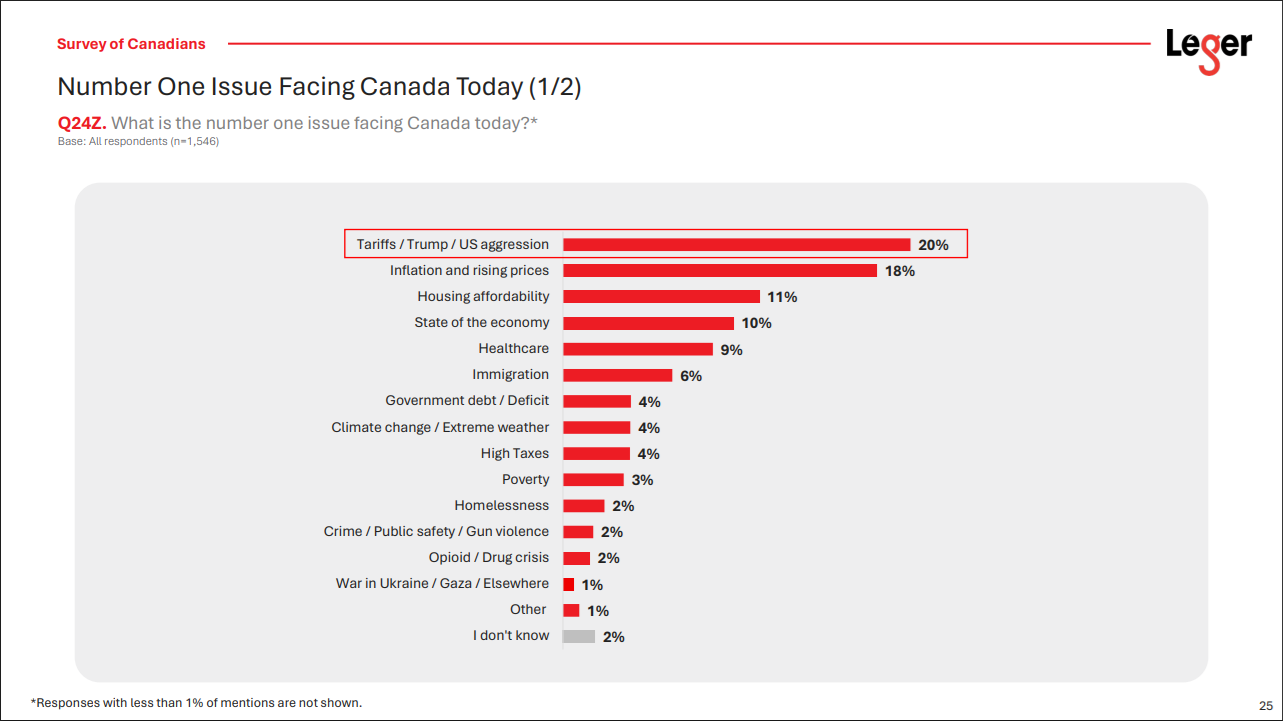
Canadian Supreme Court justices rendered an opionion regarding climate change that does not bear up under scrutiny. Former government litigator Jack Wright exposes the errors in his C2C Journal article Supreme Screw-up: How Canada’s Highest Court Got Climate Change Wrong. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Many Canadians think of the Supreme Court as a wise and august body that can be trusted to give the final word on the country’s most important issues. But what happens when most of its justices get it wrong? Former government litigator Jack Wright delves into the court’s landmark ruling upholding the federal carbon tax and uncovers mistakes, shoddy reasoning and unfounded conclusions. In this exclusive legal analysis, Wright finds that the key climate-related contentions at the heart of the court’s decision were made with no evidence presented, no oral arguments and no cross-examination – and are flat wrong. Now being held up as binding judicial precedent by climate activists looking for ever-more restrictive regulations, the decision is proving to be not just flawed but dangerous.
