Background from previous post Rise and Fall of CAGW
On January 8, 2018 Ross Pomeroy published at RealClearScience an interesting article The Six Stages of a Failed Psychological Theory
The Pomeroy essay focuses on theories in the field of psychology and describes stages through which they rise, become accepted, challenged and discarded. It has long seemed to me that global warming/climate change theory properly belongs in the field of social studies and thus should demonstrate a similar cycle.
Formerly known as CAGW (catastrophic anthropogenic global warming), the notion of “climate change” is logically a subject of social science rather than physical science. “Climate Change” is a double abstraction: it refers to the derivative (change) in our expectations (patterns) of weather. Thus studies of “Climate Change” are properly a branch of Environmental Sociology.
As a social psychology theory, CAGW/climate change bundles together three interdependent assertions.

From the beginning the claimed science, impacts and policies were bundled, which makes CAGW theory unusual. Psychological theories do not typically give rise to activism for changes in social and political policies. Thus the six stages above focus on the rise and fall of a scientific conclusion, with little or no reference to impacts and policies. At the end of this post are links to resources regarding these latter two points.
Examples of Failed Psychology Theories: The “Backfire Effect” and others
Ross Pomeroy (my bolds):
With the publication of his exhaustingly researched and skillfully reported article, “LOL Something Matters,” science writer Daniel Engber convincingly demonstrated that the “backfire effect,” the notion that contradictory evidence only strengthens entrenched beliefs, does not hold up under rigorous scientific scrutiny. Bluntly stated, the “backfire effect” probably isn’t real.
The debunking of this longstanding psychological theory follows similar academic takedowns of ego depletion, social priming, power posing, and a plethora of other famous findings. Indeed, much of what we “know” in psychology seems to be false.
There’s a good reason for this: psychology, as a discipline, is a house made of sand, based on analyzing inherently fickle human behavior, held together with poorly-defined concepts, and explored with often scant methodological rigor. Indeed, there’s a strong case to be made that psychology is barely a science.
How Theories Advance and Collapse
Seeing how disarray defines psychology, it makes perfect sense that the field’s leading theories are vulnerable to collapse. Having watched this process play out a number of times, a clear pattern has emerged. Let’s call it the “Six Stages of a Failed Psychological or Sociological Theory.”
Stage 1: The Flashy Finding. An intriguing report is published with subject matter that lends itself to water cooler conversation, say, for example, that sticking a pen in your mouth to force a smile makes things seem funnier. Media outlets provide gushing coverage.
Stage 1 CAGW Theory
For Climate Change, by many accounts the flashy finding was James Hansen’s famous 1988 testimony in the US Senate. Hansen’s claim to detect global warming was covered by all the main television network news services and it won for him a New York Times front page headline: “Global warming has begun, expert tells Senate.”
While Hansen’s appearance was a PR coup, he actually jumped the gun. By 1995 IPCC scientists had not yet agreed that humans are causing global warming. The story of that problem and the subsequent claim of first detection by John Houghton and Ben Santer is described in detail in Bernie Lewin’s fine historical account. (My synopsis is linked at the end.)
So in this sense, the actual Flashy Finding was published by Santer et al. just before Rio COP in Nature July 1996 entitled: A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere
B. D. Santer, K. E. Taylor, T. M. L. Wigley, T. C. Johns, P. D. Jones, D. J. Karoly, J. F. B. Mitchell, A. H. Oort, J. E. Penner, V. Ramaswamy, M. D. Schwarzkopf, R. J. Stouffer & S. Tett From the abstract:
The observed spatial patterns of temperature change in the free atmosphere from 1963 to 1987 are similar to those predicted by state-of-the-art climate models incorporating various combinations of changes in carbon dioxide, anthropogenic sulphate aerosol and stratospheric ozone concentrations. The degree of pattern similarity between models and observations increases through this period. It is likely that this trend is partially due to human activities, although many uncertainties remain, particularly relating to estimates of natural variability.
An article published the same month in World Climate Report was entitled:“Clearest Evidence” For Human “Fingerprint?” Results clouded if more complete data used The WCR essay concluded:
We are frankly rather amazed that this paper could have emerged into the refereed literature in its present state; that is not to say that the work is bad, but that there are serious questions—similar to ours—that the reviewers should have asked.
The inescapable conclusions:
1. The vast majority of the “fingerprints” of the greenhouse effect are found way up in the atmosphere, especially in the stratosphere.
2. The “detection” models that were used either don’t predict very much future warming or were run with the wrong greenhouse effect and produce absurd results when the right numbers are put in.
3.And finally, down here in the lower atmosphere, the evidence is much more smudged and is based upon a highly selected set of data that, when viewed in toto, shows something dramatically different than what the paper purports.
The period that Santer et al. studied corresponds precisely with a profound warming trend in this region. But when all of the data (1957 to 1995) are included, there’s no trend whatsoever! We don’t know what to call this, but we believe that at least one of the 13 prestigious authors on this paper must have known this to be the case.

Stage 2: The Fawning Replications. Other psychologists, usually in the early stages of their careers, leap to replicate the finding. Most of their studies corroborate the effect. Those that don’t are not published, perhaps because the researchers don’t want to step on any toes, or because journal editors would prefer not to publish negative findings.
Stage 2 CAGW Theory
Following the human detection claim, the media increasingly filled its time and pages with reports of “multiple lines of evidence” proving CAGW. Typically these consisted of :
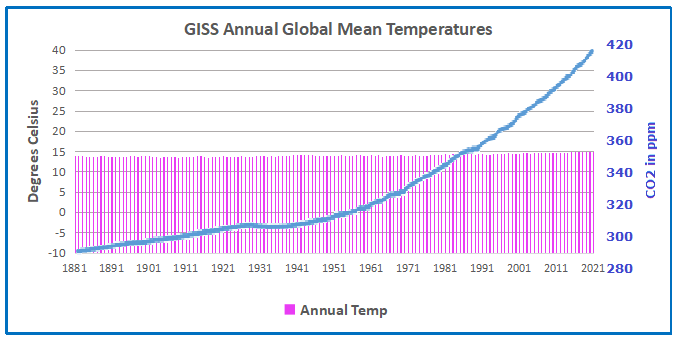
Global temperature rise
Warming oceans
Shrinking ice sheets
Glacial retreat
Decreased snow cover
Sea level rise
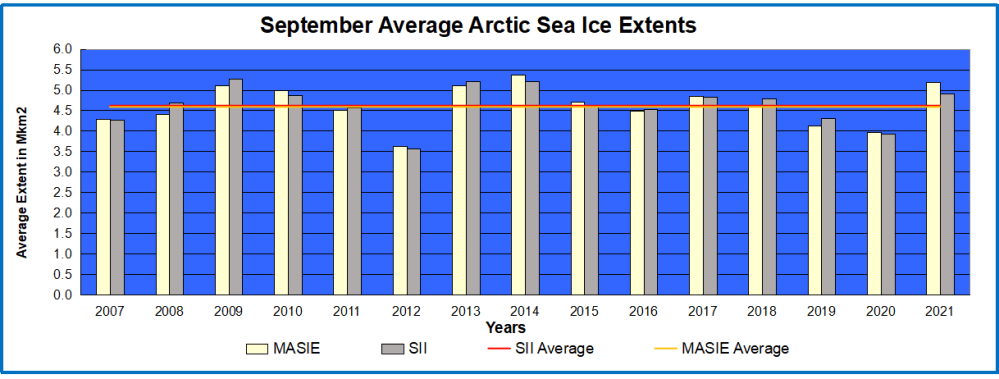
Declining Arctic sea ice
Extreme events
Ocean acidification
However, all of these are equivocal, involving signal and noise issues. And in any case, the fact of any changes does not in itself prove human causation.

Overview of the structure of a state-of-the-art climate model. From the NOAA website.
As suggested by the Santer et al. flashy finding, the claim of human causation was based upon climate models. And the effort to substantiate that claim was primarily a campaign to construct and experiment with GCMs. From History of climate modeling by Paul N. Edwards .
Like ripples moving outward from the three pioneering groups (GFDL, UCLA, and NCAR), modelers, dynamical cores, model physics, numerical methods, and GCM computer code soon began to circulate around the world. By the early 1970s, a large number of institutions had established new general circulation modeling programs. In addition to those discussed above, the most active climate modeling centers today include Britain’s Hadley Centre, Germany’s Max Planck Institute, Japan’s Earth Simulator Centre, and the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in the United States..
