land use pattern changes, disease vectors
may also move (e.g., diseases formerly only in tropical climates move northward).36 This
could lead to material increases in public health costs
But: Actual climate zones are local and regional in scope, and they show little boundary change.
But: Ice cores show that it was warmer in the past, not due to humans.
The hype is produced by computer programs designed to frighten and distract children and the uninformed. For example, there was mention above of “multi-meter” sea level rise. It is all done with computer models. For example, below is San Francisco. More at USCS Warnings of Coastal Floodings
In addition, there is no mention that GCMs projections are running about twice as hot as observations.

Omitted is the fact GCMs correctly replicate tropospheric temperature observations only when CO2 warming is turned off.

In the effort to proclaim scientific certainty, neither the media nor IPCC discuss the lack of warming since the 1998 El Nino, despite two additional El Ninos in 2010 and 2016.
Further they exclude comparisons between fossil fuel consumption and temperature changes. The legal methodology for discerning causation regarding work environments or medicine side effects insists that the correlation be strong and consistent over time, and there be no confounding additional factors. As long as there is another equally or more likely explanation for a set of facts, the claimed causation is unproven. Such is the null hypothesis in legal terms: Things happen for many reasons unless you can prove one reason is dominant.

Finally, advocates and IPCC are picking on the wrong molecule. The climate is controlled not by CO2 but by H20. Oceans make climate through the massive movement of energy involved in water’s phase changes from solid to liquid to gas and back again. From those heat transfers come all that we call weather and climate: Clouds, Snow, Rain, Winds, and Storms.
Esteemed climate scientist Richard Lindzen ended a very fine recent presentation with this description of the climate system:
I haven’t spent much time on the details of the science, but there is one thing that should spark skepticism in any intelligent reader. The system we are looking at consists in two turbulent fluids interacting with each other. They are on a rotating planet that is differentially heated by the sun. A vital constituent of the atmospheric component is water in the liquid, solid and vapor phases, and the changes in phase have vast energetic ramifications. The energy budget of this system involves the absorption and reemission of about 200 watts per square meter. Doubling CO2 involves a 2% perturbation to this budget. So do minor changes in clouds and other features, and such changes are common. In this complex multifactor system, what is the likelihood of the climate (which, itself, consists in many variables and not just globally averaged temperature anomaly) is controlled by this 2% perturbation in a single variable? Believing this is pretty close to believing in magic. Instead, you are told that it is believing in ‘science.’ Such a claim should be a tip-off that something is amiss. After all, science is a mode of inquiry rather than a belief structure.

Summary: From this we learn three things:
Climate warms and cools without any help from humans.
Warming is good and cooling is bad.
The hypothetical warming from CO2 would be a good thing.

























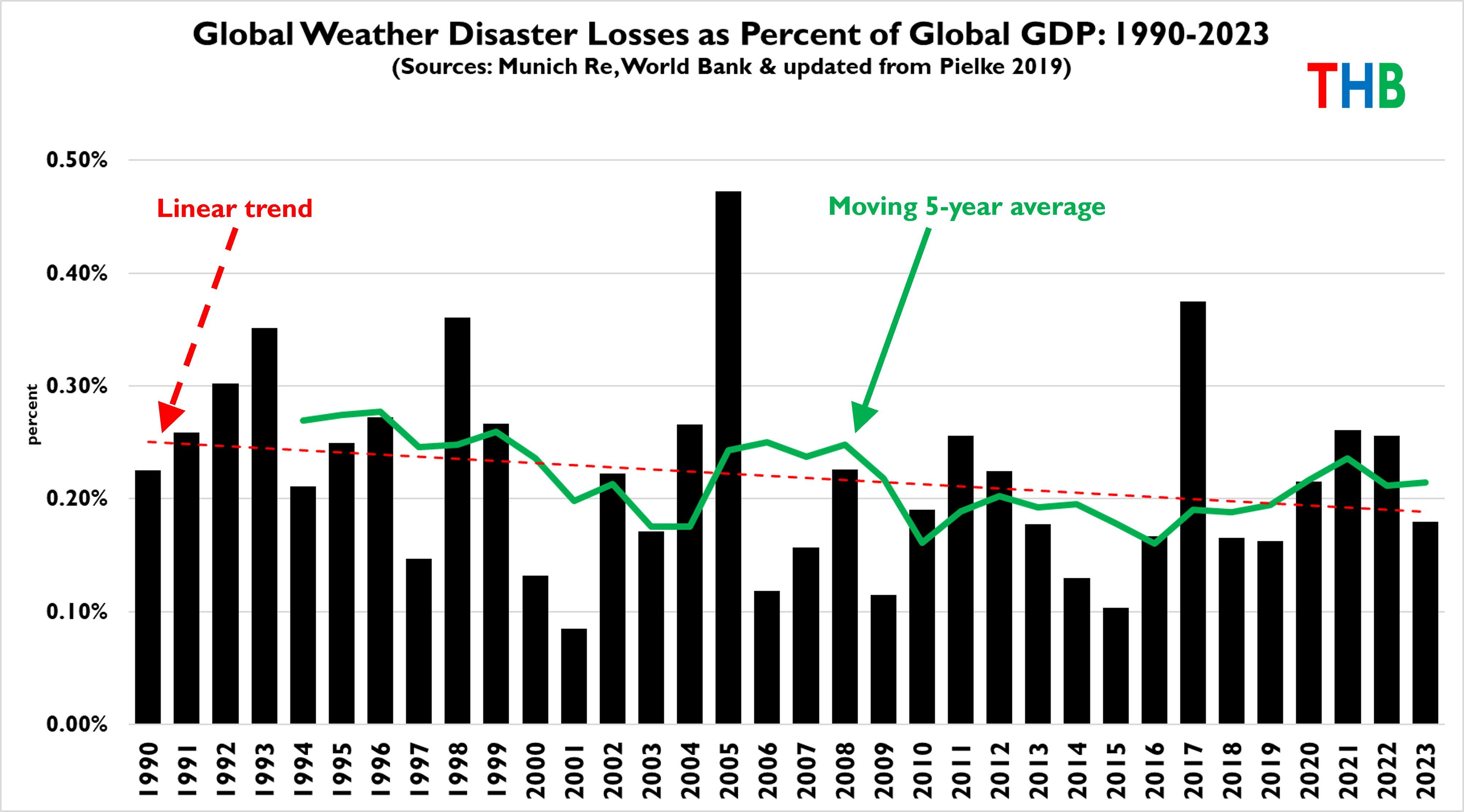







 Paul Mueller does the analysis in his AIER article
Paul Mueller does the analysis in his AIER article