The Supreme Court of Canada sits at the apex of the Canadian judicial ladder. But like any group of humans, the reasoning of its nine justices isn’t always right. What happens if the court’s reasons for decision include some mistakes and some confusing or inconsistent comments? Are all of Canada’s lower courts bound by these “precedents”? The short answer is no: a court’s decision is only precedent-setting for what it actually decided, and not concerning all of the detailed explanations for how the court got there. Still, erroneous reasoning at the top can create major problems as it often triggers unnecessary and harmful litigation that treats errors as binding precedents. That has proved to be the case with the errors in a crucial case that has profound economic, political and social implications affecting all Canadians.
Advocates for ever-increasing climate action have pounced on the decision in the case known as Reference re Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act, 2021 as precedent to justify further climate-related litigation, as if the courts or Parliament could stabilize the global climate. Such “lawfare”, as these kinds of tactics have come to be known, continues largely because of the non-binding comments in Greenhouse Gas. But the motivating claim – that these explanatory comments are binding precedents – is wrong.
They also misunderstand the special nature of a reference case.
In Canadian law a reference case is a submission by the federal or a provincial government to the courts asking for an advisory opinion on a major legal issue, usually the constitutionality of particular legislation. The opinion given by the Supreme Court is in the form of a judicial decision; strictly speaking, it is not legally binding, although no government has ever ignored such an opinion.
In Greenhouse Gas, the provinces of Ontario, Saskatchewan and Alberta sought the Supreme Court’s opinion on the constitutionality of the federal carbon tax, with all arguing that it is unconstitutional. In March 2021, a 7-2 majority upheld as constitutional Ottawa’s imposition of “backup” federal carbon pricing in any province which has no equivalent provincial measures. It did so based on the national concern doctrine (under the “peace, order and good government” clause in Canada’s Constitution).

In doing so, the majority unusually delved into the wisdom of climate and energy policy, which requires complicated scientific knowledge and resolving conflicting political priorities. The majority assumed – without any evidence – some crucial scientific facts about the causes and effects of climate change. There was no such evidence because a reference case is initiated at the appellate level and, unlike lower trial courts, appellate courts normally have no fact-finding function.
The majority made two important scientific assumptions. First, it assumed that climate change poses a threat to the survival of humanity. Second, it assumed that Canada’s climate is substantially controlled by Canada’s own emissions of greenhouse gases, chiefly carbon dioxide (CO2). Based on these assumptions, it would follow that Canada can avert the harms of climate change to Canadians by reducing Canadian CO2 emissions through a carbon tax.
Suffice it to say that the high court’s two critical premises around which the whole reference case hinged were not proven material facts because there was no evidence before the Court. They were merely the untested assumptions of the seven justices. The first of these key assumptions is highly arguable; the second is outright fallacious. I will address the second of these assumptions first.
The Fantasy of a “Carbon Wall” Around Canada and its Provinces
The majority’s written decision, authored by Chief Justice Richard Wagner, contains a crucial assumption about the physics and chemistry of climate change. . . It held that severely harmful effects of emissions will mostly be caused by – and affect – people situated closest to the geographical origin of the emissions. This is a fallacy which I have termed the “Carbon Wall”.
The Carbon Wall fallacy leads to the error that the federal government can more easily control what the majority termed “grievous” interprovincial impacts caused by CO2 emissions from adjacent provinces. In essence, that government action can “wall off” the effects of greenhouse gas emissions around their area of origin. In fact, there is no CO2 “wall” around any country, nor can one ever be placed around a province by judicial finding or bureaucratic regulation. Unlike local pollutants, CO2 molecules emitted in the United States or China can flow over Canada and all around the planet, and vice-versa. Weather may be largely local, but climate is ultimately global, and so is the movement (and any climate effects) of CO2.