How many GCMs and climate modeling groups exist worldwide? The exact number can be expanded or contracted under various criteria. About 33 groups submitted GCM output to the Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project (AMIP) in the 1990s.A few years later, however, only about 25 groups contributed coupled AOGCM outputs to the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP)—reflecting the greater complexity and larger computational requirements of coupled models. Notably, while the AMIP models included entries from Russia, Canada, Taiwan, China, and Korea, all of the CMIP simulations came from modeling groups based in Europe, Japan, Australia, and the USA, the historical leaders in climate modeling.
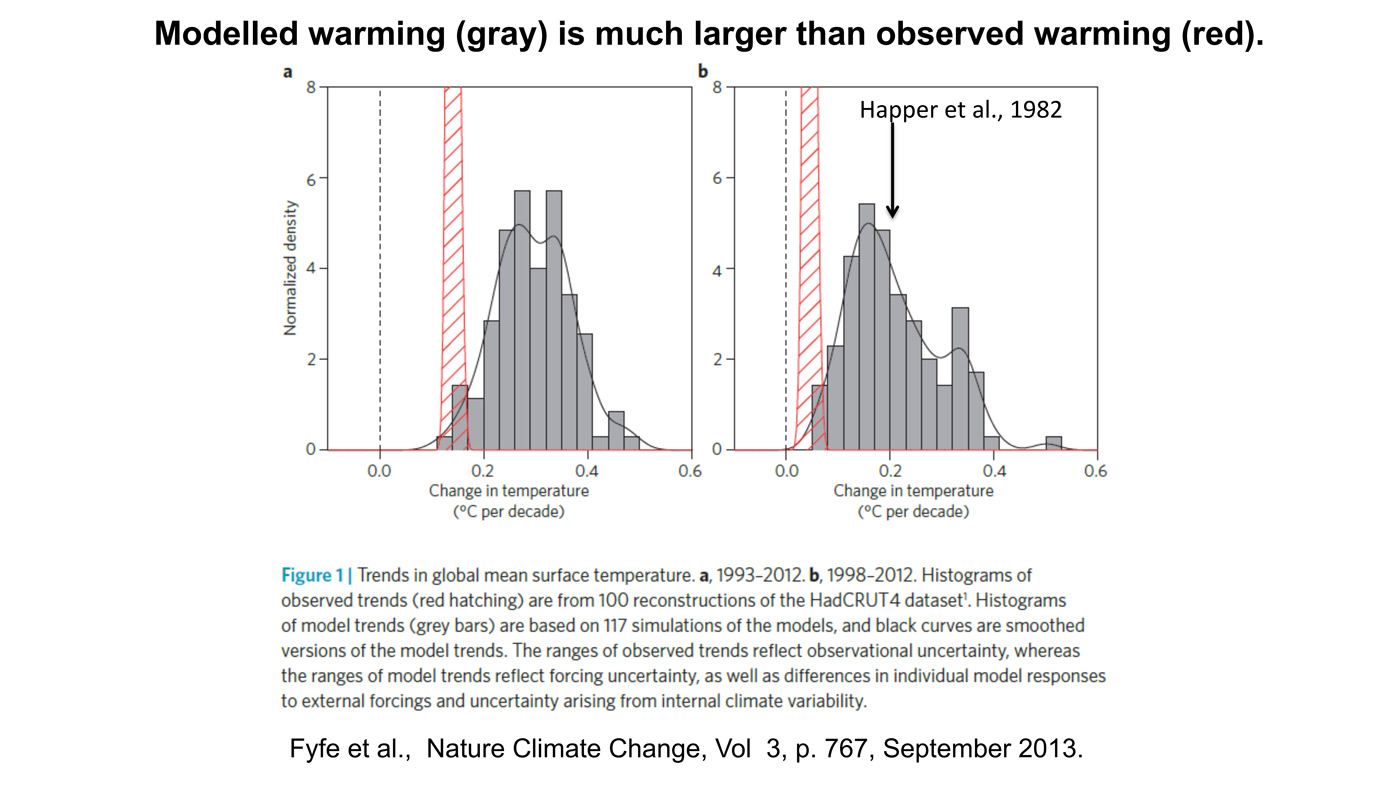
The difficulties and uncertainties with climate models have been long understood, and have not been overcome through the decades, as indicated by the failure to reduce the range estimates of climate sensitivity to CO2. From Modeling climatic effects of anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions: unknowns and uncertainties Willie Soon et al.
Specifically, we review common deficiencies in general circulation model (GCM) calculations of atmospheric temperature, surface temperature, precipitation and their spatial and temporal variability. These deficiencies arise from complex problems associated with parameterization of multiply interacting climate components, forcings and feedbacks, involving especially clouds and oceans. We also review examples of expected climatic impacts from anthropogenic CO2 forcing.
Given the host of uncertainties and unknowns in the difficult but important task of climate modeling, the unique attribution of observed current climate change to increased atmospheric CO2 concentration, including the relatively well-observed latest 20 yr, is not possible. We further conclude that the incautious use of GCMs to make future climate projections from incomplete or unknown forcing scenarios is antithetical to the intrinsically heuristic value of models. Such uncritical application of climate models has led to the commonly held but erroneous impression that modeling has proven or substantiated the hypothesis that CO2 added to the air has caused or will cause significant global warming.
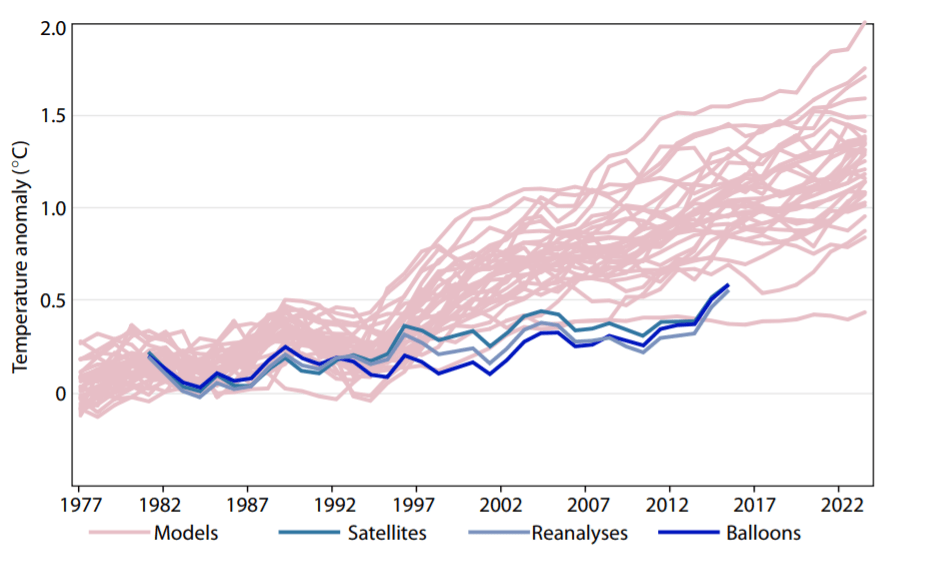
Figure 7 (Christy 2019): Tropical mid-tropospheric temperatures, models vs. observations.
Models in pink, against various observational datasets in shades of blue. Five-year averages
1979–2017. Trend lines cross zero at 1979 for all series.
Stage 3: A Consensus Forms. The finding is now taken for granted, regularly appearing in pop psychology stories and books penned by writers like Malcolm Gladwell or Jonah Lehrer. Millions of people read about it and “armchair” explain it to their friends and family.
Stage 3 CAGW Theory
The Claims of 97% Consensus of scientists on the question of CAGW stem from five papers, conveniently referenced on NASA’s website (though none of them were written by NASA scientists).
The first claim of 97% came from a survey sample of 77 climate scientists who said “Yes” to 2 statements: “It has warmed since 1850.”; “Human activity has contributed to the warming.” That survey questionnaire was deliberately not sent to those known to be skeptical: scientists not employed by government or universities; astronomers; solar scientists; physicists; meteorologists.

Another paper noted by NASA on their website is by W. R. L. Anderegg, at the time a PhD student in the department of Biology at Stanford University. He went on to become a professor at Princeton and Utah Universities in the field of ecology and biological sciences, studying the effects of global warming on forests.
Two papers were produced by John Cook who has an undergraduate education in physics from the University of Queensland and a post-graduate honors year studying solar physics, worked as a self-employed cartoonist before founding a website pushing climate alarmism. For this he was given the title of the Climate Communication Fellow for the Global Change Institute at the University of Queensland. He is currently completing a PhD in cognitive psychology, researching how people think about climate change.
Finally, a key paper was from Naomi Oreskes who received her PhD degree in the Graduate Special Program in Geological Research and History of Science at Stanford in 1990. Her fields are History of Science and Economic Geology, and she is a prominent activist for IPCC activities.
All five of these papers have been extensively criticized in the peer-reviewed literature for their poor quality. For example:
Regarding Anderegg et al. and climate change credibility, PNAS, Dec. 28, 2010 by Lawrence Bodenstein
The study by Anderegg et al. (1) employed suspect methodology that treated publication metrics as a surrogate for expertise.
In the climate change (CC) controversy, a priori, one expects that the much larger and more “politically correct” side would excel in certain publication metrics. They continue to cite each other’s work in an upward spiral of self-affirmation.
Here, we do not have homogeneous consensus absent a few crackpot dissenters. There is variation among the majority, and a minority, with core competency, who question some underlying premises. It would seem more profitable to critique the scientific evidence than count up scientists, publications, and the like.
Regarding purely scientific questions, it may be justified to discount nonexperts. However, here, dissenters included established climate researchers. The article undermined their expert standing and then, extrapolated expertise to the more personal credibility. Using these methods to portray certain researchers as not credible and, by implication, to be ignored is highly questionable. Tarring them as individuals by group metrics is unwarranted.
Publication of this article as an objective scientific study does a true disservice to scientific discourse. Prominent scientific journals must focus on scientific merit without sway from extracurricular forces. They must remain cautious about lending their imprimatur to works that seem more about agenda and less about science, more about promoting a certain dogma and less about using all of the evidence to better our understanding of the natural world.
A more complete list of published papers refuting these studies is here: All “97% Consensus” Studies Refuted by Peer-Review
More inclusive surveys with more pointed questions show much more diverse opinions. Most scientists agree it has warmed since 1850, the end of the Little Ice Age. Geologists have evidence that the earth was warmer than now during the Medieval Warm Period, more warm during the Roman Warm Period, warmer still in the Minoan period. So the overall trend is a cooling over the last 11,500 years.
Most agree that human land use, such as making dams, farming, building cities, airports and highways, all affect the climate in those locations. The idea that rising CO2 is causing dangerous warming is controversial, with dissenters a large minority.
Stage 4: The Rebuttal. After a few decades, a new generation of researchers look to make a splash by questioning prevailing wisdom. One team produces a more methodologically-sound study that debunks the initial finding. Media outlets blare the “counterintuitive” discovery.
Stage 4 CAGW Theory
There have been many rebuttals of CAGW theory and in the blogosphere they are proclaimed and shared among skeptics. But it is still rare for mass media outlets to acknowledge any finding that contradicts the prevailing “consensus” view of CAGW. On the multiple lines of evidence, the NIPCC series of reports provide references to a trove of peer-reviewed literature that do not support CAGW. The most recent report is Climate Change Reconsidered II and the list of scientists, authors and reviewers includes people who have objected to CAGW over the years.
An important proof against the CO2 global warming claim was included in John Christy’s testimony 29 March 2017 at the House Committee on Science, Space and Technology. The text below is from that document which can be accessed here.

Figure 5. Simplification of IPCC AR5 shown above in Fig. 4. The colored lines represent the range of results for the models and observations. The trends here represent trends at different levels of the tropical atmosphere from the surface up to 50,000 ft. The gray lines are the bounds for the range of observations, the blue for the range of IPCC model results without extra GHGs and the red for IPCC model results with extra GHGs.The key point displayed is the lack of overlap between the GHG model results (red) and the observations (gray). The nonGHG model runs (blue) overlap the observations almost completely.
Main Point: IPCC Assessment Reports show that the IPCC climate models performed best versus observations when they did not include extra GHGs and this result can be demonstrated with a statistical model as well.