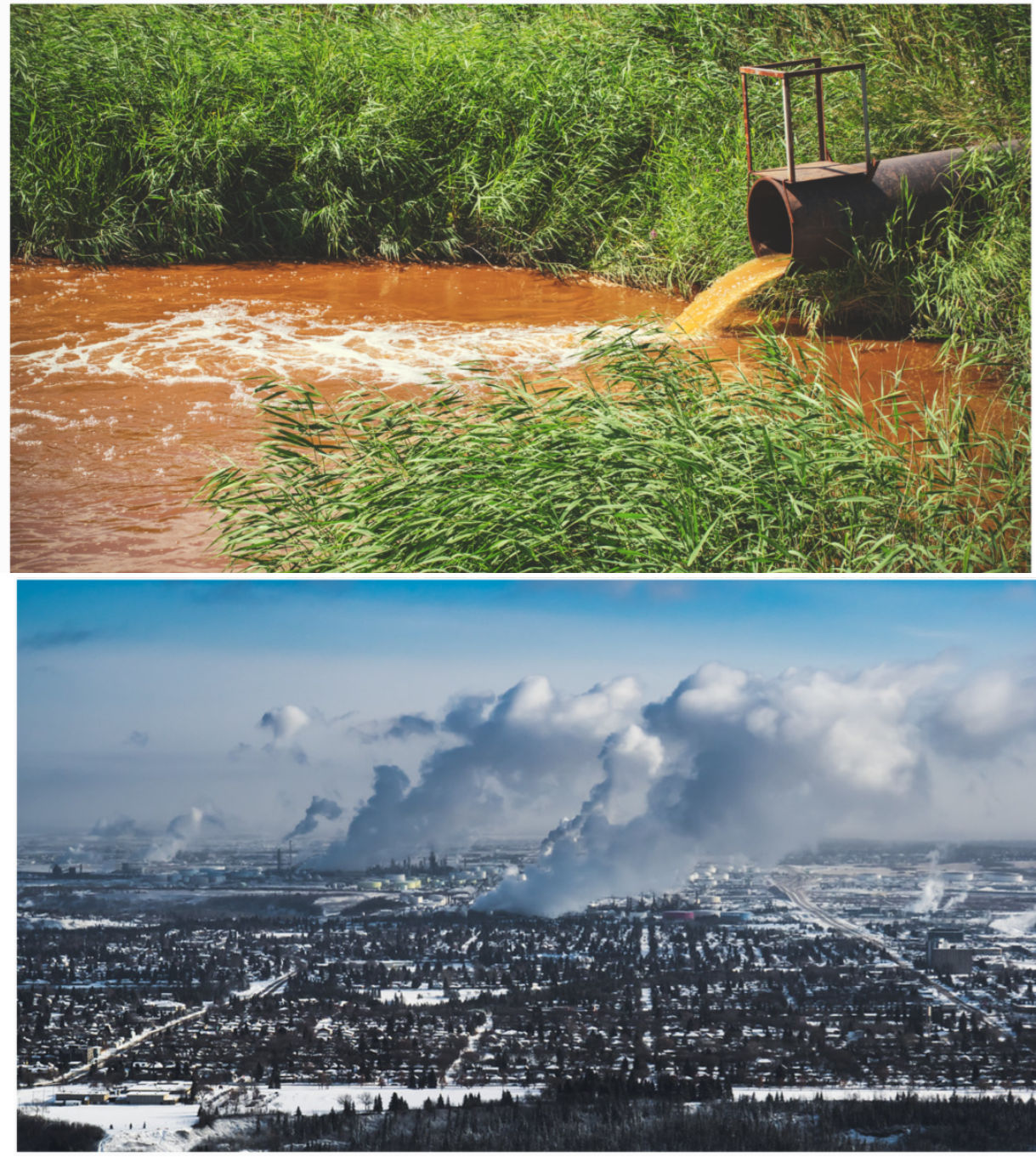

The “Carbon Wall” fallacy: The idea that local CO2 emissions cause local climate change is a common misunderstanding; Canada’s top justices accepted it, envisioning CO2 as akin to traditional pollution that might flow down rivers and cross provincial boundaries, and whose damage can therefore be locally controlled. (Sources of photos: (top) Shutterstock; (bottom) Daveography.ca, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
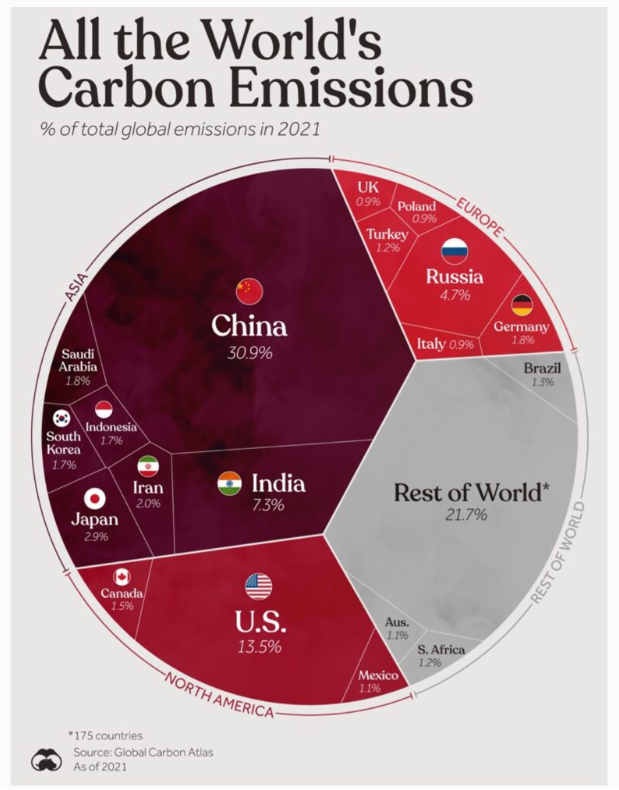
Thus, the majority assumed that climate change consists of CO2, following its emission, having a direct noxious climate impact upon geographically contiguous areas. We are not told, however, what particular form that harm takes, how it is caused or on what evidence it is based. But if Canada’s senior-most justices truly understood the basic mechanics of climate, they would have realized that virtually the entire impact of which they speak must come from outside the country, since Canada generates only 1.5 percent of global CO2 emissions, making each province only a tiny contributor to total global emissions.
Other Fallacious or Unsupported “Carbon Wall” Thinking
The majority also incorrectly suggested (para. 10) that, “The effects of climate change have been and will be particularly severe and devastating in Canada.” There is no evidence to support this assumption. While basic climatology holds that the Earth’s polar regions will warm more than lower latitudes, this is not unique to Canada. And rising levels of CO2 have also generated benefits through increasing agricultural productivity and forest and plant growth.
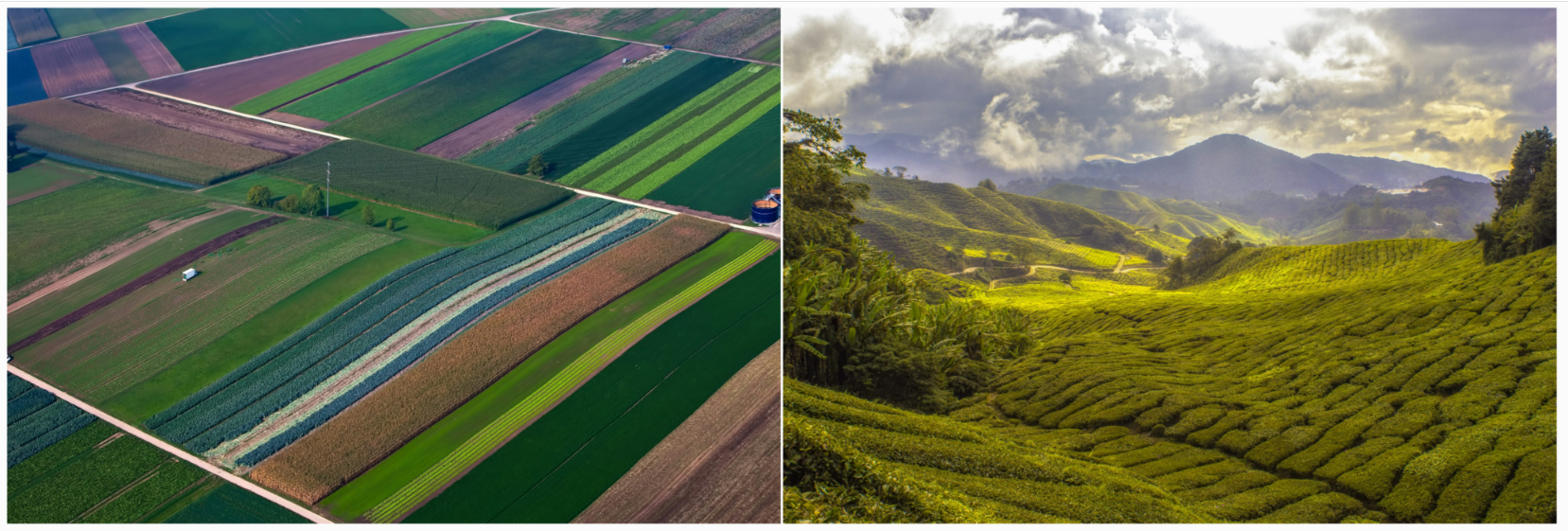