More discussion on this rebuttal is at Warming from CO2 Unlikely
See also Global Warming Theory and the Tests It Fails
But the mass media is still in thrall of the catastrophic theory (bad news is good for business).
Stage 5: Proper Replications Pour In. Research groups attempt to replicate the initial research with the skepticism and precise methodology that should’ve been used in the first place. As such, the vast majority fail to find any effect.
Stage 5 CAGW Theory
In the case of climate change, the rewards are all skewed in favor of CAGW. Not only is that bundle of beliefs politically correct, the monopoly of research funding for consensus projects leaves contrarian scientists high and dry. And to the degree that the case rests on complex and expensive computer climate models, few centers are in a position to challenge the conventional wisdom, and almost none would be rewarded for doing so.
Despite this, every year there are hundreds of new research papers published challenging CAGW. Kenneth Richard at No Tricks Zone has done yeoman work compiling and summarizing and linking to such studies. His most recent review is Hundreds More Papers Published In 2021 Support A Skeptical Position On Climate Alarm
The papers are sorted into four categories of views questioning climate alarm.
N(1) Natural mechanisms play well more than a negligible role (as claimed by the IPCC) in the net changes in the climate system, which includes temperature variations, precipitation patterns, weather events, etc., and the influence of increased CO2 concentrations on climatic changes are less pronounced than currently imagined.
N(2) The warming/sea levels/glacier and sea ice retreat/hurricane and drought intensities…experienced during the modern era are neither unprecedented or remarkable, nor do they fall outside the range of natural variability, as clearly shown in the first 150 graphs (from 2017) on this list.
N(3) The computer climate models are not reliable or consistently accurate, and projections of future climate states are little more than speculation as the uncertainty and error ranges are enormous in a non-linear climate system.
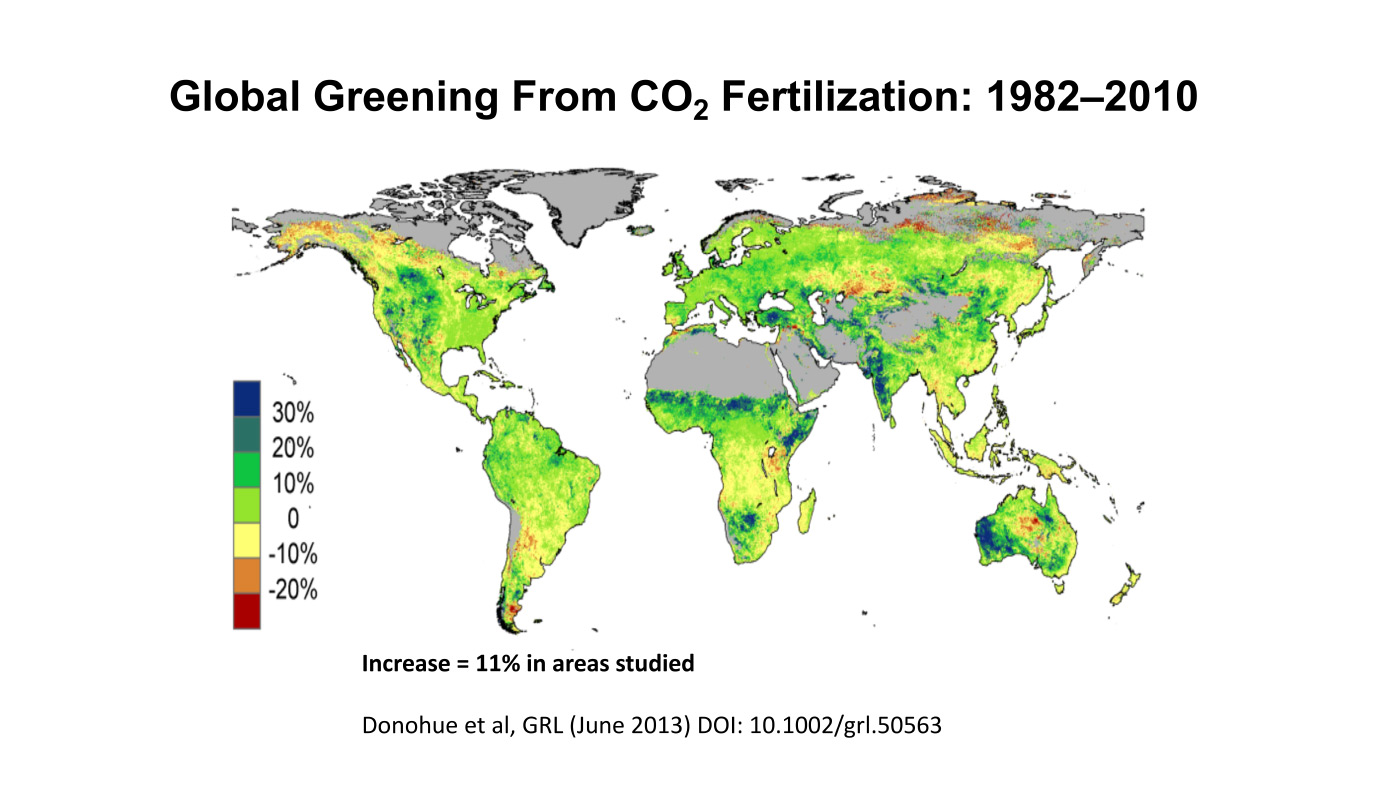
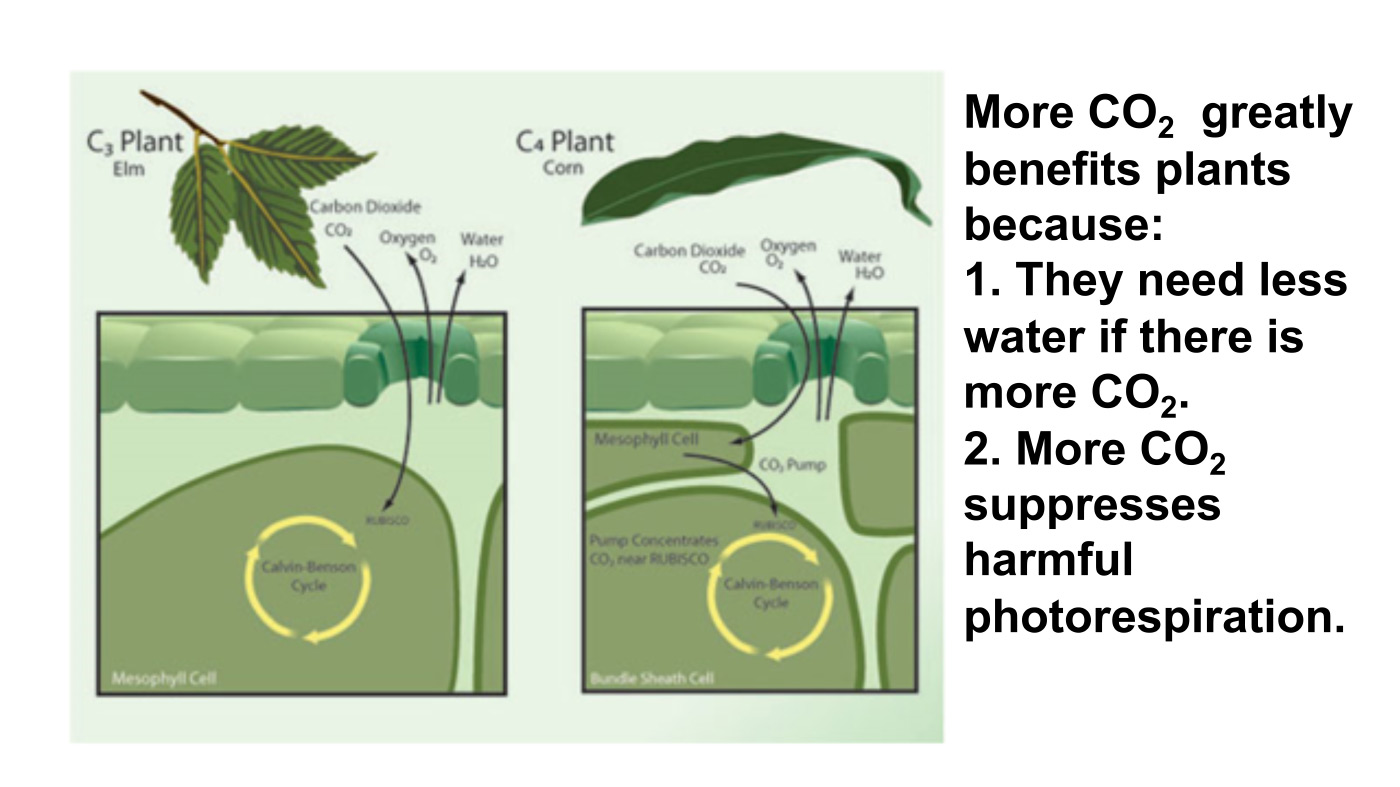
N(4) Current emissions-mitigation policies, especially related to the advocacy for renewables, are often ineffective and even harmful to the environment, whereas elevated CO2 and a warmer climate provide unheralded benefits to the biosphere (i.e., a greener planet and enhanced crop yields).
As for climate models, there is a single center (the Russian Institute of Numerical Mathematics), working on GCMs that produce unalarming results. Out of 33 CMIP5 generation models the INMCM4 appears in the earlier graph above as the only one tracking close to temperature observations. And reports of the upgrade to INMCM5 appear promising. For more on this topic:
Climate Models: Good, Bad and Ugly

Stage 6: The Theory Lives On as a Zombie. Despite being debunked, the theory lingers on in published scientific studies, popular books, outdated webpages, and common “wisdom.” Adherents in academia cling on in a state of denial – their egos depend upon it.

Stage 6 CAGW Theory
Clearly, we are still a long ways from CAGW going to zombie status. There is still way too much money and fame attached to climate advocacy. But it is fair to say that the position of CAGW has become more precarious. The presence of a skeptical US President, and the withdrawal of funding and political support for alarmists makes it possible for others to express doubts and explore flaws in the consensus theory. The collapse of green energy schemes in places like Germany and Australia may also portend the onset of stage six.
Of course, the only sure sign of a theory’s failure is when it becomes the butt of jokes and ridicule in mainstream media. For that I do appreciate the work of cartoonist Rick McKee of the Augusta Chronicle:
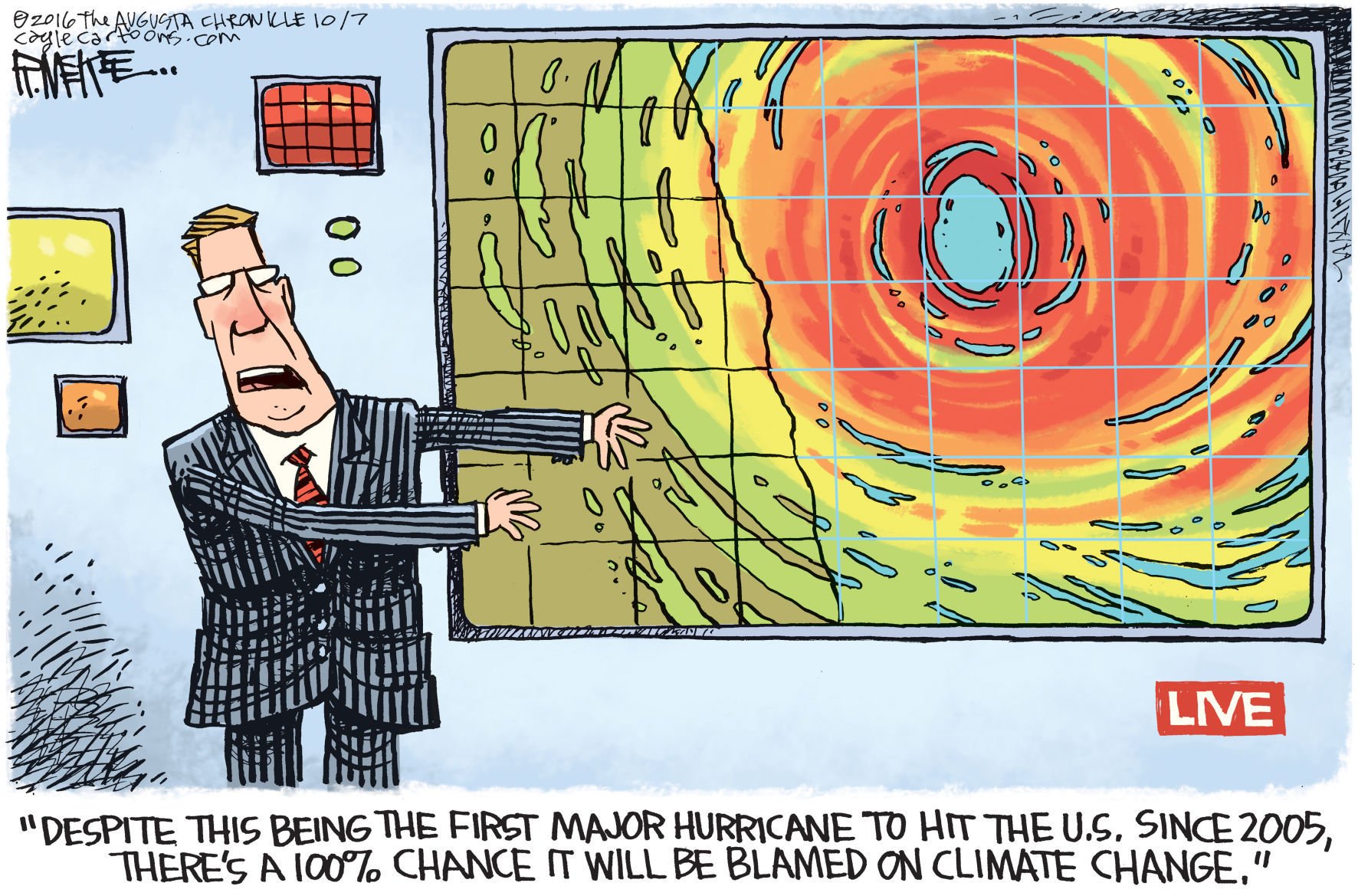

More humor at Cavemen Climate Comics for Sunday
Background Articles
The Flashy Finding: Progressively Scaring the World (Lewin book synopsis)
The Fawning Replications: Climate Models Explained
A Consensus Forms: Talking Climate, NASA and Climate Dogma
The Rebuttal: Fossil Fuels ≠ Global Warming
Proper Replications: Climate Reductionism
Zombie CAGW: World of Hurt from Climate Policies
Postscript: Charles MacKay on Collective Delusions
Of course the classical masterwork in this field is the book Extraordinary Popular Delusions And The Madness Of Crowds By Charles MacKay 1841. Title is link to full pdf text. Excerpts below with my bolds.
In the present state of civilization, society has often shown itself very prone to run a career of folly from the last-mentioned cases. This infatuation has seized upon whole nations in a most extraordinary manner. France, with her Mississippi madness, set the first great example, and was very soon imitated by England with her South Sea Bubble. At an earlier period, Holland made herself still more ridiculous in the eyes of the world, by the frenzy which came over her people for the love of Tulips. Melancholy as all these delusions were in their ultimate results, their history is most amusing. A more ludicrous and yet painful spectacle, than that which Holland presented in the years 1635 and 1636, or France in 1719 and 1720, can hardly be imagined.
Some delusions, though notorious to all the world, have subsisted for ages, flourishing as widely among civilized and polished nations as among the early barbarians with whom they originated, — that of duelling, for instance, and the belief in omens and divination of the future, which seem to defy the progress of knowledge to eradicate entirely from the popular mind. Money, again, has often been a cause of the delusion of multitudes. Sober nations have all at once become desperate gamblers, and risked almost their existence upon the turn of a piece of paper. To trace the history of the most prominent of these delusions is the object of the present pages. Men, it has been well said, think in herds; it will be seen that they go mad in herds, while they only recover their senses slowly, and one by one.
MacKay’s study was exhaustive for its time, comprising three volumes;
VOL I. Considered National Delusions, including:
THE MISSISSIPPI SCHEME
THE SOUTH SEA BUBBLE
THE TULIPOMANIA.
RELICS.
MODERN PROPHECIES.
POPULAR ADMIRATION FOR GREAT THIEVES.
INFLUENCE OF POLITICS AND RELIGION ON THE HAIR AND BEARD.
DUELS AND ORDEALS
THE LOVE OF THE MARVELLOUS AND THE DISBELIEF OF THE TRUE.
POPULAR FOLLIES IN GREAT CITIES
THE O.P. MANIA.
THE THUGS, or PHANSIGARS.
VOL. II described Peculiar Follies, including:
THE CRUSADES
THE WITCH MANIA.
THE SLOW POISONERS.
HAUNTED HOUSES.