The good news: The Supreme Court said climate change would be “particularly severe and devastating in Canada”, an assumption for which there is no evidence; rising levels of atmospheric CO2 have actually led to a “greening” of the Earth, increasing agricultural productivity and forest and plant growth. (Source of photos: Pexels)
All that the Supreme Court’s ‘twice as fast’ alarm about Canadian warming shows is that Canadians live on land and not the ocean. The statement, while technically true, communicates nothing of significance. But it is highly misleading.
Canada is not bound in any meaningful way by the Paris Agreement, its contents should not influence decisions by Canadian courts, and the Supreme Court majority in Greenhouse Gas found nothing from the Paris Agreement that would be meaningfully precedential for those seeking to save themselves from ‘climate damage’.
The Assumption of an Existential Threat to Humanity
Climate change, Greenhouse Gas declares emphatically (para. 167), is “an existential challenge…a threat of the highest order to the country, and…[an] undisputed threat to the future of humanity [that] cannot be ignored.” It would seem to follow from this resounding pronouncement that the planet requires rapid decarbonization, with a massive and very costly diversion of resources to do so, and without regard to the cost trade-offs for other important human needs such food, housing and transportation or for such matters as safety and security.
Weighing such competing human needs is a political process, not a judicial judgment. Yet the Supreme Court’s assertions of catastrophe stand alone in mid-judgment, devoid of expert sources, of any investigation of facts, or of any reasoning from facts. This is unfortunate, because the court majority’s seemingly unqualified belief is anything but “undisputed”.