VOL. III compiled more general popular madnesses under three categories:
BOOK I: Philosophical Delusions, down through history with particular recent attention to Alchemists
BOOK II: Fortune Telling
BOOK III: The Magnetisers, a fad only subsiding when the book was written.





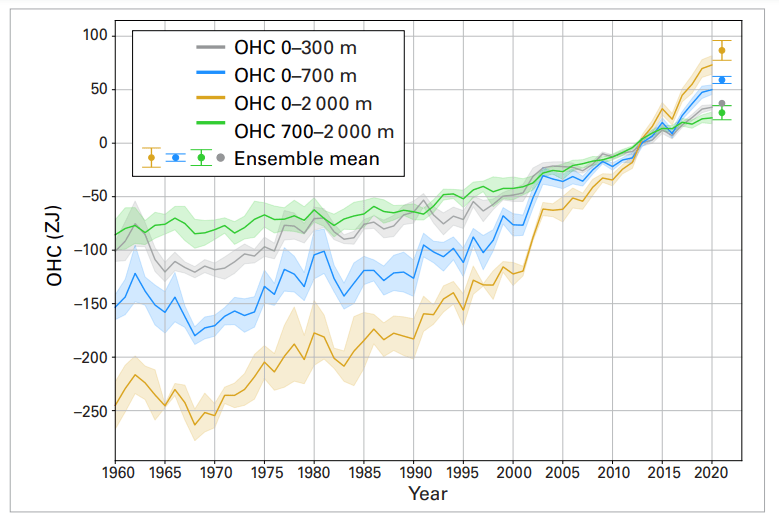
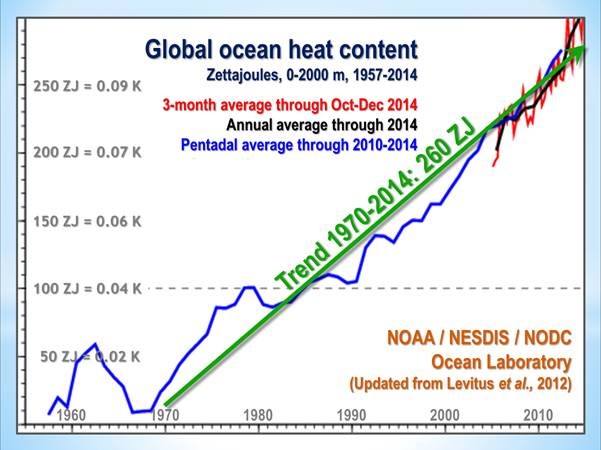












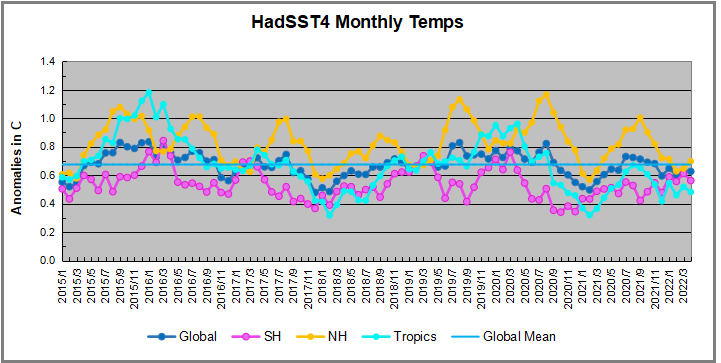
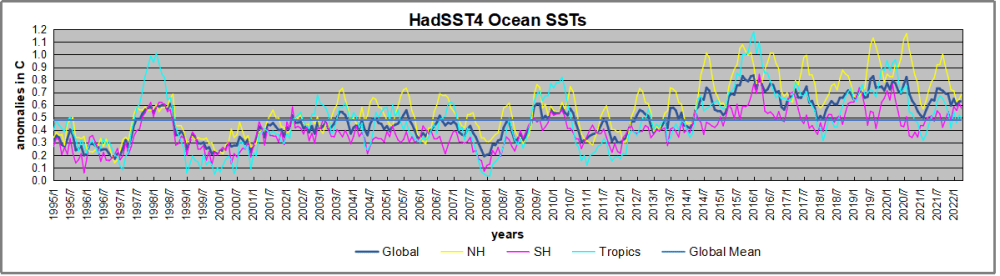
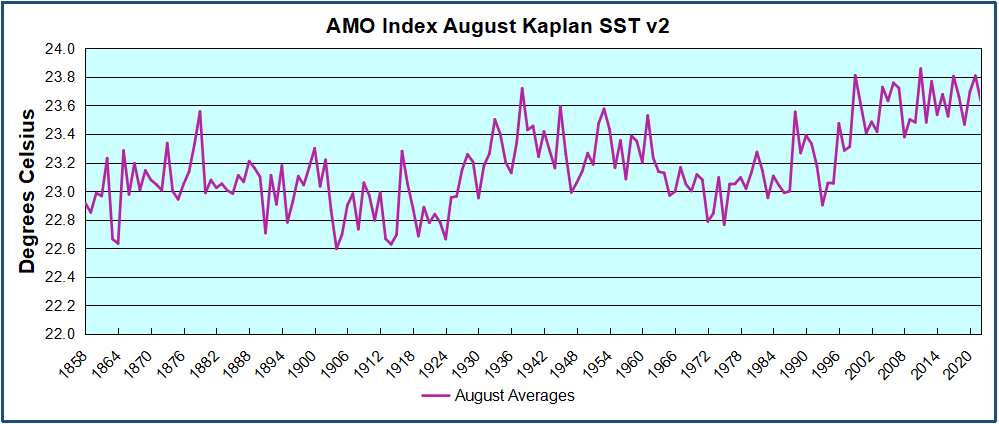
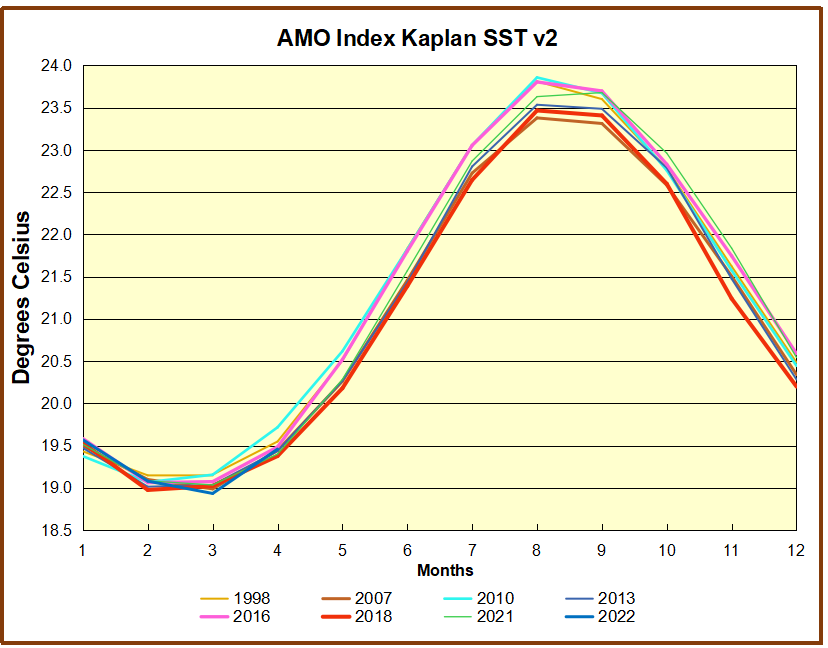

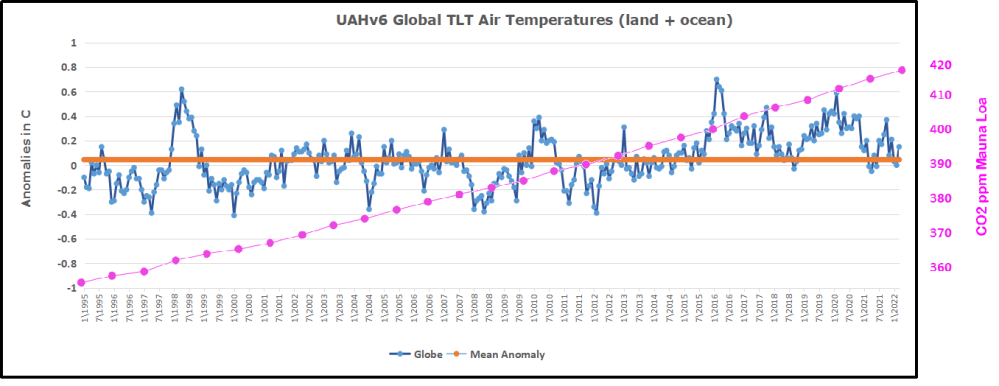
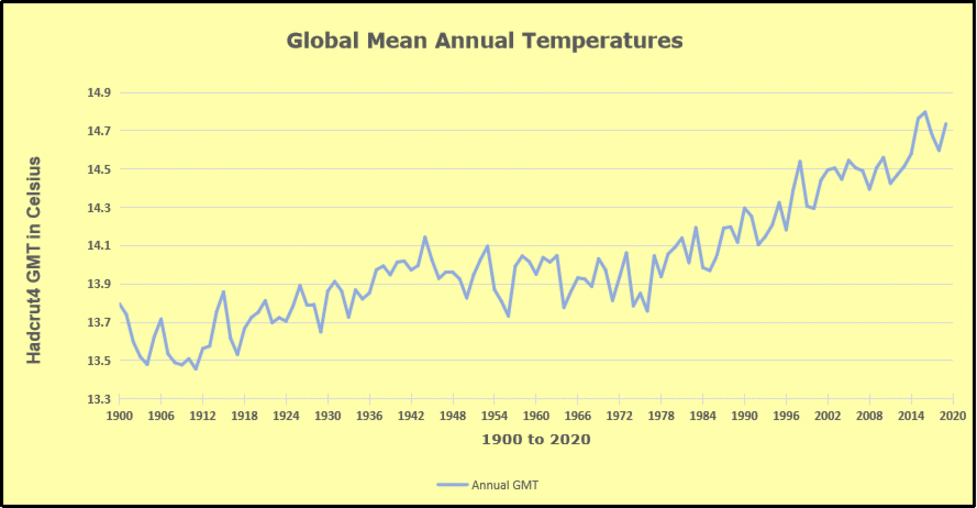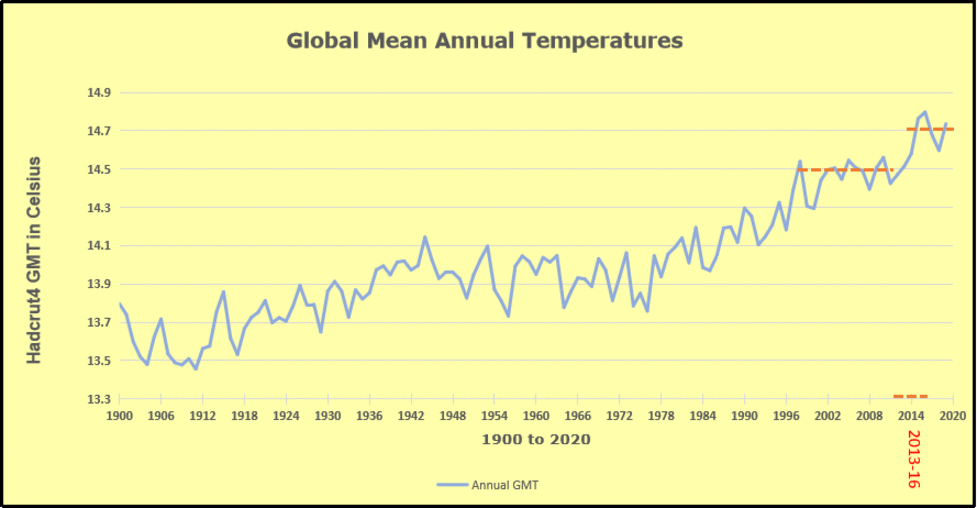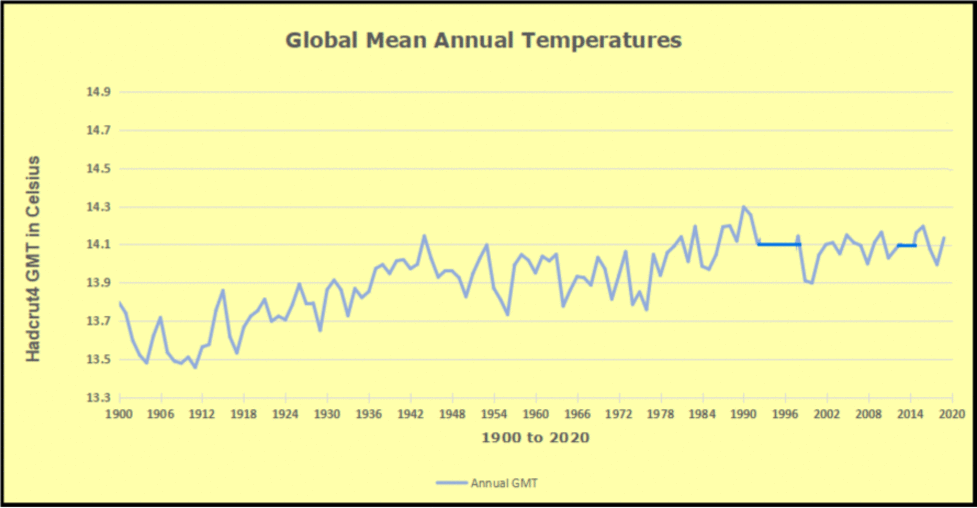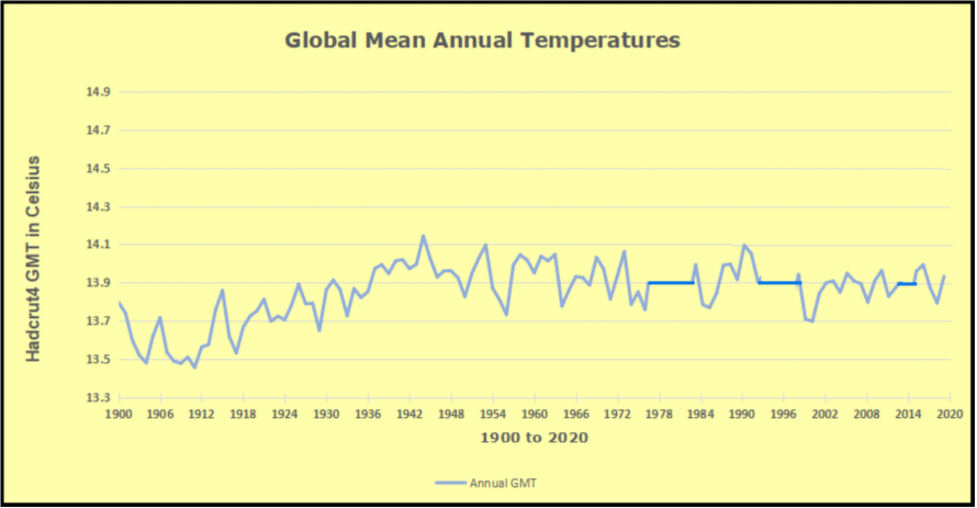
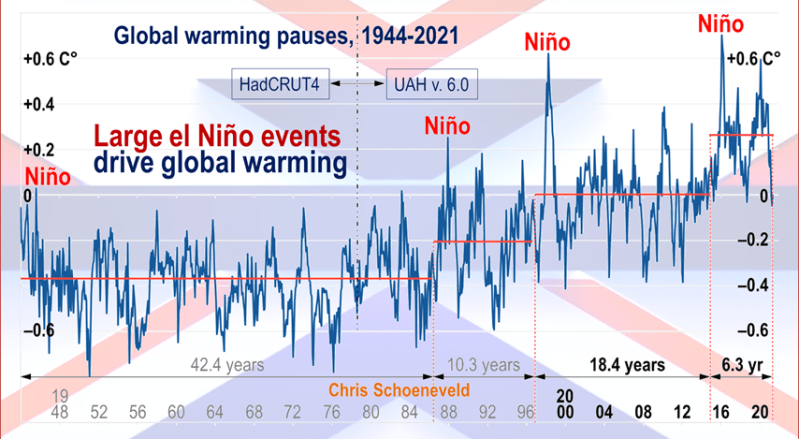



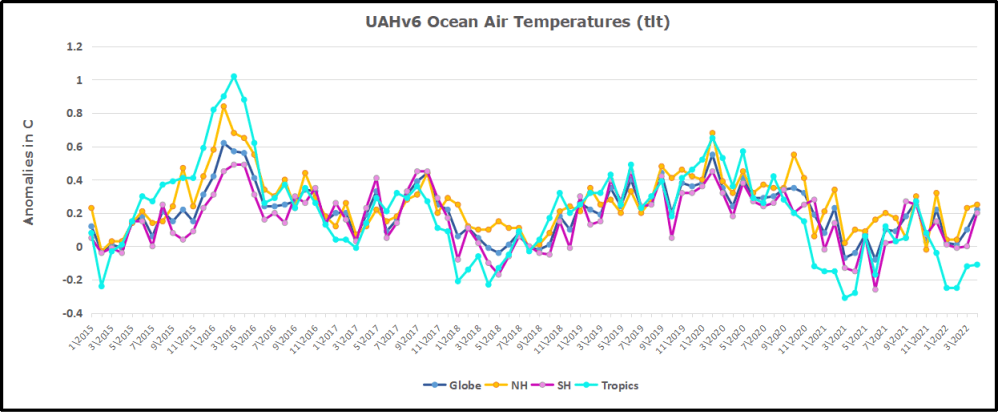
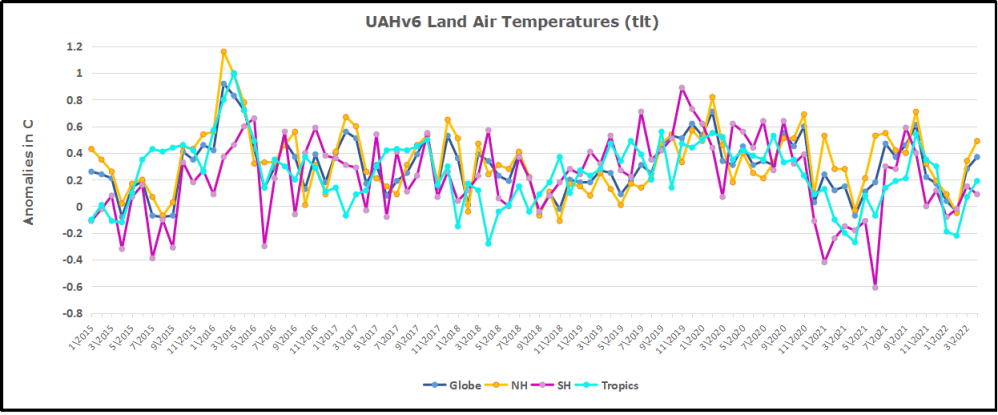
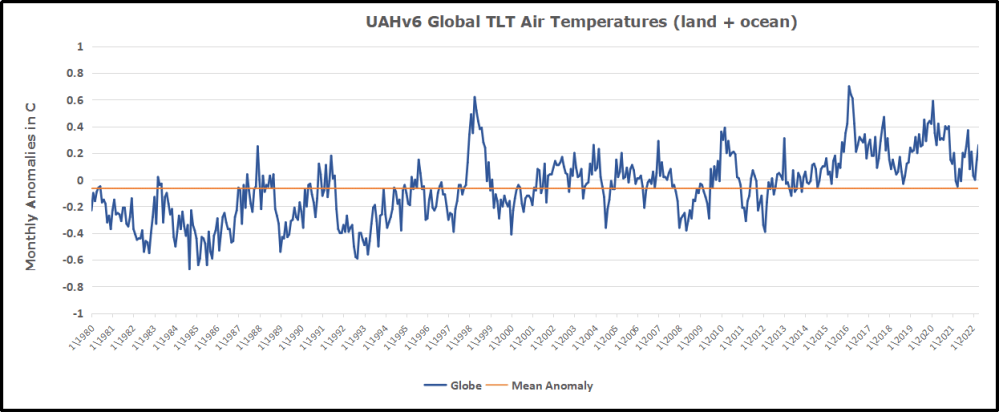
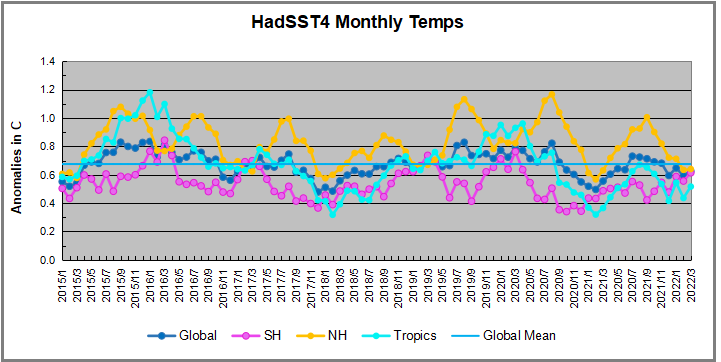
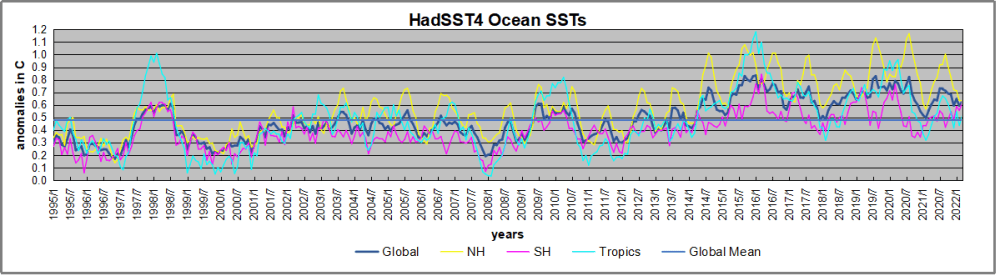
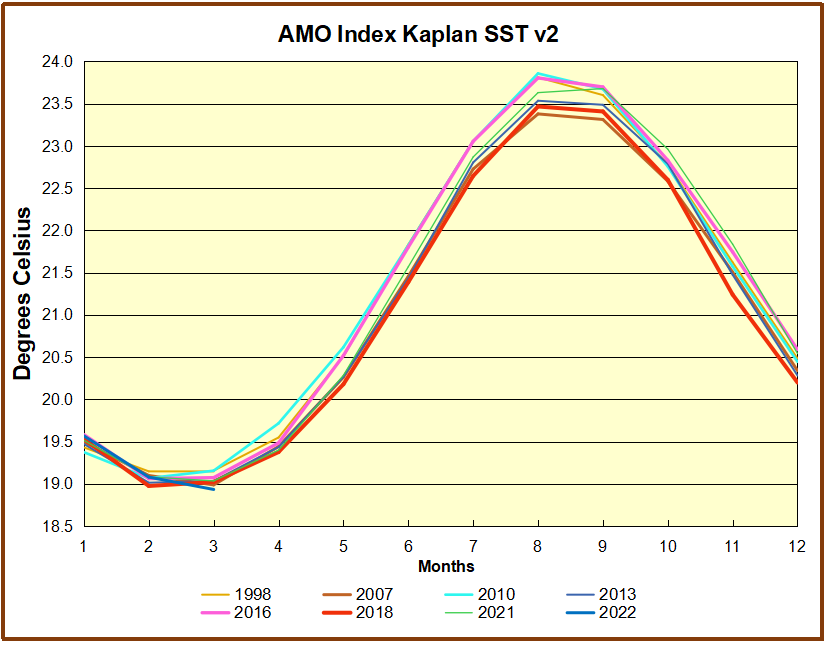



 But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.
But: Sea Level Rise is not accelerating.






















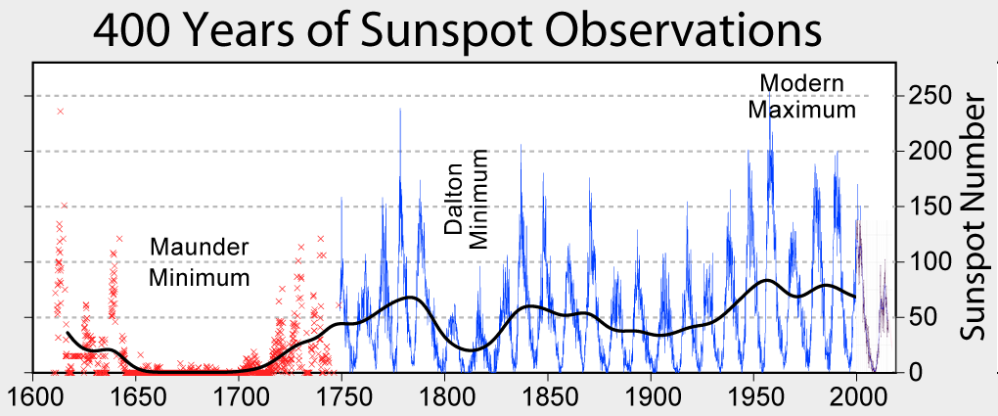
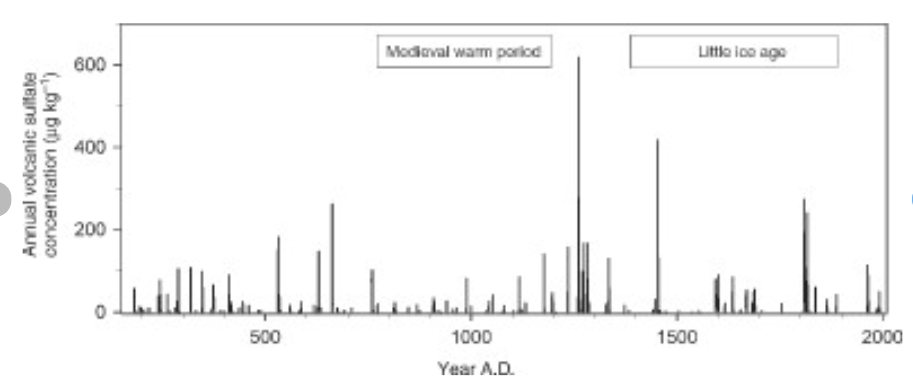
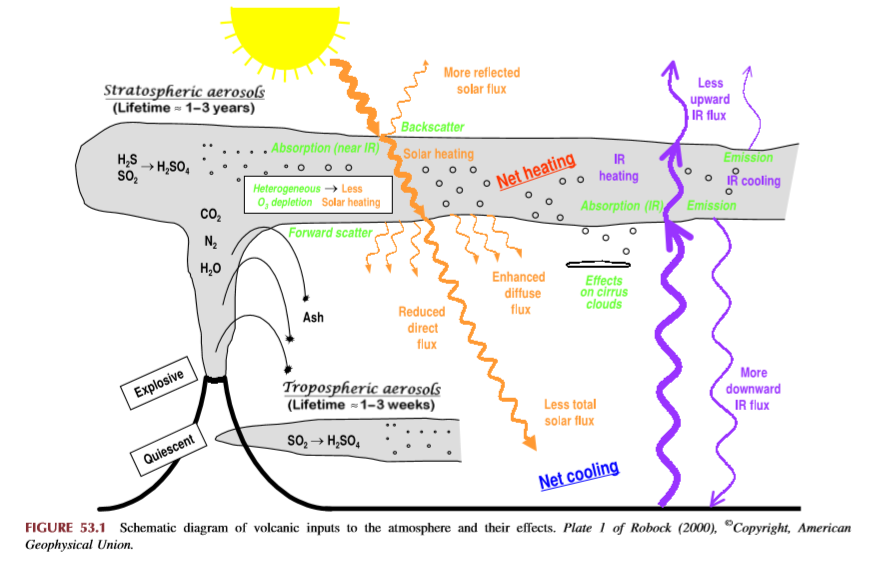
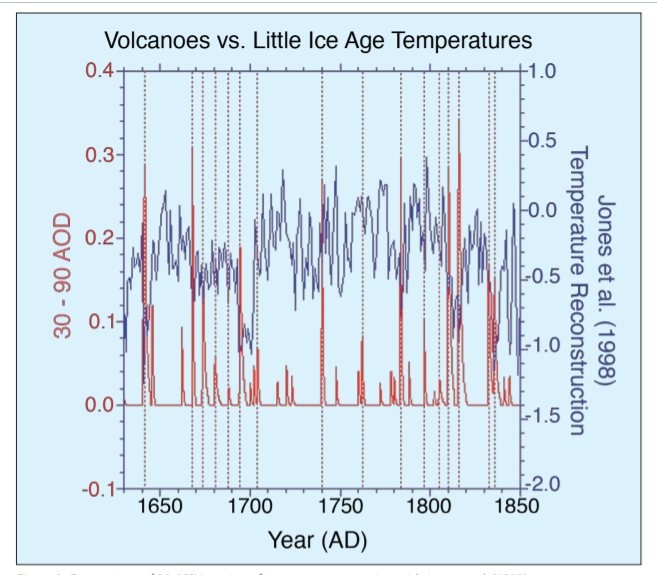
 When I presented this diagram to my warmist friends, they would respond, “But you don’t know what caused the LIA or what ended it!” To which I would say, “True, but we know it wasn’t due to burning fossil fuels.” Now I find there is a body of evidence suggesting what caused the LIA and why the temperature rebound may be over. Part of it is a familiar observation that the LIA coincided with a period when the sun was lacking sunspots, the Maunder Minimum, and later the Dalton.
When I presented this diagram to my warmist friends, they would respond, “But you don’t know what caused the LIA or what ended it!” To which I would say, “True, but we know it wasn’t due to burning fossil fuels.” Now I find there is a body of evidence suggesting what caused the LIA and why the temperature rebound may be over. Part of it is a familiar observation that the LIA coincided with a period when the sun was lacking sunspots, the Maunder Minimum, and later the Dalton.