Many experts specifically dispute that humanity’s survival is at stake. Nobel Laureate William Nordhaus, the Yale University economist who is considered the “father” of the carbon tax, does so in his book The Climate Casino (page 134). Nor does the IPCC itself make such a claim.
“For most economic sectors, the impact of climate change will be small relative to the impacts of other drivers. Changes in population, age, income, technology, relative prices, lifestyle, regulation, governance, and many other aspects of socioeconomic development will have an impact on the supply and demand of economic goods and services that is large relative to the impact of climate change.” IPCC Report, Working Group 2, 2014
As Greenhouse Gas involved no evidentiary procedures, then what could have been the source of the Supreme Court’s ‘existential threat’ declaration? A search of the court files shows that this was assembled from an affidavit in Canada’s Record by a federal manager, John Moffet, an assistant deputy minister with Environment and Climate Change Canada.
Suffice it here to note that Canadian evidentiary rules do not allow for reliance upon a federal government manager’s affidavit for dispositive proof of an existential threat to an entire nation and indeed the whole planet. Moffet was neither disinterested in the dispute nor an expert on any aspect of climate science or any related scientific discipline that would qualify him as an independent expert witness.
The Unfolding Danger in the Supreme Court’s Climate Assumptions
There is no sense in parsing each of the assertions made by the majority in the Background, quite a few of which are highly questionable. But there is no existential threat inference to be drawn even if all are accepted. Climate change may be a serious problem, but it is only one among many other serious and resource-consuming human problems to be weighed and balanced.
If the Supreme Court of Canada chooses to evaluate complex climate policy in future (which the Court really lacks the institutional capacity to do), it should at least make arrangements for a full evidentiary record. For climate change, that would be enormous and would take months of hearings. A Royal Commission would be better placed to handle such a mission.
But judgments like Greenhouse Gas are wholly inadequate. It contains no true factual findings of an existential threat to humanity, or of a Carbon Wall around Canada, or of a possible Carbon Wall controllable by federal regulation around each of our provinces. There is no federal claim to be saving Canadians from interprovincial climate “pollution” and only a diffuse and very insignificant Canadian contribution to overall planetary climate change. Thus, the majority’s assumptions cannot serve as authority for the lower courts to adjudicate the cases that come before them under the guise of saving Canadians from climate change.
We cannot allow single-issue adherents (often wielding generous federal funding)
to repurpose our courts on pretextual bases and achieve goals
that they were denied through the ballot box.


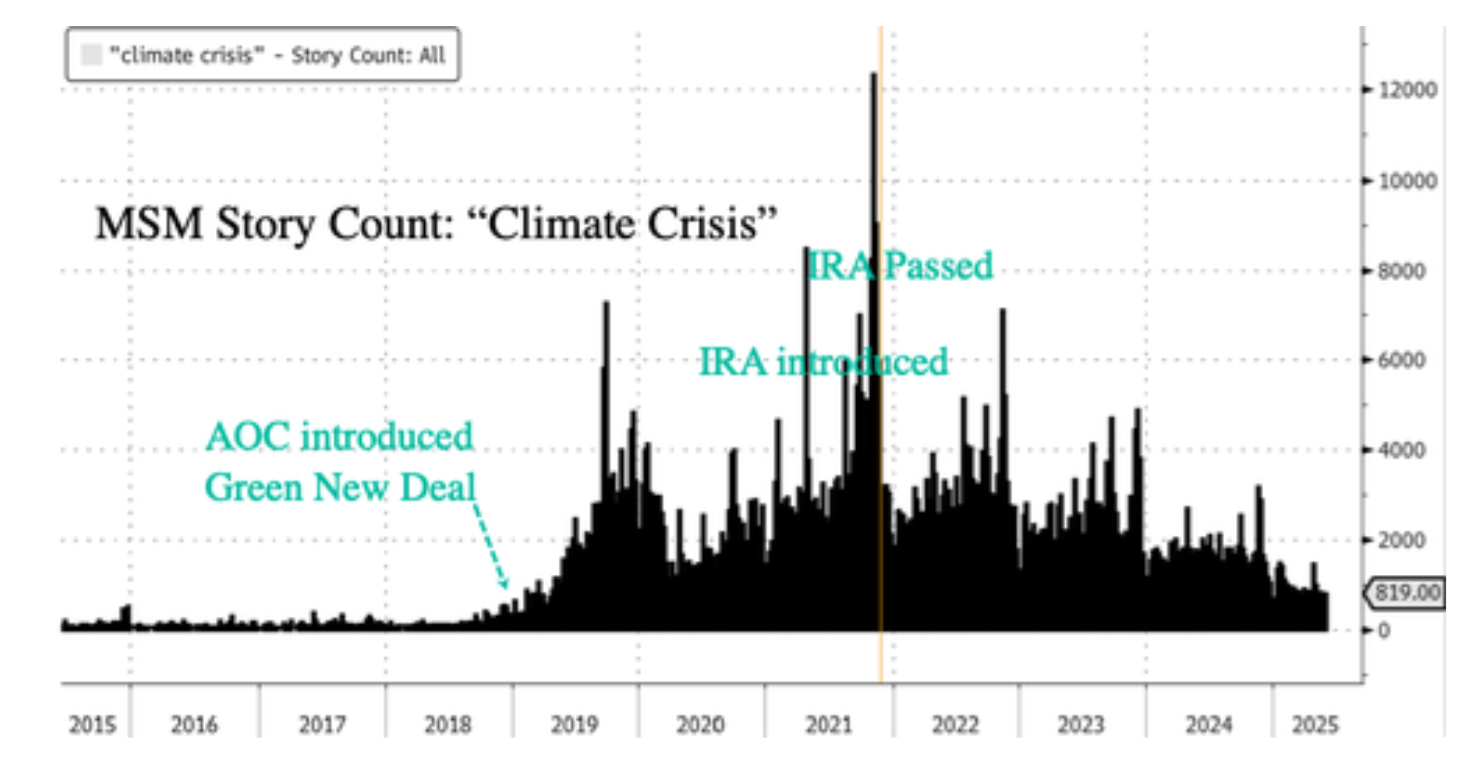


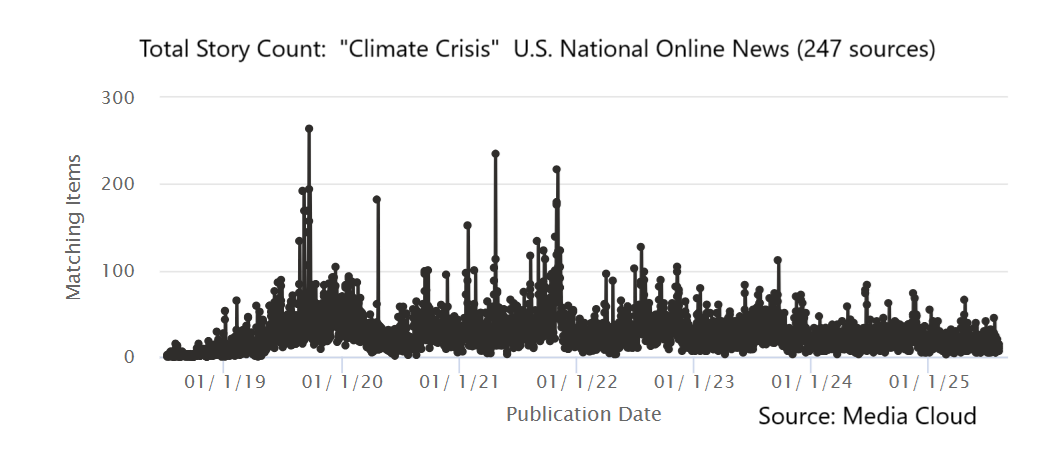




















 Once perched atop the climate movement’s moral high ground, the self-anointed “climate hawks” are now watching their influence dwindle, and nowhere is that retreat more visible than in California. Long the epicenter of progressive climate ambition, the Golden State is now backpedaling. Democrats who once championed aggressive environmental mandates are hitting pause, reworking regulations, and distancing themselves from policies that have driven up energy and housing costs. A post-2024 reality check has swept the party: climate may still poll well in theory, but not when it collides with affordability.
Once perched atop the climate movement’s moral high ground, the self-anointed “climate hawks” are now watching their influence dwindle, and nowhere is that retreat more visible than in California. Long the epicenter of progressive climate ambition, the Golden State is now backpedaling. Democrats who once championed aggressive environmental mandates are hitting pause, reworking regulations, and distancing themselves from policies that have driven up energy and housing costs. A post-2024 reality check has swept the party: climate may still poll well in theory, but not when it collides with affordability.


 What’s replacing the hawks isn’t apathy. It’s realism. A new generation is emerging – leaders who are less interested in preaching and more interested in producing. They view climate not as a moral crusade, but as a challenge of engineering, economics, and national renewal. They understand that the future won’t be built through degrowth or doomerism, but through innovation, adaptation, and strategic investment in America’s strengths.
What’s replacing the hawks isn’t apathy. It’s realism. A new generation is emerging – leaders who are less interested in preaching and more interested in producing. They view climate not as a moral crusade, but as a challenge of engineering, economics, and national renewal. They understand that the future won’t be built through degrowth or doomerism, but through innovation, adaptation, and strategic investment in America’s strengths.